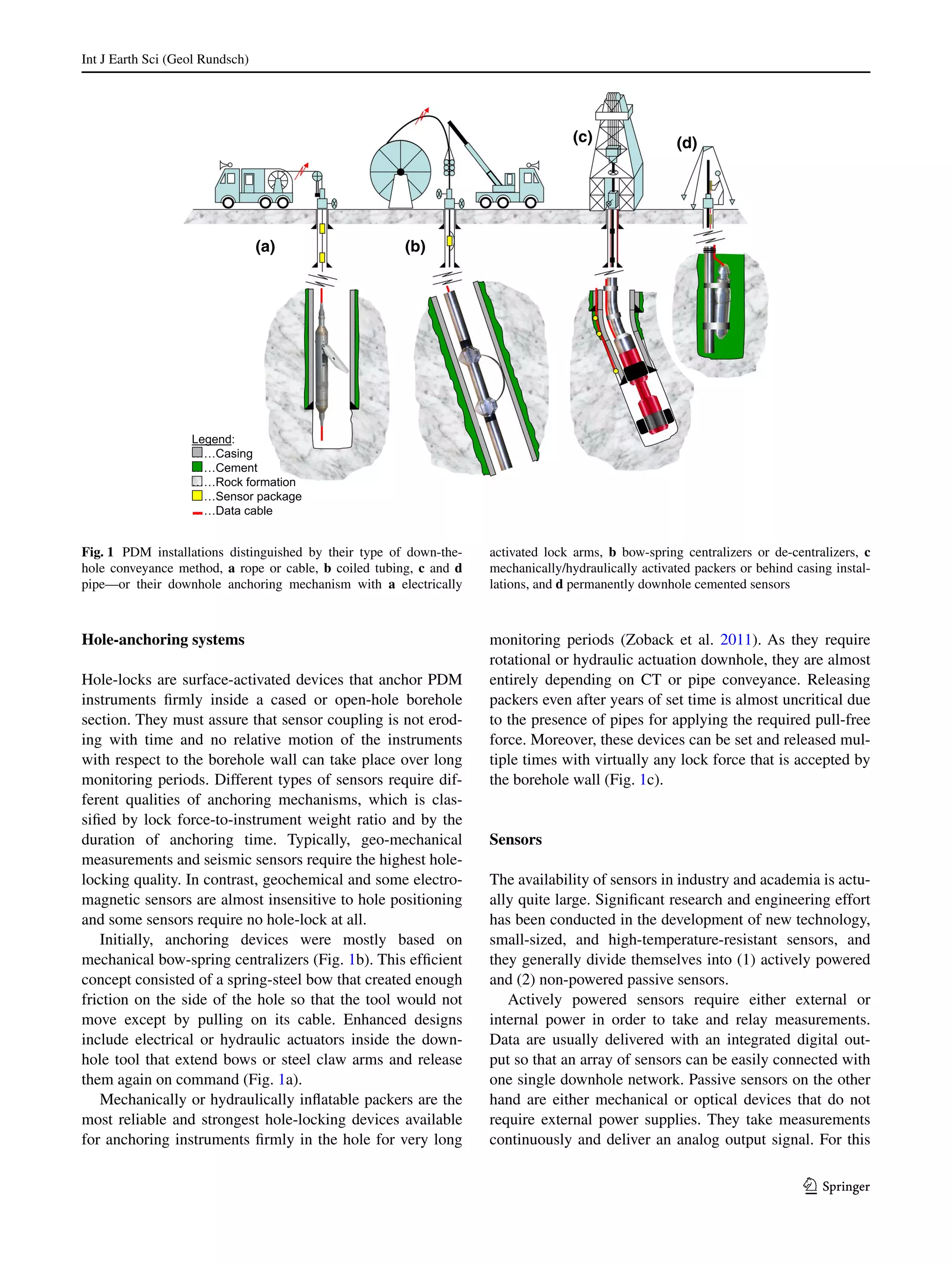
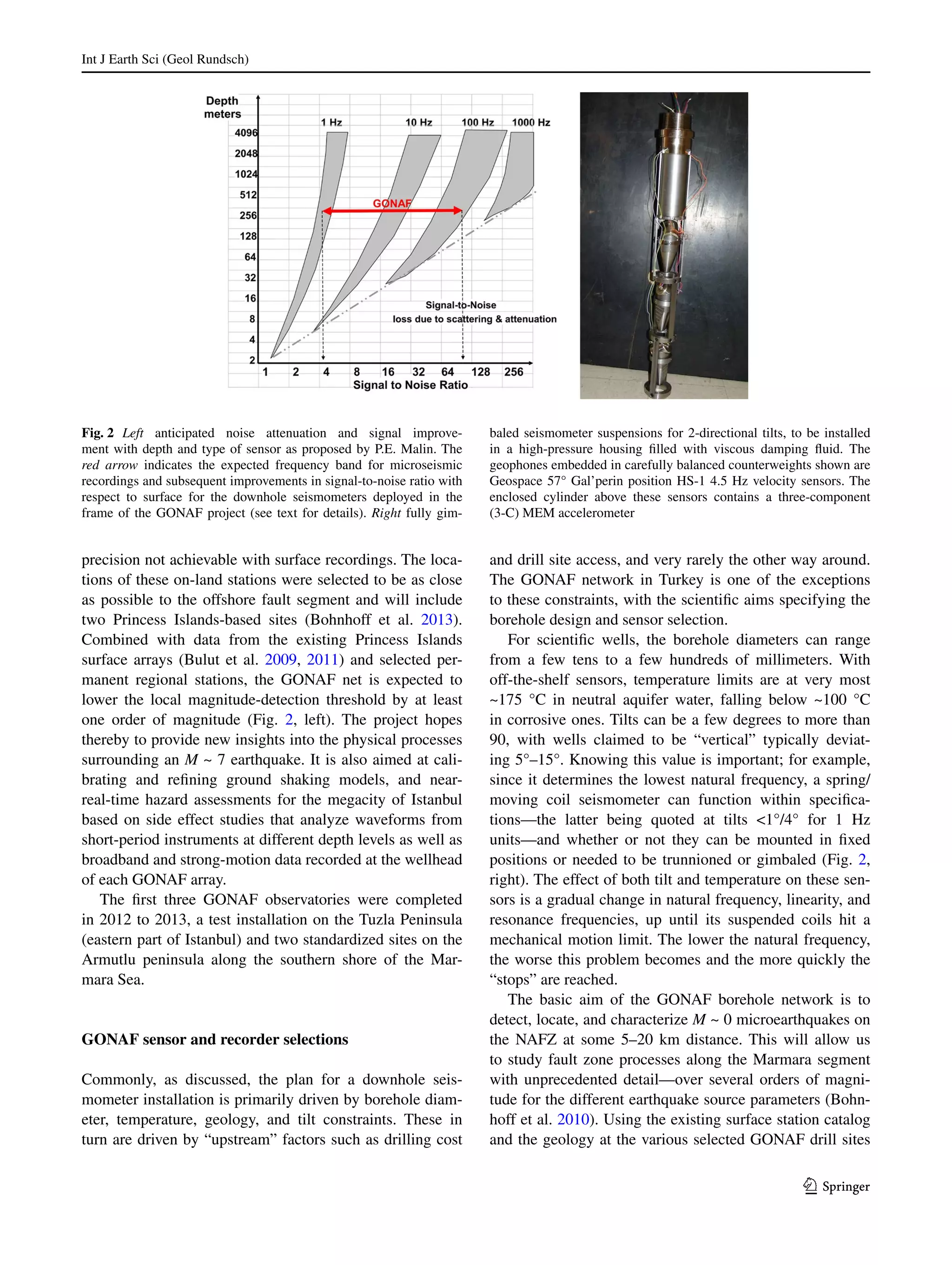
This document discusses best practices for installing downhole geophysical observatories. It describes two main types of permanent downhole monitoring installations: permanently cemented sensors behind casing, and instruments deployed inside casing or open holes using hole-locks or cement to anchor them. The document also discusses deployment systems like cable, coiled tubing, and drill pipe. Maintaining long-term stability and coupling of sensors to measure signals without surface noise is important. A case study of a new downhole observatory installation in Turkey along the North Anatolian Fault Zone is also presented.