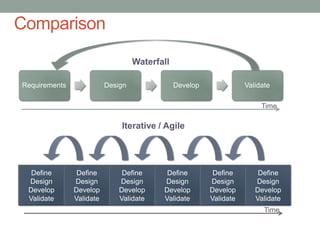
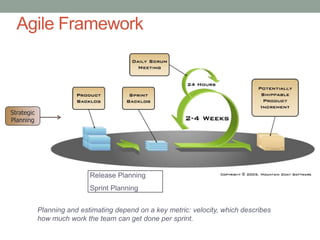
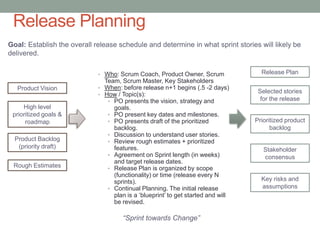
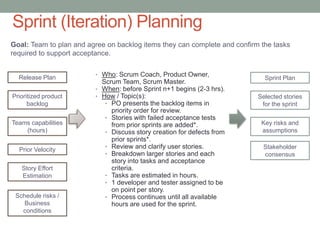
The document discusses Agile planning processes. Release planning occurs before each release and involves the product owner, Scrum team, and stakeholders prioritizing features and setting release dates. Sprint planning occurs before each sprint and involves the Scrum team and product owner selecting stories for the sprint from the prioritized backlog, estimating work, and establishing a plan. The document provides details on participants, timing, objectives, inputs, and outputs for both release and sprint planning meetings in Agile. It also notes that estimations may be inaccurate initially but will improve over time as teams gain experience.