This document contains 50 multiple choice questions related to chemistry concepts. The questions cover topics such as atomic structure, periodic trends, chemical bonding, stoichiometry, gases, and thermochemistry. Sample questions include determining the percentage of an isotope in natural boron, identifying an element based on its electron configuration, calculating gas volumes and pressures using the ideal gas law, and explaining experimental results related to atomic structure and periodic trends.
![A) 0% B) 20% C) 50% D) 80% E) 100%
1. Naturally occurring boron consists of two isotopes,
boron–10 and boron–11. If the atomic mass of natural
boron is 10.8, what is the percentage that is boron–10?
A)
B)
C)
D)
2. Which mass spectrometer graph represents naturally
occurring magnesium?
A) Mass spectrometer beam distribution
B) Emission spectra of gaseous elements
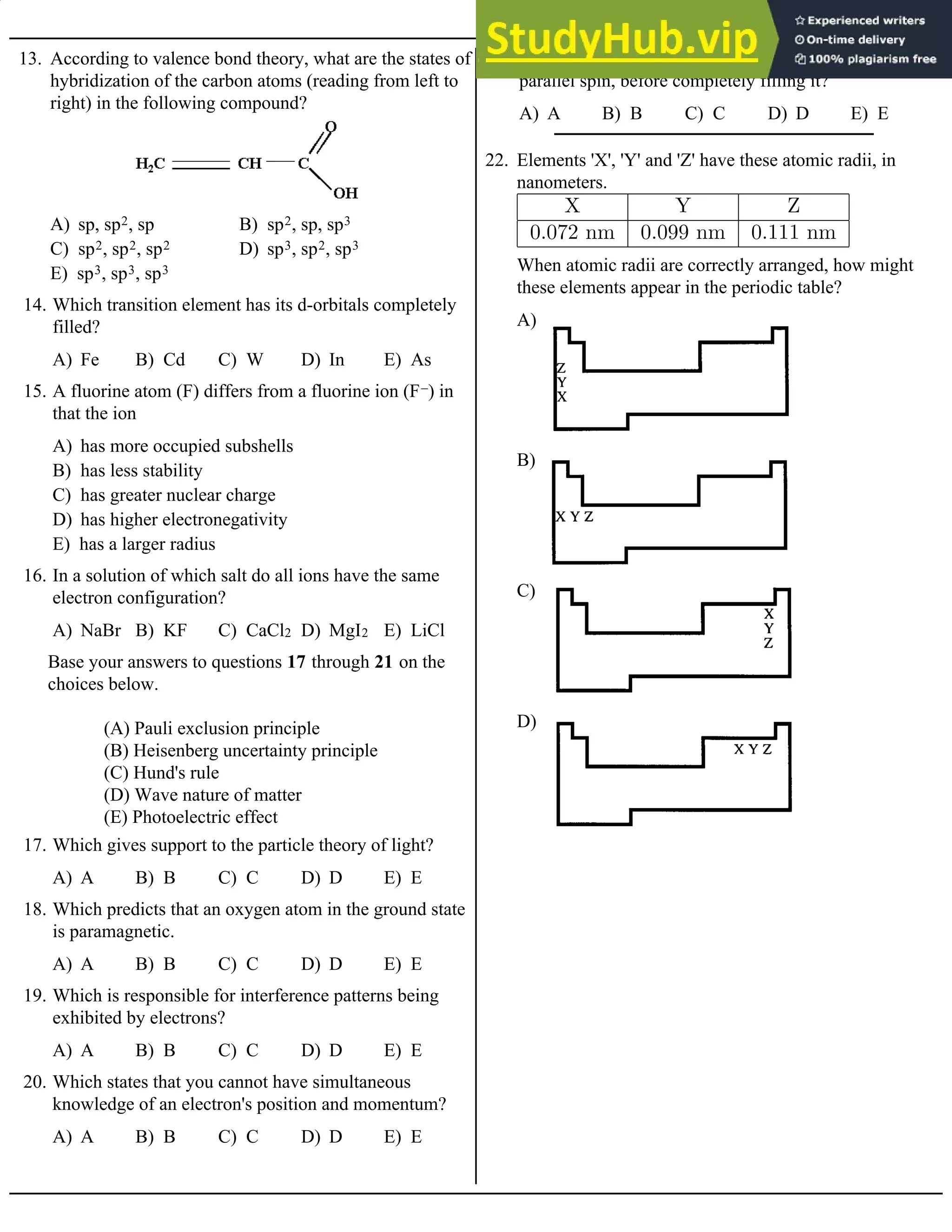
C) Cathode ray deflection by a magnetic field
D) Scattering of alpha particles by metal foil
E) Radioactive transmutation of elements
3. Which supports the conclusion that the energy of
electrons in atoms are quantized?
A) Rn B) Ra C) Fm D) Md E) No
4. An ion which has the electron configuration [[Rn] 5f14]
2– has the symbol
A) Barium B) Sodium
C) Potassium D) Lithium
E) Calcium
5. When a chloride solution of an element is vaporized in a
flame, the color of the flame is purple. What element
could be in the solution?
A) [Ar]4s23d3 B) [Ar]3d3
C) [Ar]4s23d1 D) [Ar]4s13d2
E) [Ar]3d5
6. What would be the most likely electron configuration for
a Vanadium 2+ ion?
7. Base your answer to the following question on the
following atomic orbitals.
(A) 1s2 2s1 2p
1
(B) 1s2 2s2 2p
1
(C) 1s2 2s2 2p
6
(D) [Ar] 4s2
(E) [Ar] 4s2 3d4
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
This atom is in an excited state.
Base your answers to questions 8 through 11 on the
following electron configurations
(A) [Xe] 4f145d106s
2
(B) [Kr] 4d105s
1
(C)
[Ar] 3d104s24p
5
(D) [Ar]
(E) [Ne] 3s23p2
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
8. The configuration of a metallic diatomic element
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
9. The configuration of a metalloid
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
10. A common ion of an alkali metal
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
11. The ground state of a halogen
A) Zinc B) Cadmium
C) Calcium D) Cobalt
E) Magnesium
12. Which of the following elements will present a
paramagnetic electron configuration?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apchemmidtermreview-230805193237-3c938c62/75/AP-CHEM-MIDTERM-REVIEW-1-2048.jpg)









![109. 2 NO (g) + O2 (g) ® 2 NO2 (g)
A) (0.60)(0.082)(293) atm
B) (0.45)(0.082)(293) atm
C) (0.30)(0.082)(293) atm
D) (0.60)(0.082)(20) atm
E) (0.45)(0.082)(20) atm
A mixture containing 0.30 mol NO and 0.30 mol O2
reacts in a 1.0 L flask at a constant temperature of
20ºC. What is the pressure in the flask when the
reaction is complete?
110. 4 HF (g) + SiO2 (s) ® SiF4 (g) +2 H2O (l)
A) 2.3 g B) 4.5 g C) 9.0 g D) 18. g E) 36. g
If 10. g of HF (formula mass 20. g/mol) reacts with
15. g of SiO2 (formula mass 60. g/mol), how much
water is produced?
111. An experiment was conducted to determine the rate
law of the reaction 2 A + 2 B ® C + D. The data
collected is shown below.
A) k = [A][B] B) k = [A]2[B]
C) k = [A][B]2 D) k = [A]2[B]2
E) k = [A][B]2
What is the rate law for this equation?
A) 7.9 × 10–3 h–1 B) 8.77 × 10–3 h–1
C) 79 h D) 39.5 h
E) 4.39 × 10–3 h–1
112. A first order reaction goes to half completion in 79
hours. What is the rate constant for this reaction?
113. Base your answer to the following question on the
possible rate laws below for the reaction:
A + B C
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
When [A] is tripled and [B] is constant then the initial
rate of reaction remains constant.
114. A + 2 B ®2 C + 4 D
A) [C]2[D]4
B) k[C]2[D]4
C) second order
D) first order
E) impossible to find without experimental data
The rate law for the above reaction is
115.
A) Rate = k[H2]/[ICl]
B) Rate = k[H2][ICl]
C) Rate = k[H2][ICl]2
D) Rate = k[H2]2[ICl]2
E) Rate = k[H2]2[ICl]
The above chart contains experimental data obtained
from the following reaction:
H2 + 2 ICl ® I2 + 2 HCl
What is the experimental rate law for this reaction?
A) cooling the system
B) adding more sodium, Na
C) increasing the volume of the system
D) removing sodium chloride, NaCl
E) using gaseous chlorine, Cl2
116. Given the reaction:
Cl2(l) + 2 Na(s) ® 2 NaCl(s)
The reaction rate can be significantly increased by:
A) the Drake equation
B) the Clausius-Claperon Equation
C) the Arrhenius equation
D) the Nernst equation
E) Avogadro's equation
117. The temperature of a reaction is increased from 350 K
to 400 K. The reaction rate is tripled. Which of the
following equations can be used to find the activation
energy of the reaction?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apchemmidtermreview-230805193237-3c938c62/75/AP-CHEM-MIDTERM-REVIEW-12-2048.jpg)
![Base your answers to questions 118 and 119 on on the table below, for the following reaction:
2 SO2 + O2 ® 2 SO3
A) 4.0 × 10–8 B) 2.0 × 10–8 C) 1.0 × 10–8 D) 4.0 × 10–9 E) 2.0 × 10–9
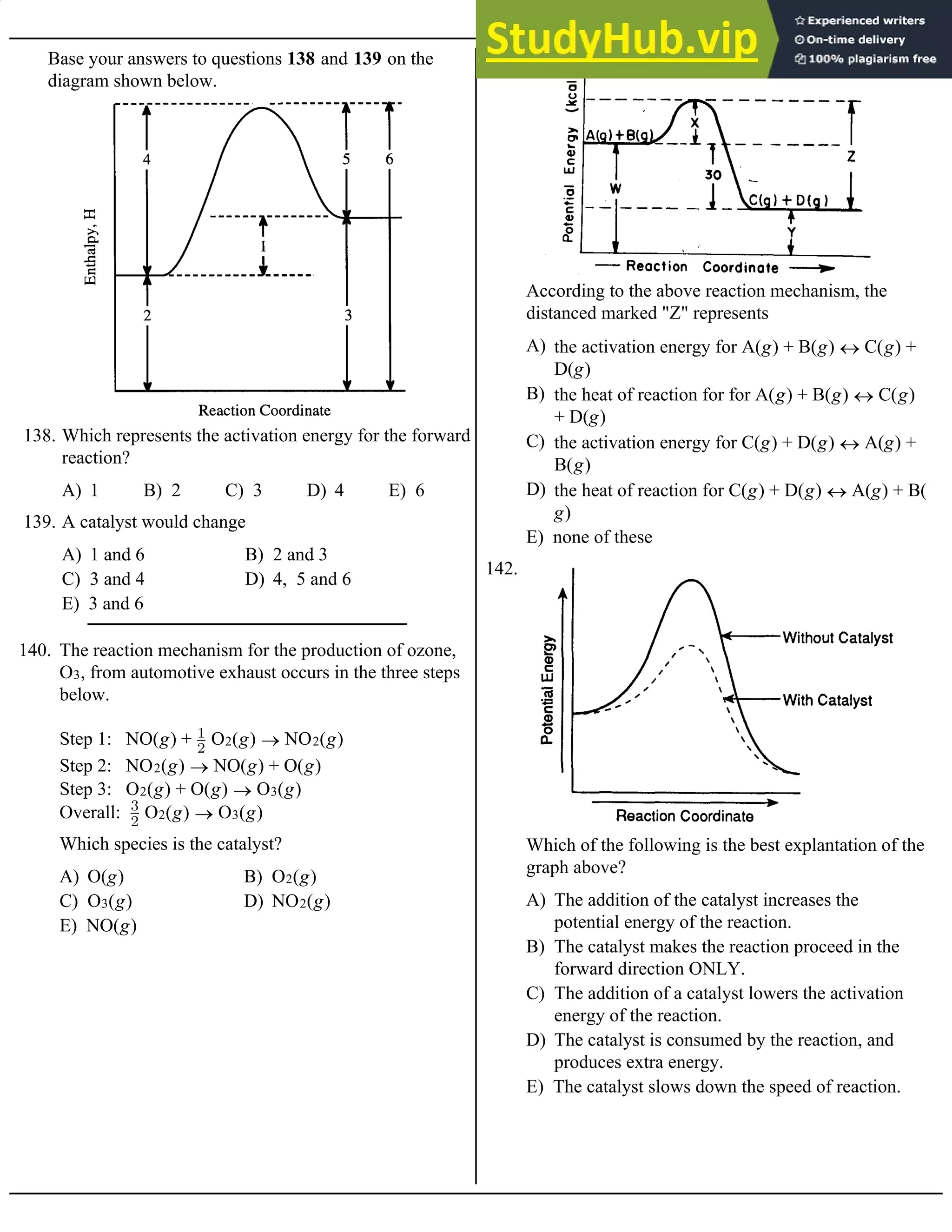
118. The value of the rate constant, k, for this reaction is
A) Rate = k[SO2][O2]3 B) Rate = k[SO2]3[O2]2
C) Rate = k[SO2][O2] D) Rate = k[SO2]3[O2]
E) Rate = k[SO2]3
119. What is the experimental rate law for the reaction above?
Base your answers to questions 120 and 121 on the table of data for the following reaction:
CO(g) + O2(g) ® CO2(g)
A) 1.6 × 10–4 M/s B) 8.0 × 10–5 M/s C) 4.0 × 10–5 M/s D) 1.0 × 10–5 M/s E) 3.2 × 10–4 M/s
120. The value of the rate constant, k, is
A) 2.0 × 10–5 M/s B) 1.6 × 10–4 M/s C) 1.0 × 10–5 M/s D) 0.50 × 10–5 M/s E) 8.0 × 10–5 M/s
121. When [CO] = [O2] = 1.0 M, the rate of reaction will be
A) rate = k [XO]2[O2]–1
B) rate = k [XO][O2]–1
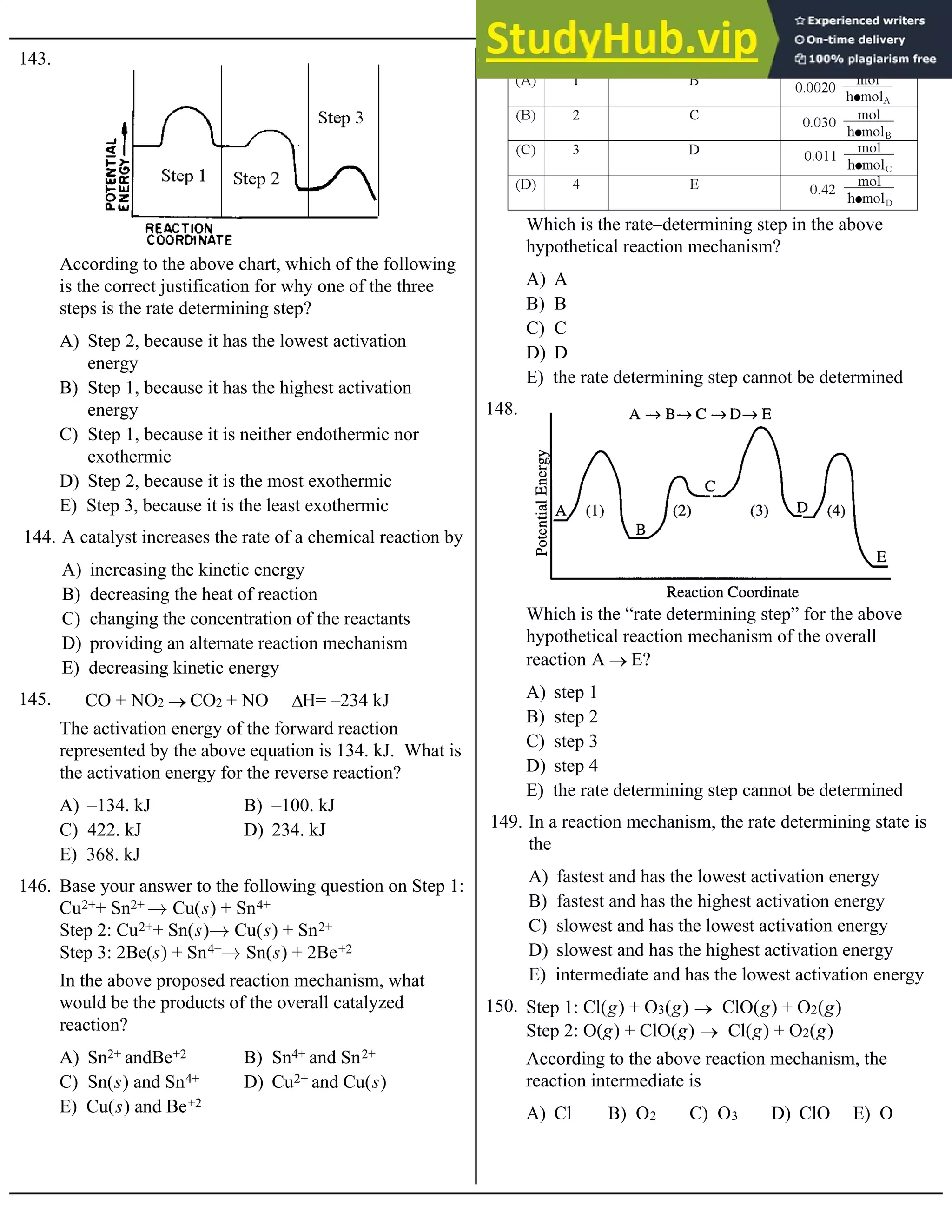
C) rate = k [XO]2 [O2]
D) rate = k [XO] [O2]2
E) rate = k [XO]2 [O2]2
122. A student collected the initial-rate data in the chart
below.
What is the experimental rate law for this reaction?
A) rate = k B) rate = k [Z]
C) rate = k [Z]2 D) rate = [Z]
E) rate = [Z]2
123. For which of the following rate laws would the graph
of ln [Z] versus time be a straight line?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apchemmidtermreview-230805193237-3c938c62/75/AP-CHEM-MIDTERM-REVIEW-13-2048.jpg)
![A) I only B) II and III only
C) I and III only D) I, II, III and IV
E) I, II and III only
124. Consider the following factors:
I. Reactant particles collide
II. Sufficient kinetic energy is present
III. A favorable geometry exists
IV. Catalysts are present
Which combination of the above factors is required
for all successful collisions?
A) rate of dissolving increases; rate of crystallization
increases
B) rate of dissolving decreases; rate of
crystallization increases
C) rate of dissolving increases; rate of crystallization
decreases
D) rate of dissolving decreases; rate of
crystallization decreases
E) rate of dissolving remains constant; rate of
crystallization decreases
125. When solid AgBr is added to saturated solution of
AgBr, the reaction rates can be described as
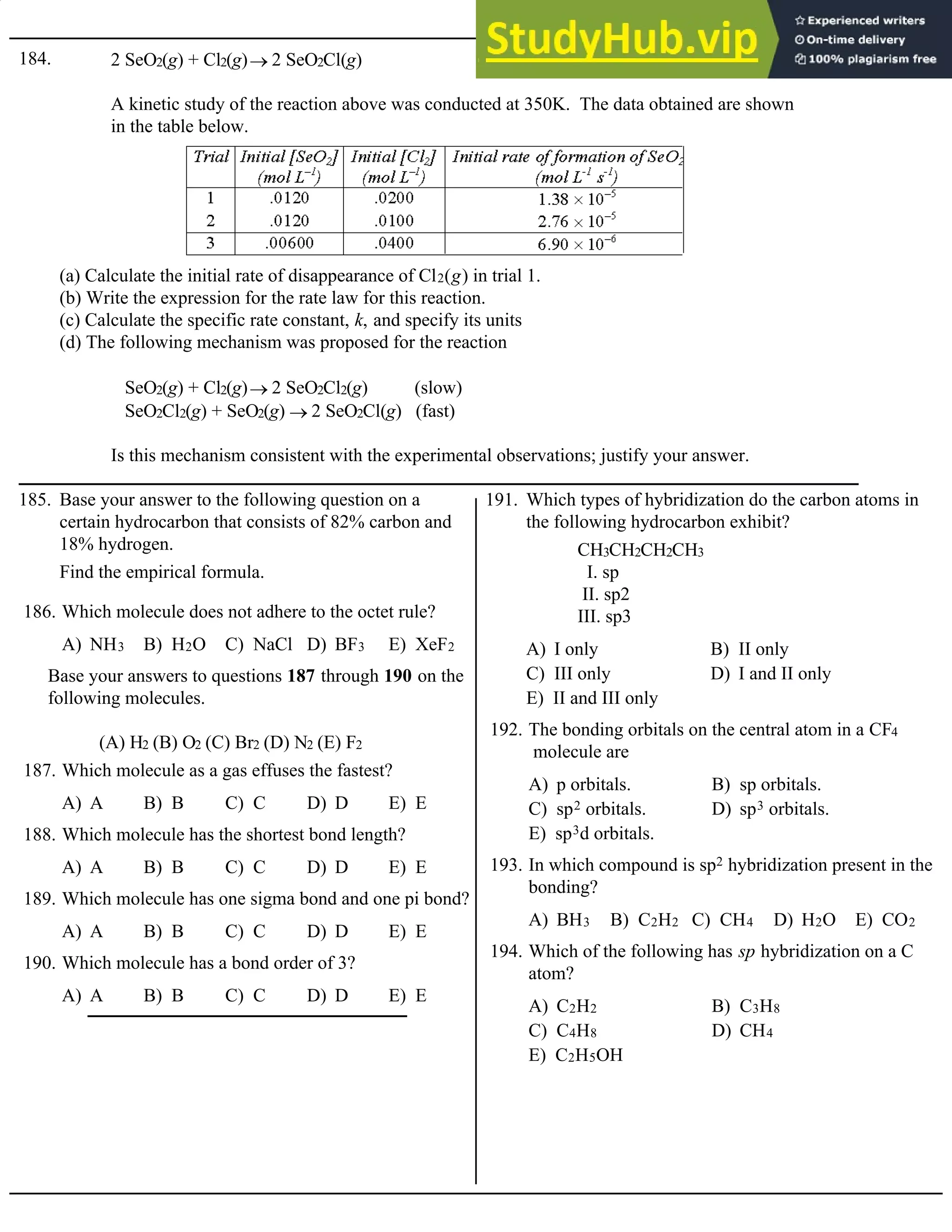
Base your answers to questions 126 through 128 on the
rate law given below for the reaction A + B + C ® D.
Rate = k[A]2[B][C]
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 0
126. What is the order of the reaction with respect to A?
A) Both [A] and [C] will increase.
B) Both [A] and [C] will decrease.
C) [A] will decrease and [C] will increase.
D) [A] will increase and [C] will decrease.
E) Both [A] and [C] will stay the same.
127. If the concentration of B is decreased, what will
happen?
A) The rate of the reaction increases
B) The rate of the reaction decreases
C) The value of the equilibrium constant increases
D) The value of the equilibrium constant decreases
E) Neither the equilibrium constant nor the rate
would change.
128. If the concentration of C is doubled what will happen?
A) Rate = k[A]2 B) Rate = k[B]2
C) Rate = k[A][B] D) Rate = k[A]2[B]
E) Rate = k[A][B]2
129. Base your answer to the following question on the
table below which was obtained for the reaction A + B
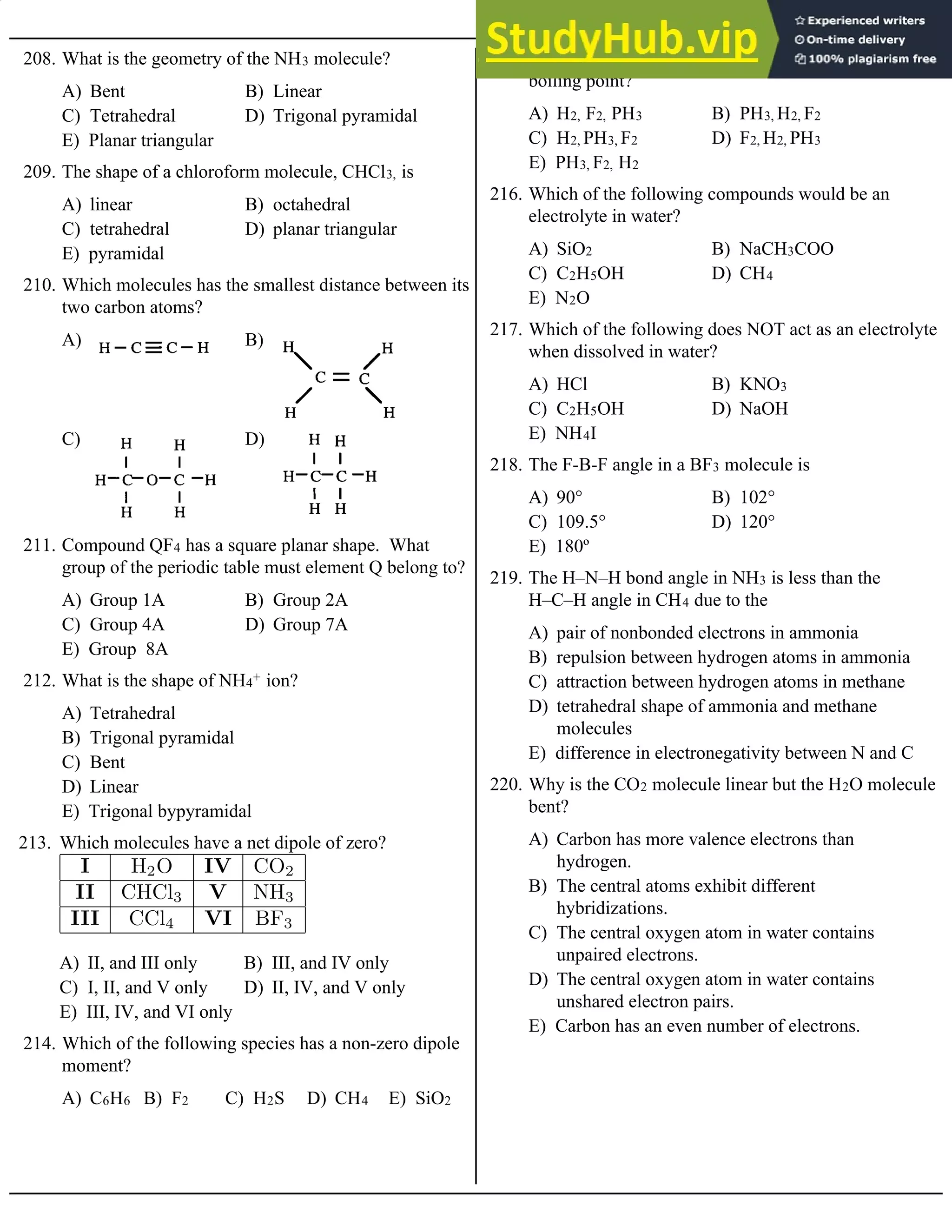
C.
What is the rate law for this reaction?
130. I. Ag+(aq) + I–(aq) ® AgI(s)
II. 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2(g) ® 2 Fe2O3(s)
A) I is faster than II
B) II is faster than I
C) I and II are both fast
D) I and II are both slow
E) The relative rates of reaction cannot be
determined
Which statement best describes the relative rates of the
above two reactions?
131. I. 4 Al(s) + 3 O2(g) ® 2 Al2O3(s)
II. Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq) ® AgCl(s)
A) I is faster than II
B) II is faster than I
C) I and II are both fast
D) I and II are both slow
E) The relative rates of reaction cannot be
determined
Which statement best describes the relative rates of the
above two reactions?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apchemmidtermreview-230805193237-3c938c62/75/AP-CHEM-MIDTERM-REVIEW-14-2048.jpg)
![A) I and II only
B) I, II, and IV only
C) III, IV, and V only
D) IV and V only
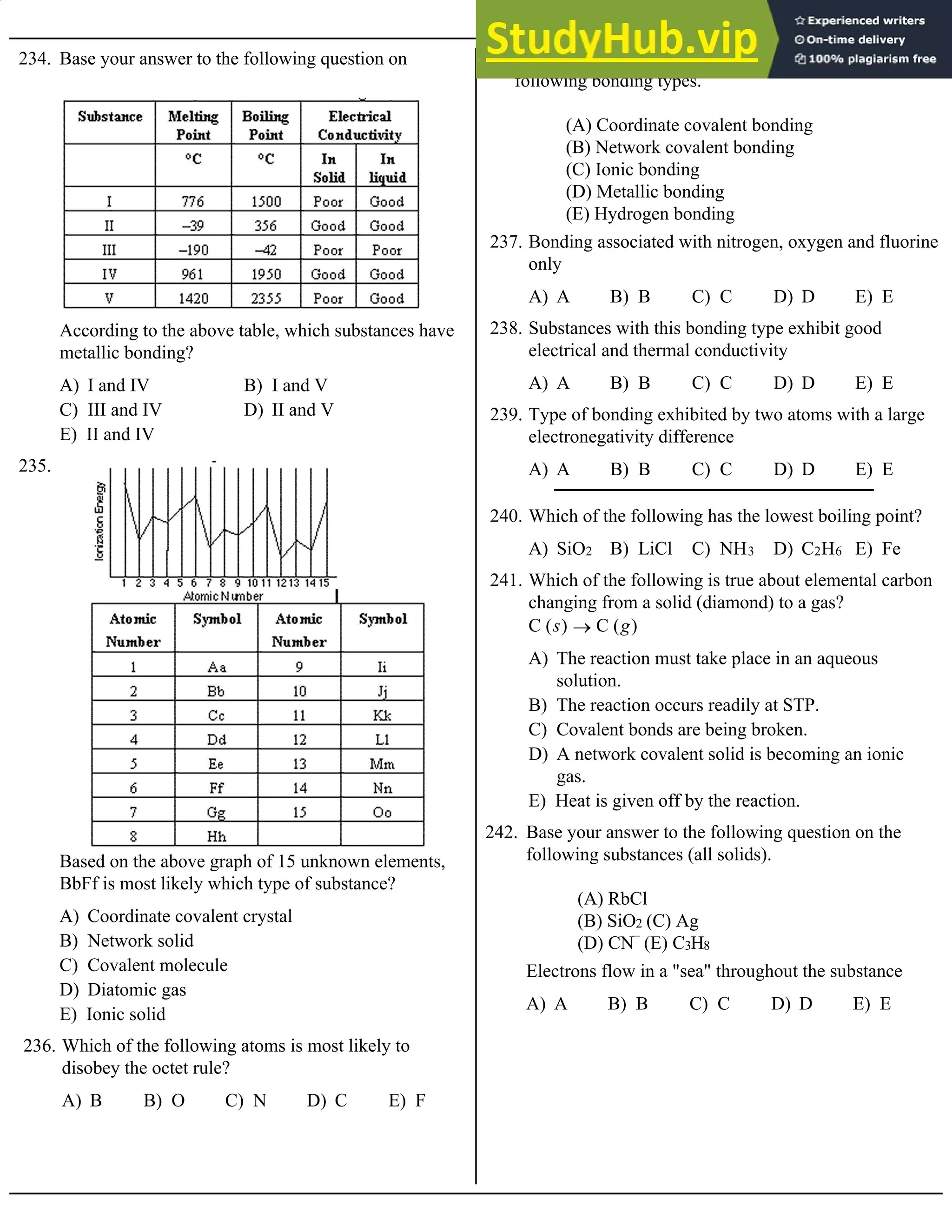
E) They are all correlated with a fast reaction rate
132. Which of the following is not correlated with a fast
reaction rate?
I. Catalysts
II. High temperature
III. High concentration of reactants
IV. Strong bonds in the products
V. Low level of activation energy
133. Base your answer to the following question on the
graph below which shows the number of molecules
with a given kinetic energy plotted as a function of
kinetic energy. Four catalysts are available, A, B, C
and D, which have associated reaction activation
energies EA, EB, EC, and ED respectively.
A) Catalyst 'A' associated with energy Ea
B) Catalyst 'B' associated with energy Eb
C) Catalyst 'C' associated with energy Ec
D) Catalyst 'D' associated with energy Ed
E) The activation energies of catalysts A, B, C and D
all result in the same reaction rate.
Which catalyst will have an activation energy which
will result in the slowest reaction rate ?
134. Base your answer to the following question on the
graph below showing the energy during a catalyzed
reaction.
A) Curve T1 B) Curve T2
C) Curve T3 D) Can’t tell
Which is the curve for the lowest temperature?
A) concentration of the reactants
B) average kinetic energy of the molecules
C) number of intermolecular collisions per unit of
time
D) number of particles with an energy above a
minimum activation energy
E) voulume of the reactants
135. Generally an increase of ten degrees centigrade
doubles the rate of reaction between gases. The
explanation for this increase in reaction rate is the
doubling of the
136. Base your answer to the following question on the
following reaction.
H2(g) + I2(g) « 2 HI(g)
A) [H2] will increase. B) [I2] will increase.
C) [HI] will decrease. D) 1 and 2
E) None of these
The reaction above is allowed to reach equilibrium.
The pressure on the system is doubled. Which of the
following is true?
A) Zn(s) + S(s) ® ZnS(s)
B) Ba2+(aq) + SO42–(aq) ® BaSO4(s)
C) NH3(g) + HCl(g) ® NH4Cl(s)
D) 2 Ag+(aq) + CO32–(aq) ® Ag2CO3(s)
E) NaCl(aq) ® Na+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
137. Which of the following reactions is slowest at room
temperature?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apchemmidtermreview-230805193237-3c938c62/75/AP-CHEM-MIDTERM-REVIEW-15-2048.jpg)
![151. Base your answer to the following question on the
reaction below.
A) B is not involved in any steps in this reaction.
B) B is not involved in the rate determining step, but
may be involved in other steps in the reaction.
C) The coefficient of B is 1, therefore it does not
affect the rate of the reaction.
D) B is a solid, therefore does not appear in the rate
expression.
E) The order of the reaction with respect to B is 1.
If the rate expression for this reaction does not depend
on B, what could be the cause of this?
A) CrCl2 B) LiCl
C) FeCl3 D) CoCl2
E) NiCl2
152. Which compound dissolves in water to form a clear
solution?
153. Base your answer to the following question on the
elements below.
(A) Fluorine
(B) Copper
(C) Phosphorous
(D) Neon
(E) Francium
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
Which element is a highly reactive metal?
A) Francium is the least electronegative.
B) They form ions with 1+ charge.
C) Lithium has the smallest atomic radius.
D) First ionization energy increases with atomic
number.
E) They are not found in pure form in nature.
154. All the following statements concerning the alkali
metals are true EXCEPT:
A) blue B) orange
C) purple D) red
E) green
155. When a solution of strontium chloride is ignited, the
color of the flame is
156. An element has lst, 2nd and 3rd ionization energies
given in kJ mol-1.
A) Alkali metals.
B) Transition elements.
C) Noble gases.
D) Halogens.
E) Alkaline earth metals.
This element is a member of which group?
Base your answers to questions 157 through 160 on the
electron configurations below.
(A) 2s1
(B) [Ar] 3d104s24p1
(C) [Kr] 4d105s25p3
(D) [Ne] 3s2
(E) [Kr] 4d105s25p6
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
157. An atom with three valence electrons
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
158. An atom in an excited state
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
159. Represents a noble gas
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
160. An alkaline earth metal
A) MgSO3 B) MgCO3
C) Mg(OH)2 D) Mg(NO3)2
E) Mg3(PO4)2
161. A soluble magnesium salt is
162. Base your answer to the following question on the
elements below.
(A) Boron
(B) Rubidium
(C) Nitrogen
(D) Mercury
(E) Plutonium
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
Usually exists as a diatomic gaseous element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apchemmidtermreview-230805193237-3c938c62/75/AP-CHEM-MIDTERM-REVIEW-18-2048.jpg)
![A) Fluorine is the least electronegative element.
B) Bromine liberates free chlorine from a solution of
chloride ions.
C) Ionization energy increases with increasing
atomic number.
D) Fluorine has the smallest atomic radius.
E) They combine with Group I metals to form
compounds of the form XY2.
163. Which of the following is true about the halogens?
A) Its valence electrons are of the form ns2np4.
B) Atomic radius decreases with increasing atomic
number.
C) It combines with group IIA metals in binary
compounds of the form XY.
D) It contains members that naturally exist in each
of the 3 states of matter.
E) All its members are monatomic.
164. Which of the following is true about the halogen
family?
165. Base your answer to the following question on the
atomic orbitals below.
(A) 1s2 2s1 2p
1
(B) 1s2 2s2 2p
1
(C) 1s2 2s2
2p
6
(D) [Ar] 4s2
(E) [Ar] 4s2 3d4
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
This element dissolves to become a colored solution.
A) iodides B) bromides
C) chromates D) phosphates
E) sulfides
166. The colored solids are formed from
A) NaCl B) MgCl2
C) AlCl3 D) NiCl2
E) ZnCl2
167. Which of the following forms a colored solution in
water?
168. Base your answer to the following question on the
chemicals below.
(A) Sulfur dioxide
(B) Hydrochloric acid
(C) Water
(D) Potassium phosphate
(E) Copper chloride
A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E
Which forms a colored solution in water?
A) Carbon has oxides that can be acid anhydrides.
B) Diamond is an example of elemental carbon in
the solid state.
C) Nearly all organic compounds contain carbon.
D) The AMU is defined as 1/12 of the weight of a
carbon-12 atom.
E) Since carbon is located between a metal and a
nonmetal, it is classified as metalloid.
169. Which of the following is FALSE about elemental
carbon?
A)
B)
C) D)
E)
170. Which of the following is an acid?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apchemmidtermreview-230805193237-3c938c62/75/AP-CHEM-MIDTERM-REVIEW-19-2048.jpg)