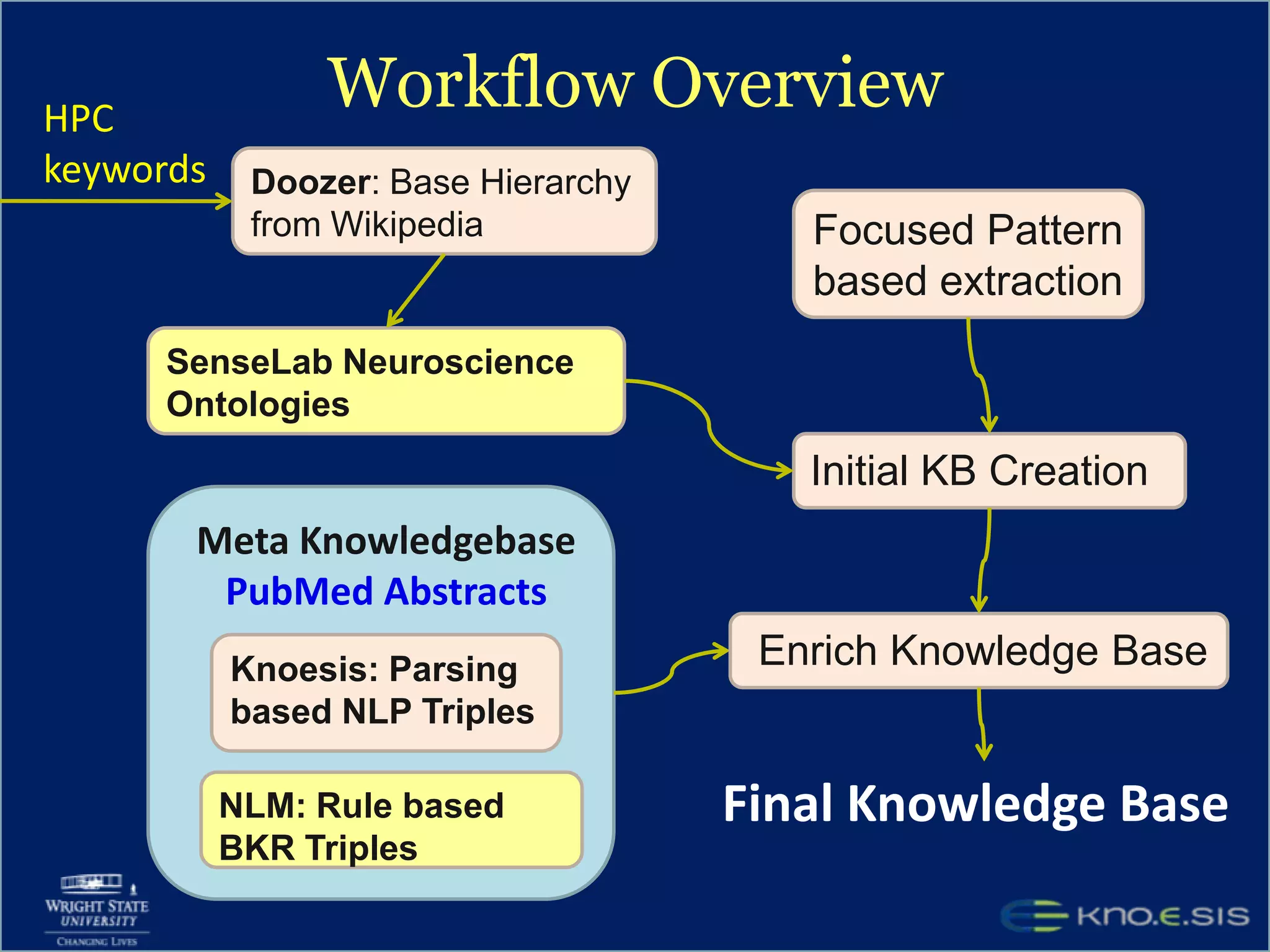
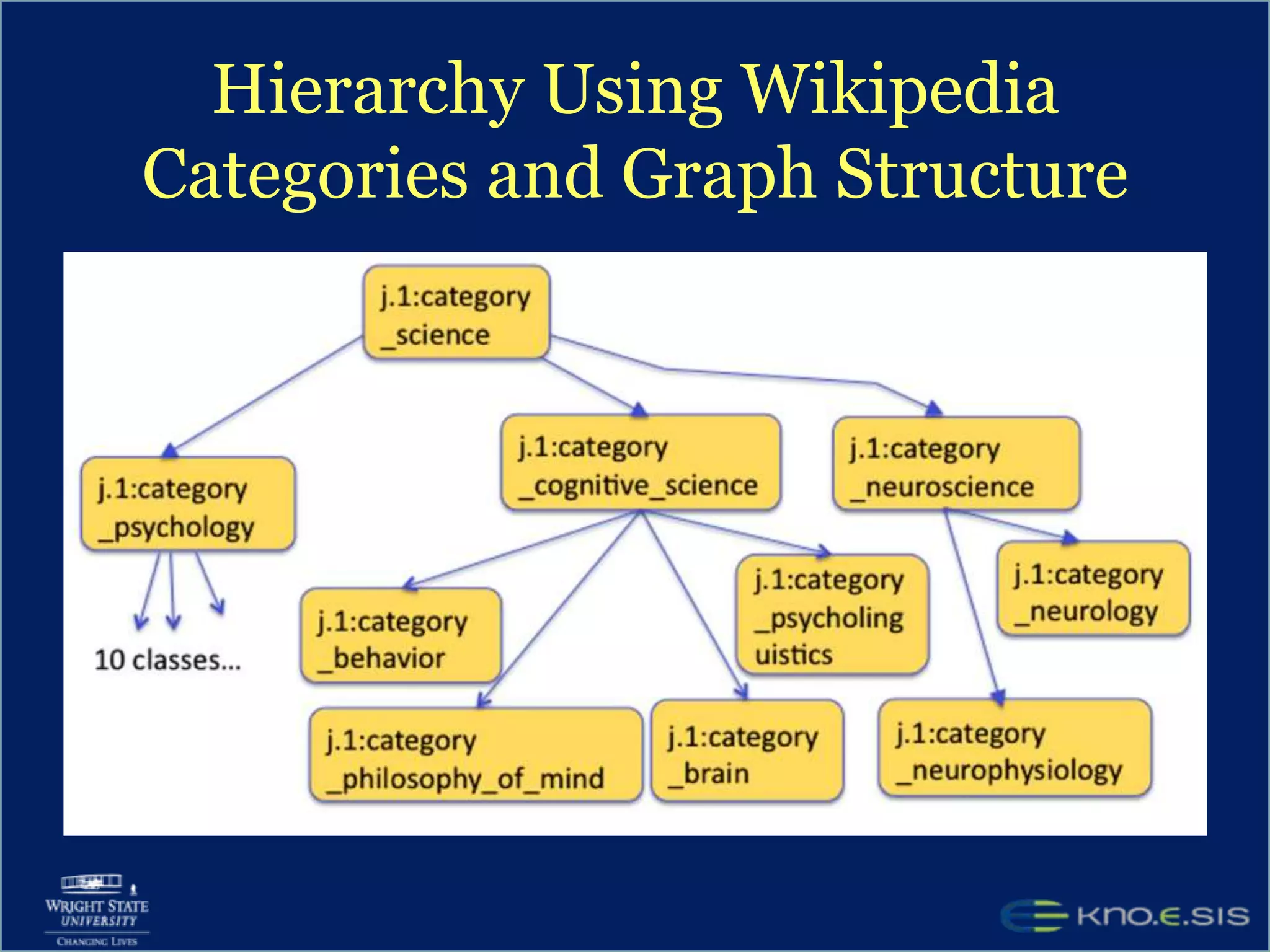
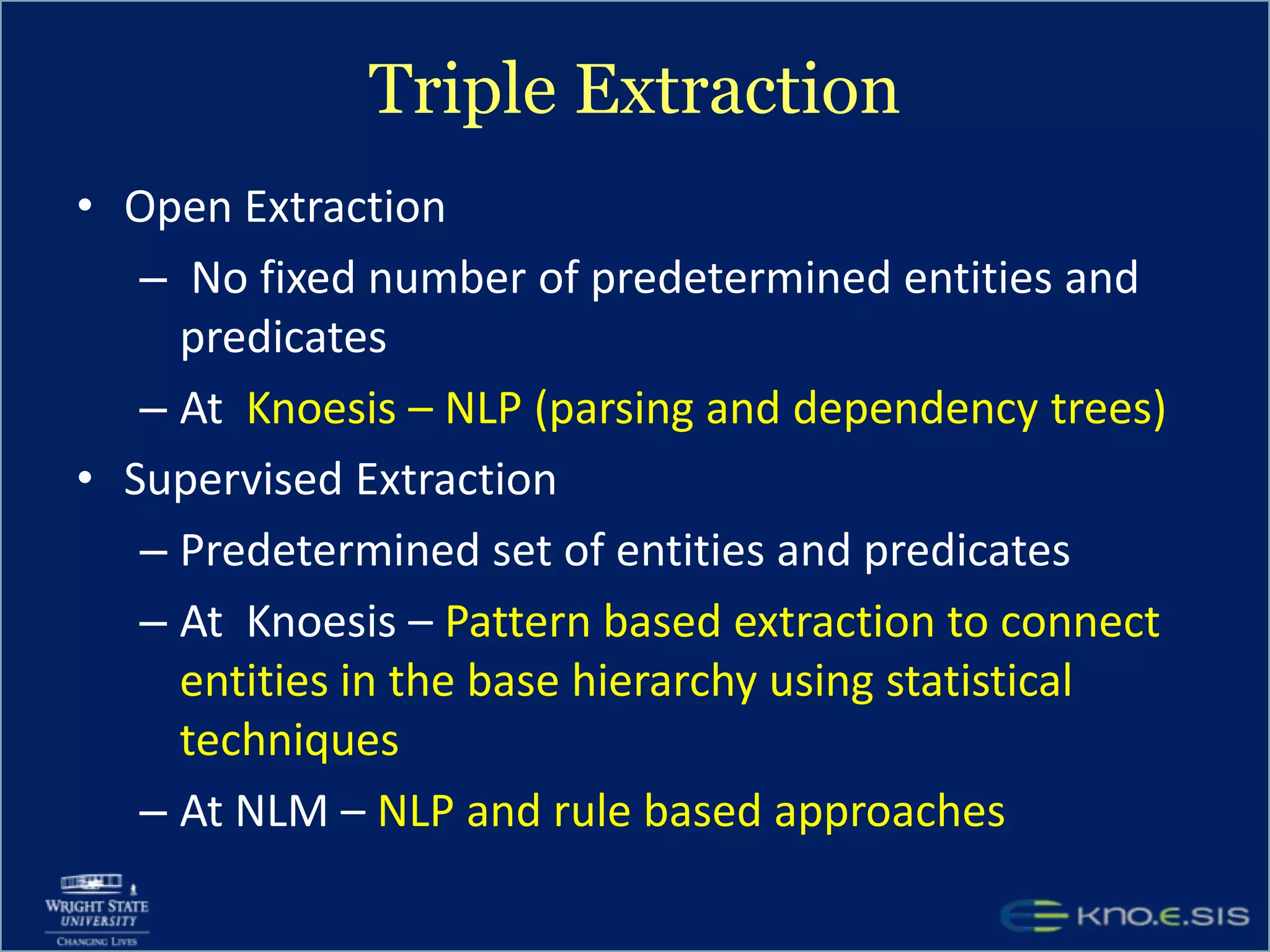
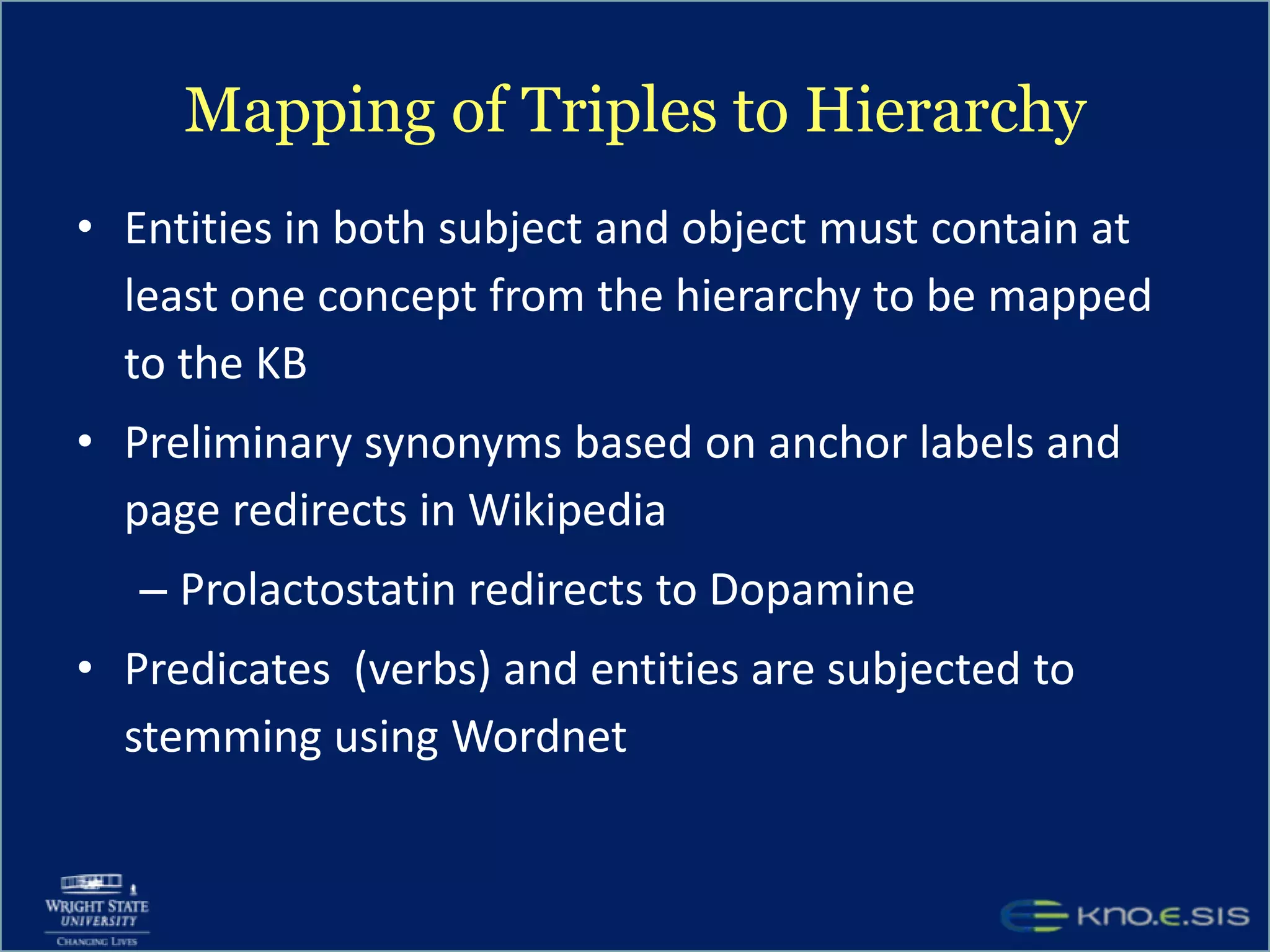
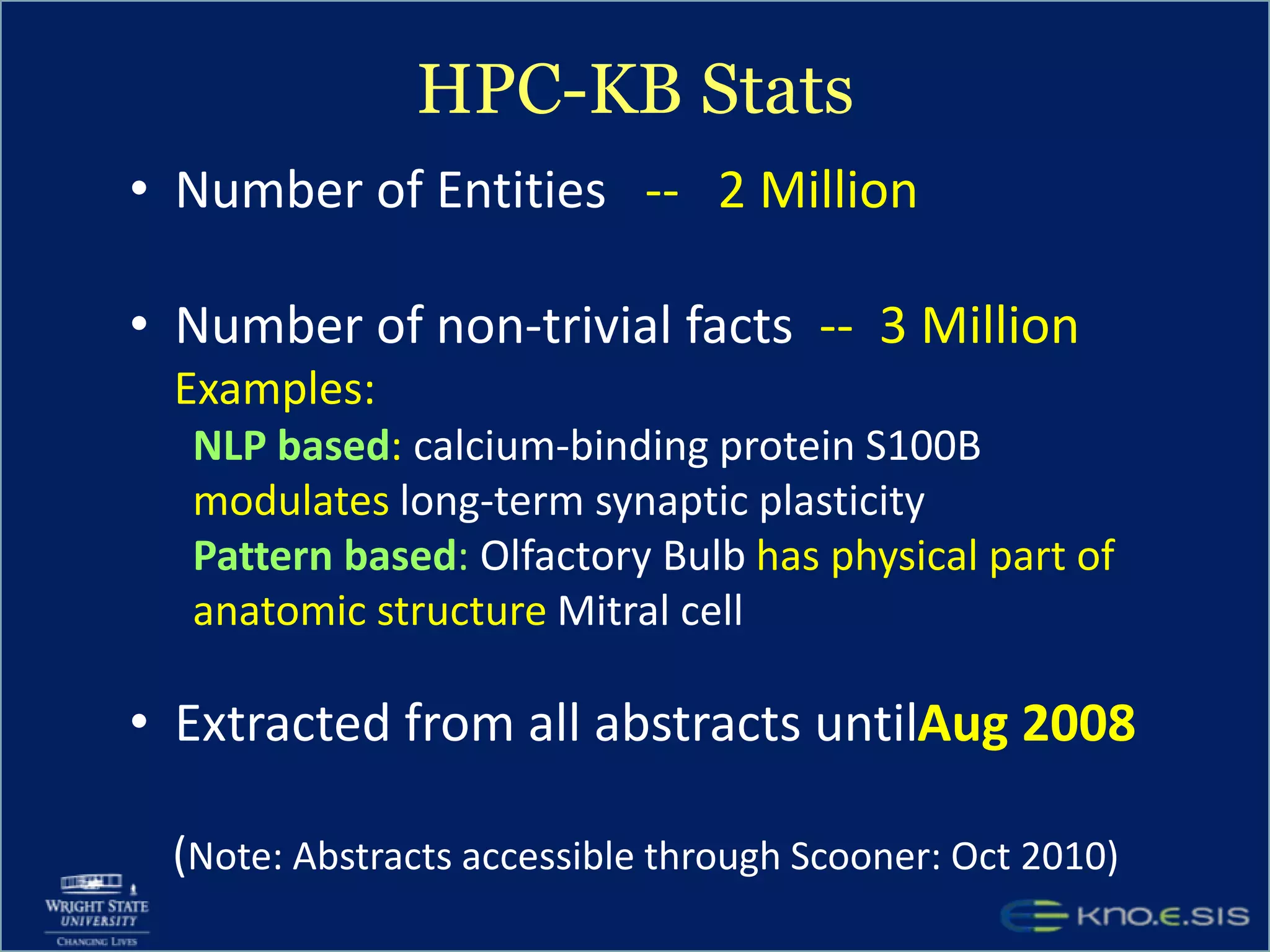
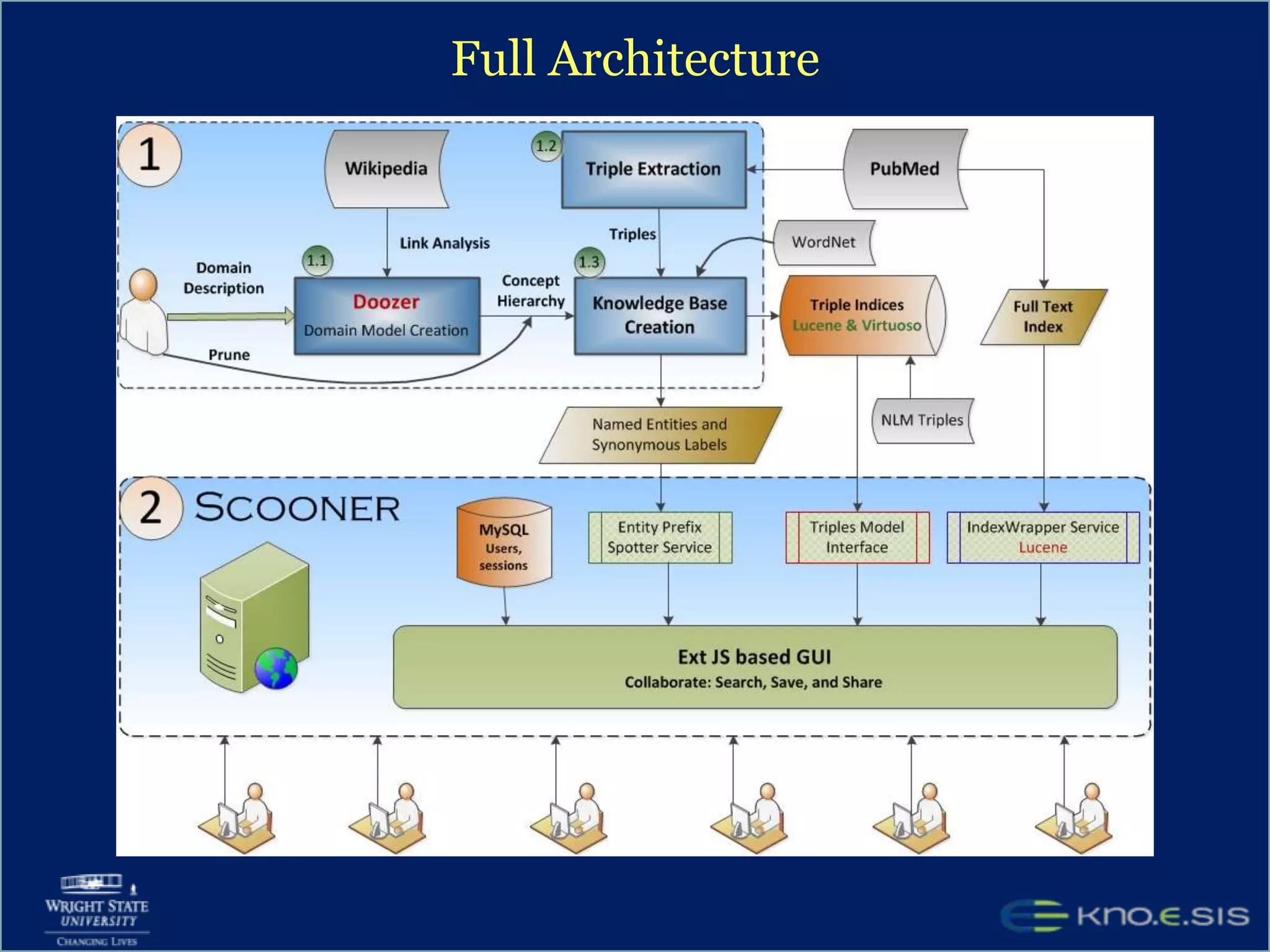
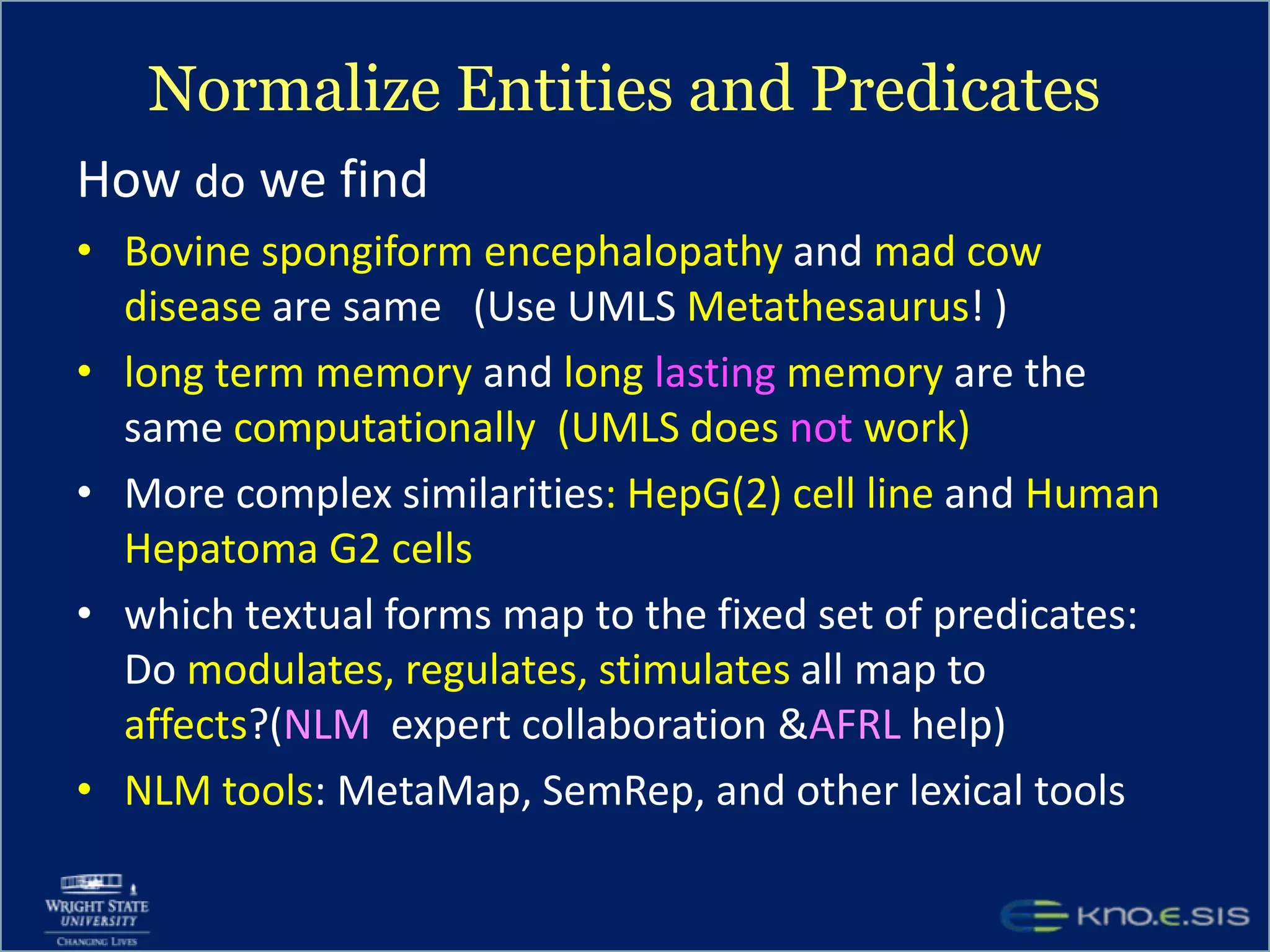
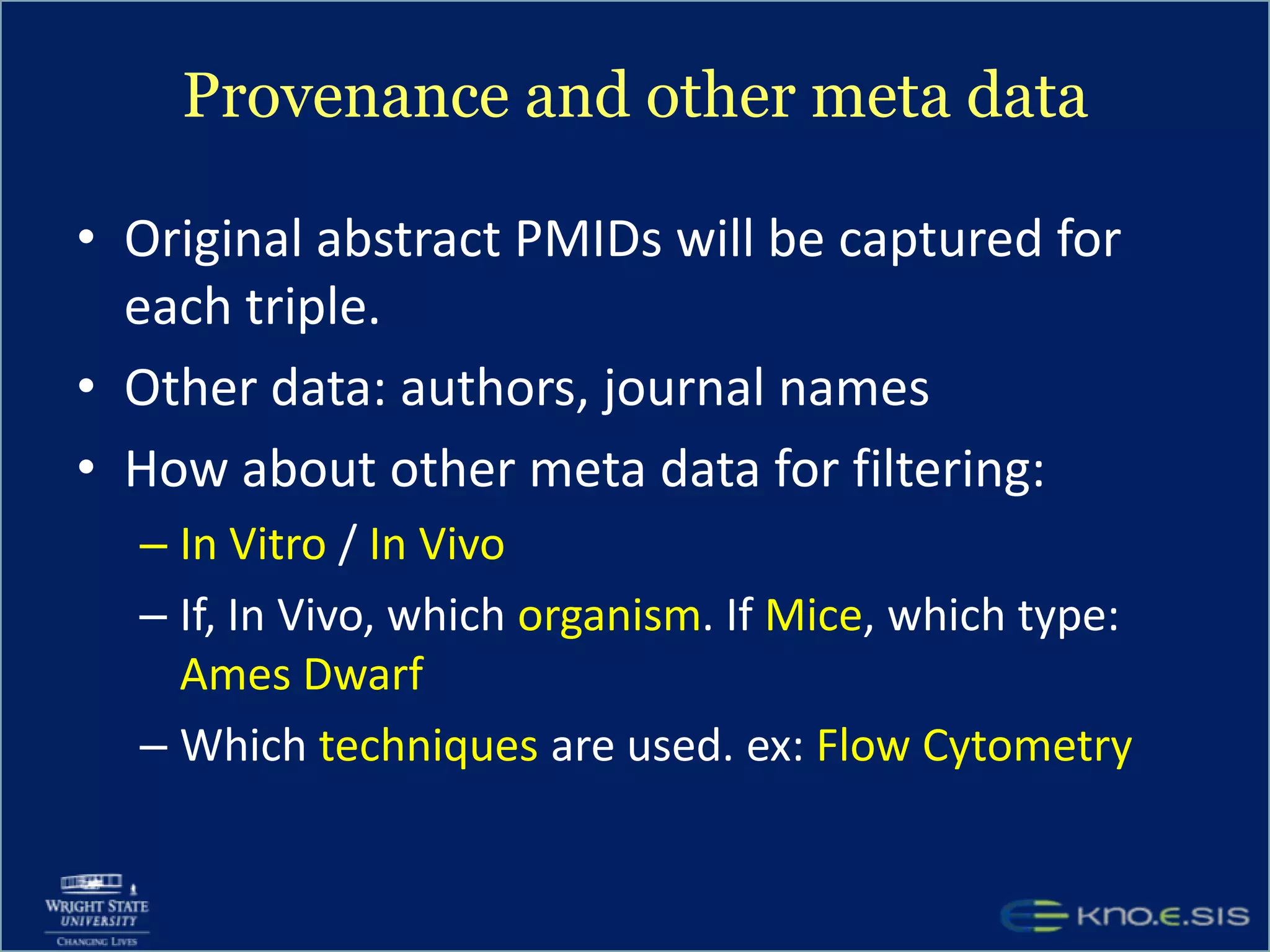
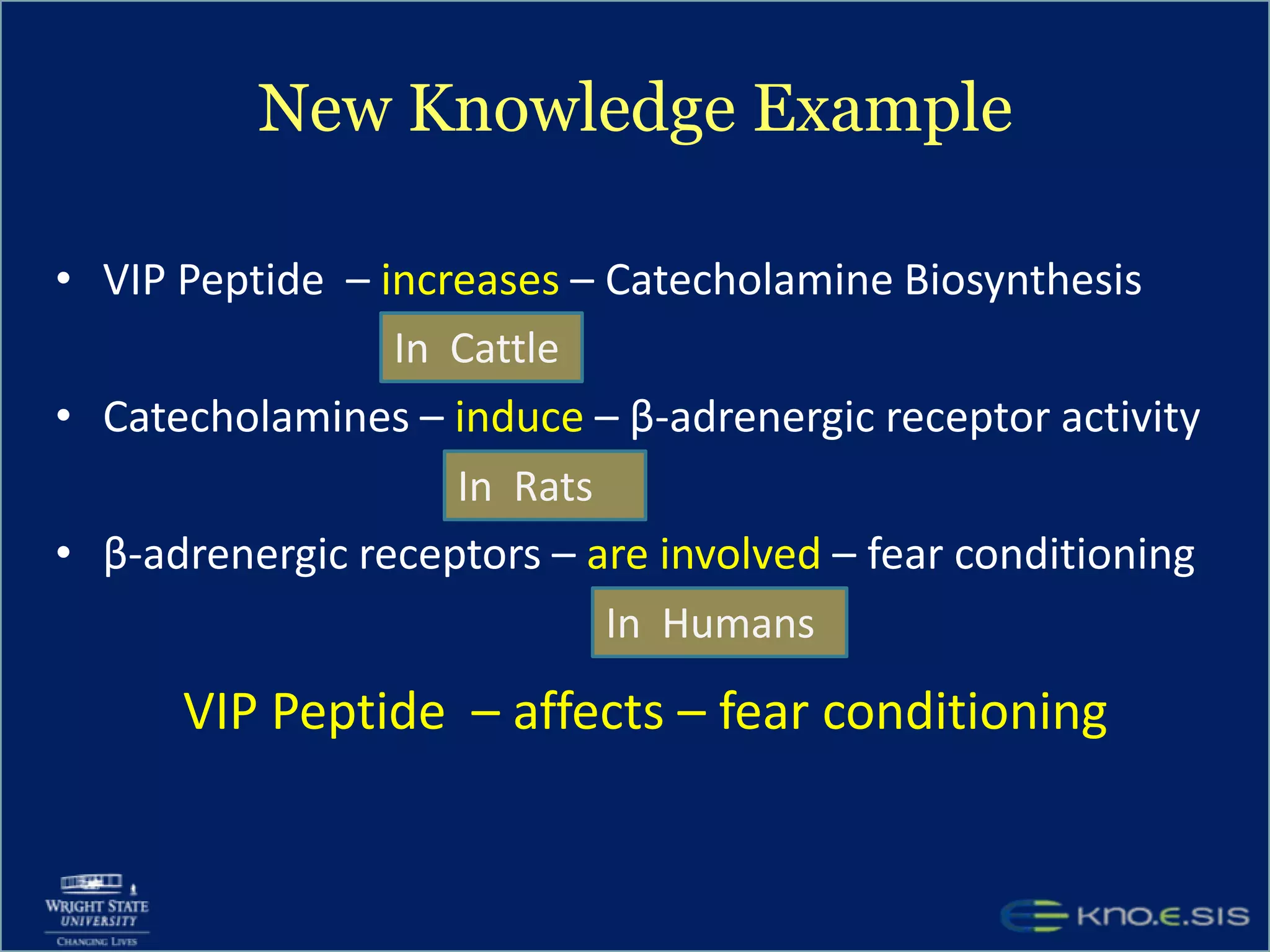
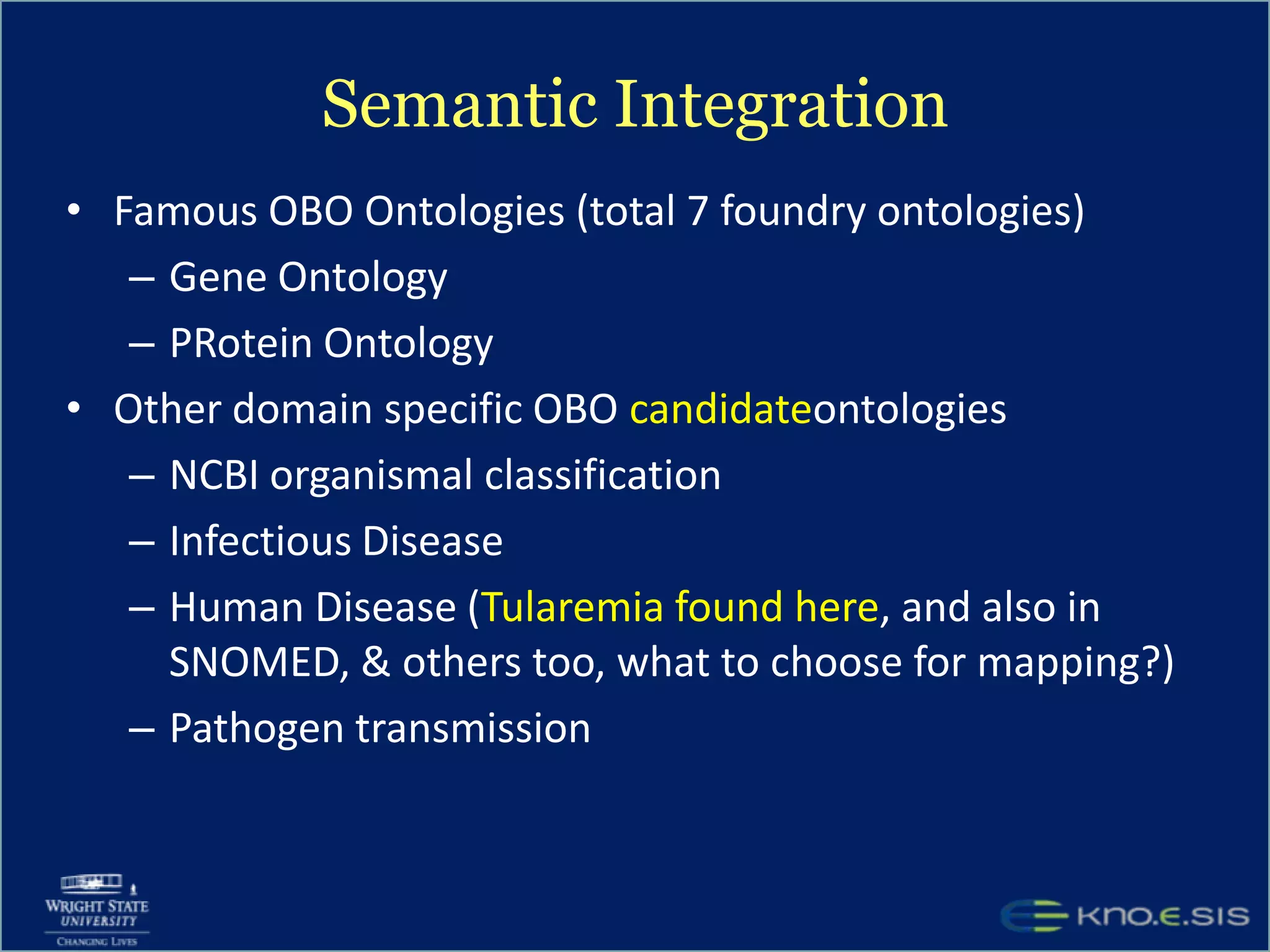
An expert knowledge base on human performance and cognition was created by extracting information from scientific literature using natural language processing and pattern-based techniques. Over 3 million facts were extracted from abstracts and mapped to a hierarchical structure derived from Wikipedia. The knowledge base was deployed through a browsing tool called Scooner that allows users to navigate relationships between concepts. Further work is focused on improving knowledge base quality by normalizing entities, filtering assertions, and integrating related ontologies and vocabularies.