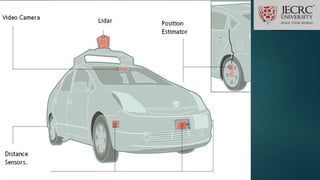
Driverless vehicles, also known as autonomous vehicles, can transport passengers from one destination to another without human involvement. They use sensors like lidar and radar along with GPS and digital maps to navigate roads automatically. Some key technologies that enable autonomous driving include adaptive cruise control, automatic emergency braking, and self-parking. Lidar systems are important for driverless cars as they use lasers to generate 3D images of the vehicle's surroundings up to 200 meters away. While driverless vehicles could improve safety and mobility, challenges remain regarding their high costs, ability to perceive environments, need for infrastructure upgrades, and ensuring they function properly in all conditions.