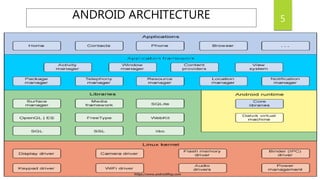
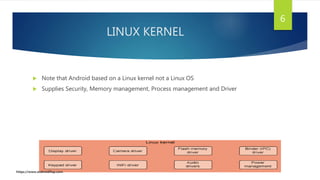
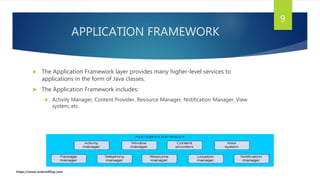
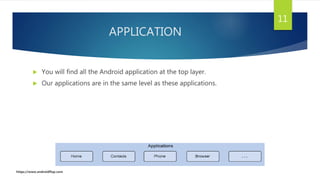
This document discusses Android app development. It describes Android as an open source, Linux-based OS used for mobile devices. It outlines Android's architecture including the Linux kernel, libraries, Android runtime, and application framework. It also discusses Android application components like activities, services, and content providers. The document concludes with describing an example app called "Learn Programming" intended to teach programming concepts.