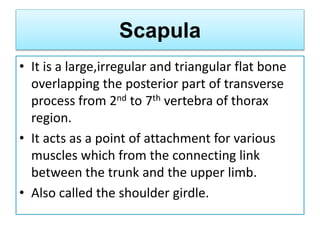
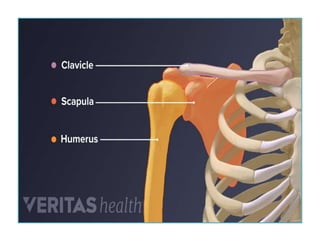
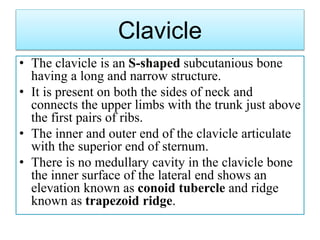
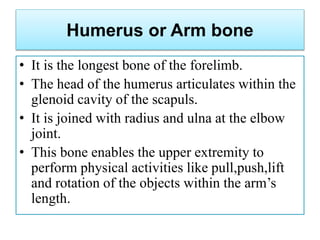
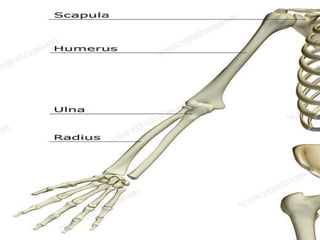
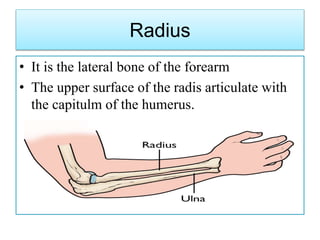
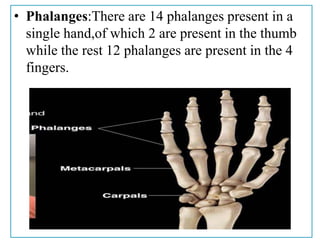
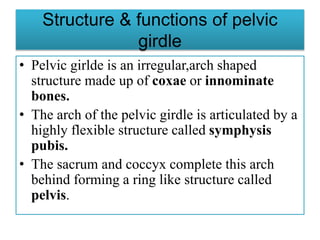
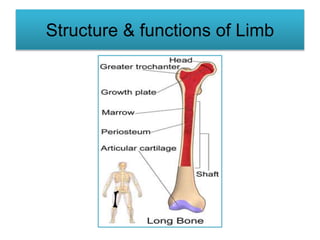
The appendicular skeleton comprises 126 bones, including the limbs and supportive girdles. The pectoral girdle, which connects the upper limbs to the axial skeleton, consists of the scapula and clavicle, providing support, shock absorption, and muscle attachment. The pelvic girdle, formed by the coxae, sacrum, and coccyx, supports the lower limbs and completes the ring structure of the pelvis.


![Pectorial Girdle
The human body has two pectorial girdles that
attach the bones of the upper limbs to the axial
skeleton
• 2 Scapula[Shoulder blade]
• 2 Clavicle[Collar bone]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicularskeltalsystemppt-240215090757-a826c93a/85/Appendicular-SkeletonSystem-PPT-pptx-3-320.jpg)