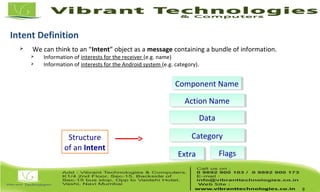
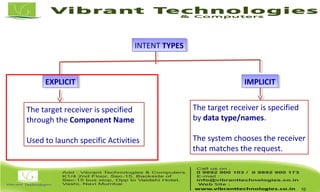
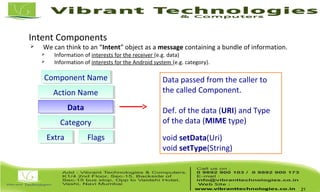
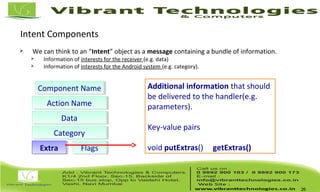
The document discusses activities and intents in Android programming. It defines an intent as a facility for late runtime binding between components in the same or different applications. Intents can be either explicit, specifying the target component, or implicit, allowing the system to choose the receiver. Key intent components include action, data, category, and extras. The document also covers activity states, saving resources, declaring activities in the manifest, and how the intent resolution process matches intents to potential receiving components.