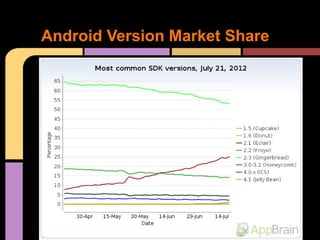
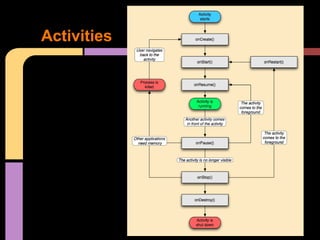
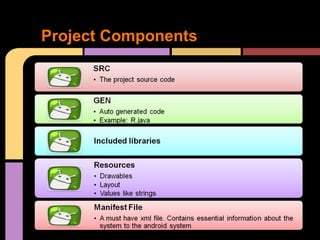
This document provides an overview of Android development for starters. It defines Android as an open mobile platform maintained by Google and the Open Handset Alliance. It lists the main Android versions and tools needed for development, including Eclipse. It describes the key application components in Android like Activities, Services, Broadcast Receivers and Content Providers. It explains how to set up a project in Eclipse with XML layouts, Java code, and run the app in an emulator or on a real device. Resources for installation and additional documentation are also provided.