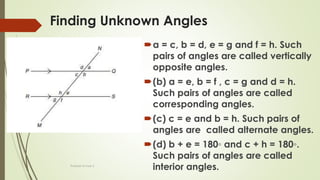
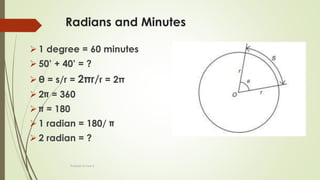
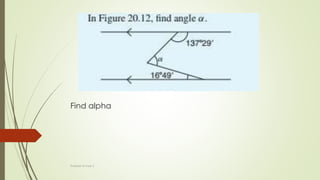
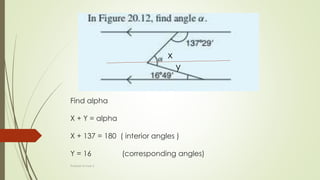
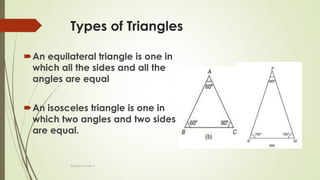
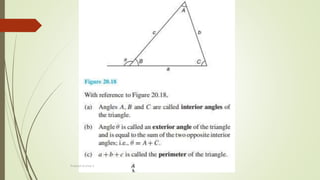
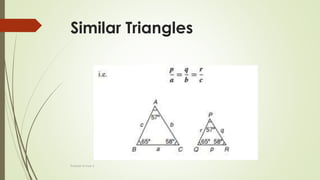
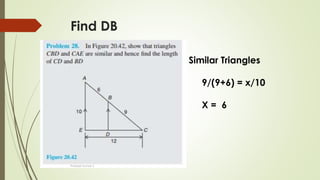
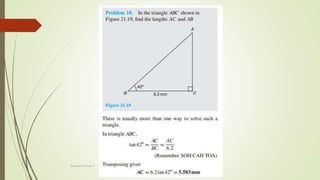
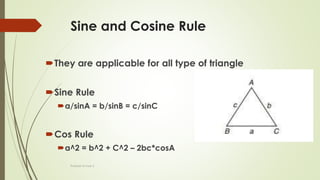
The document discusses angles and triangles, defining various types of angles and their properties, including complementary and supplementary angles. It covers the characteristics of triangles, notably that the sum of interior angles in a triangle equals 180°, and outlines types such as equilateral and isosceles triangles. Additionally, it introduces the Pythagorean theorem and the sine and cosine rules applicable to all triangles.