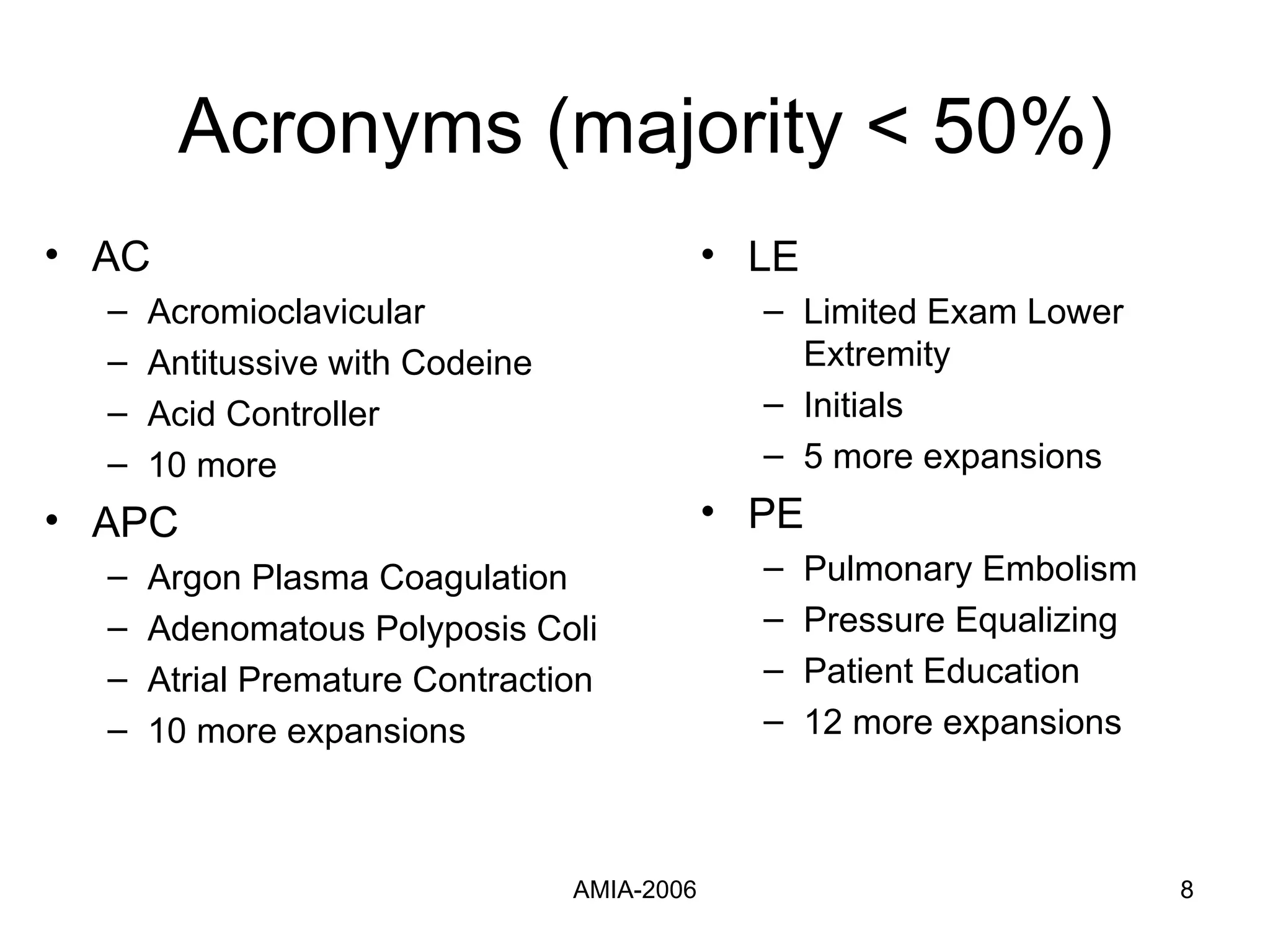
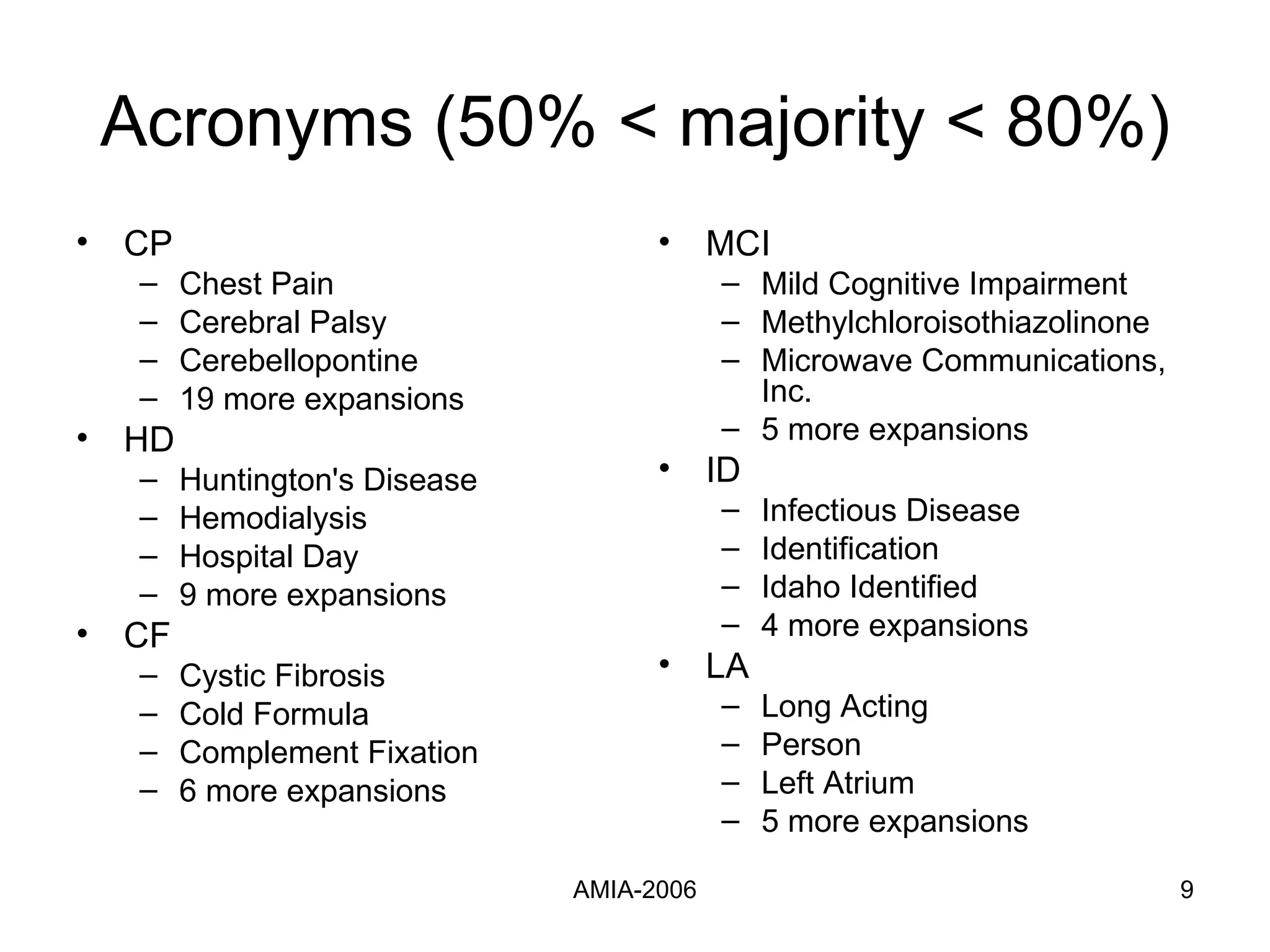
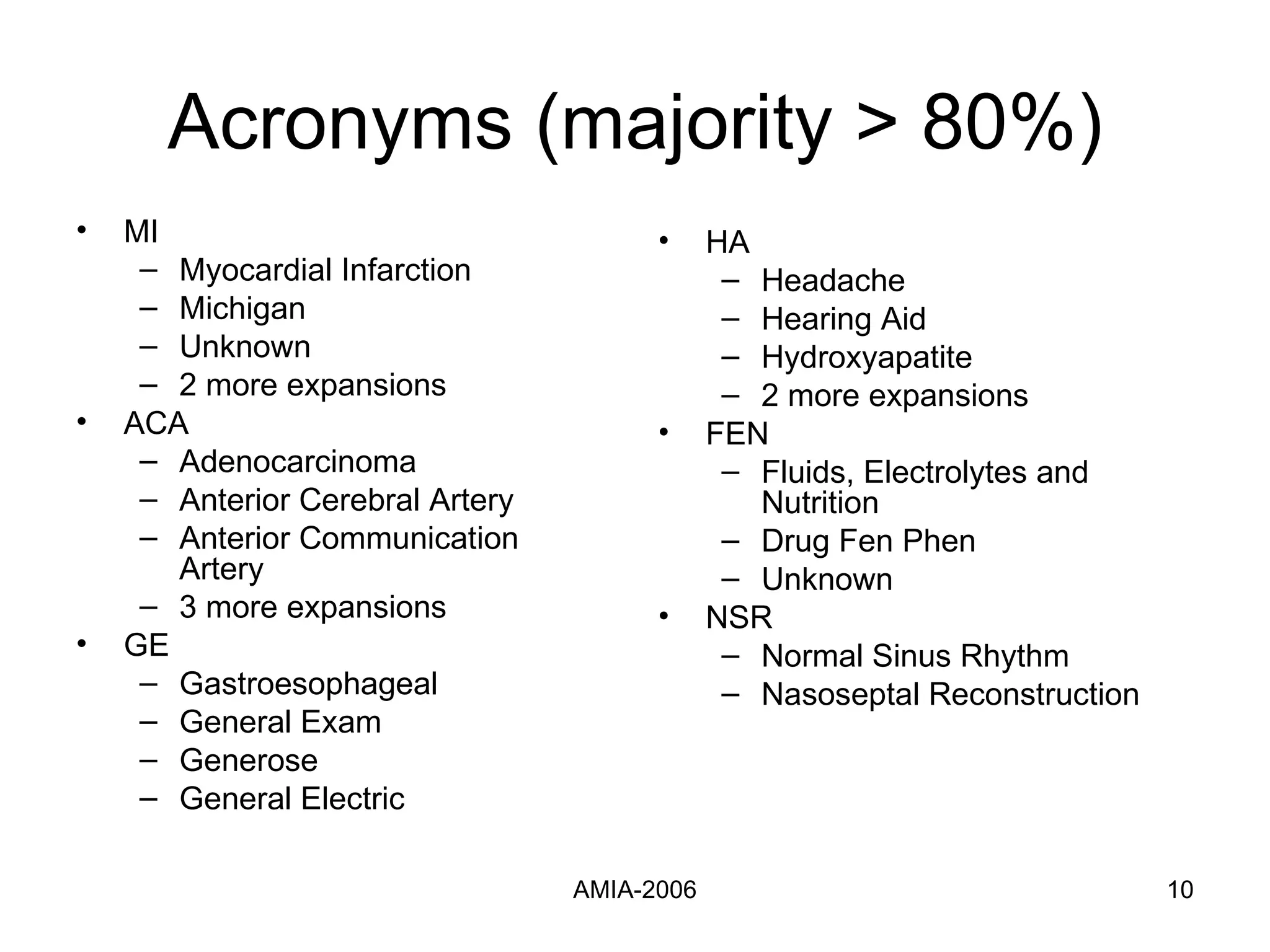
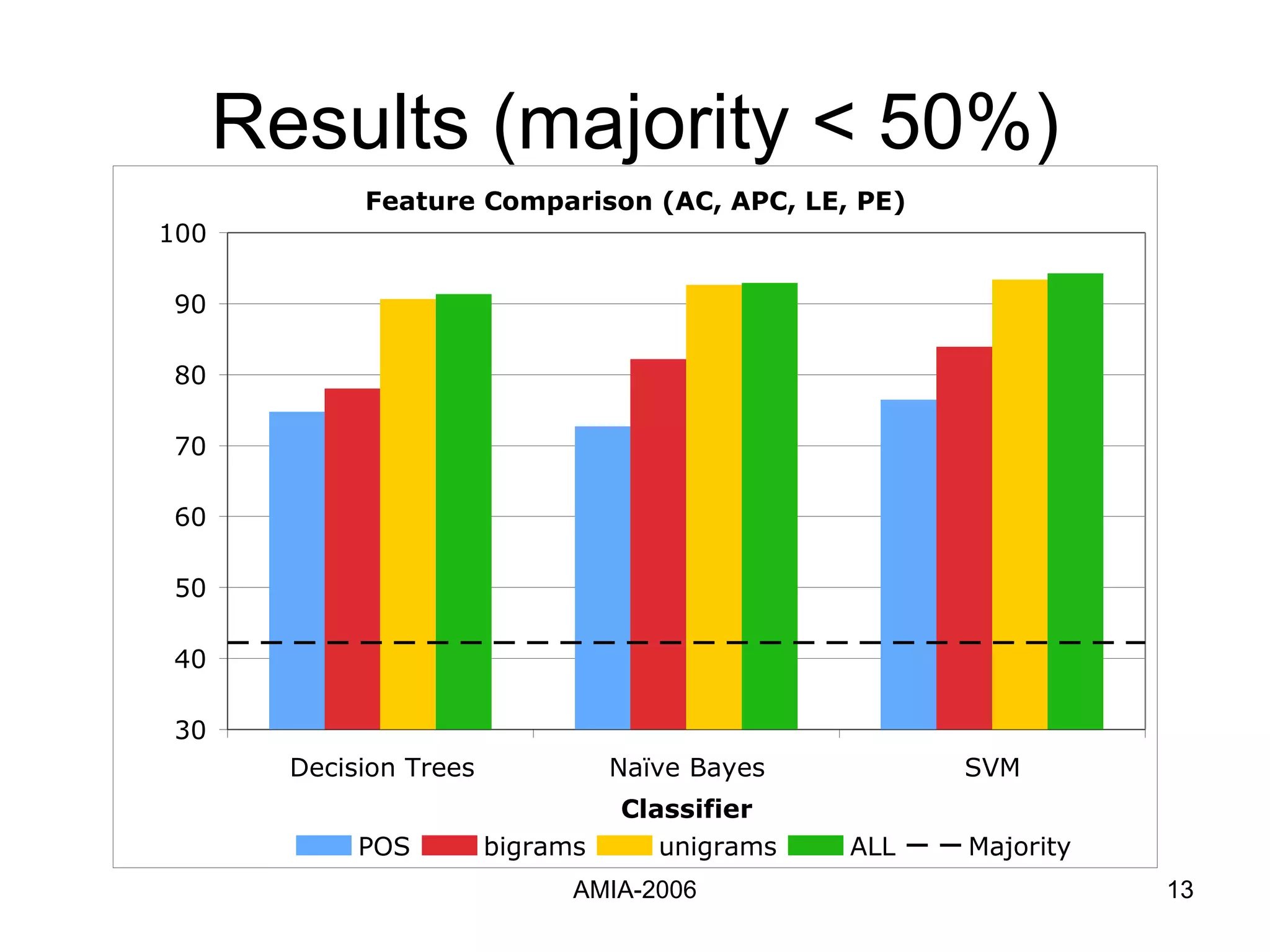
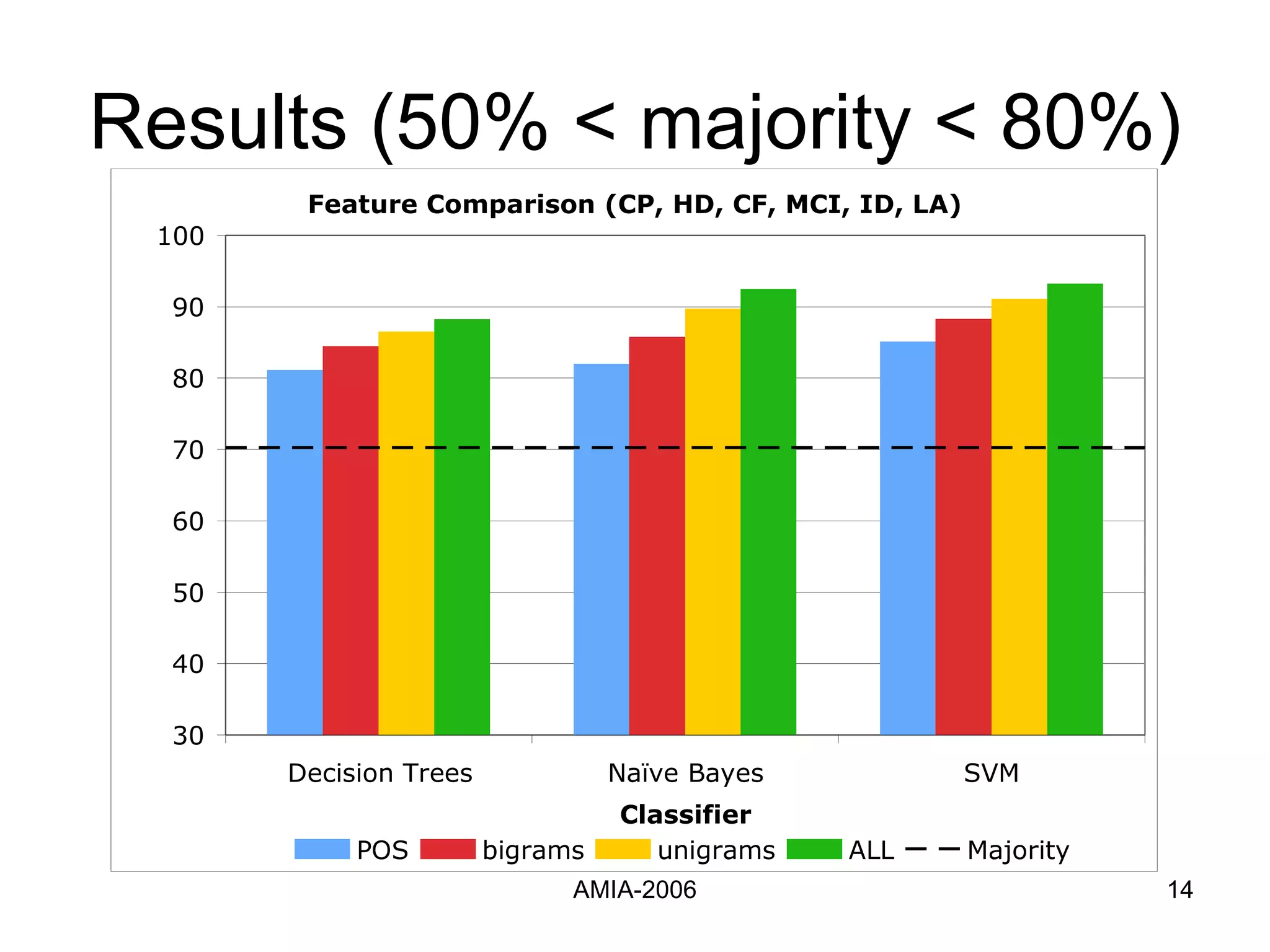
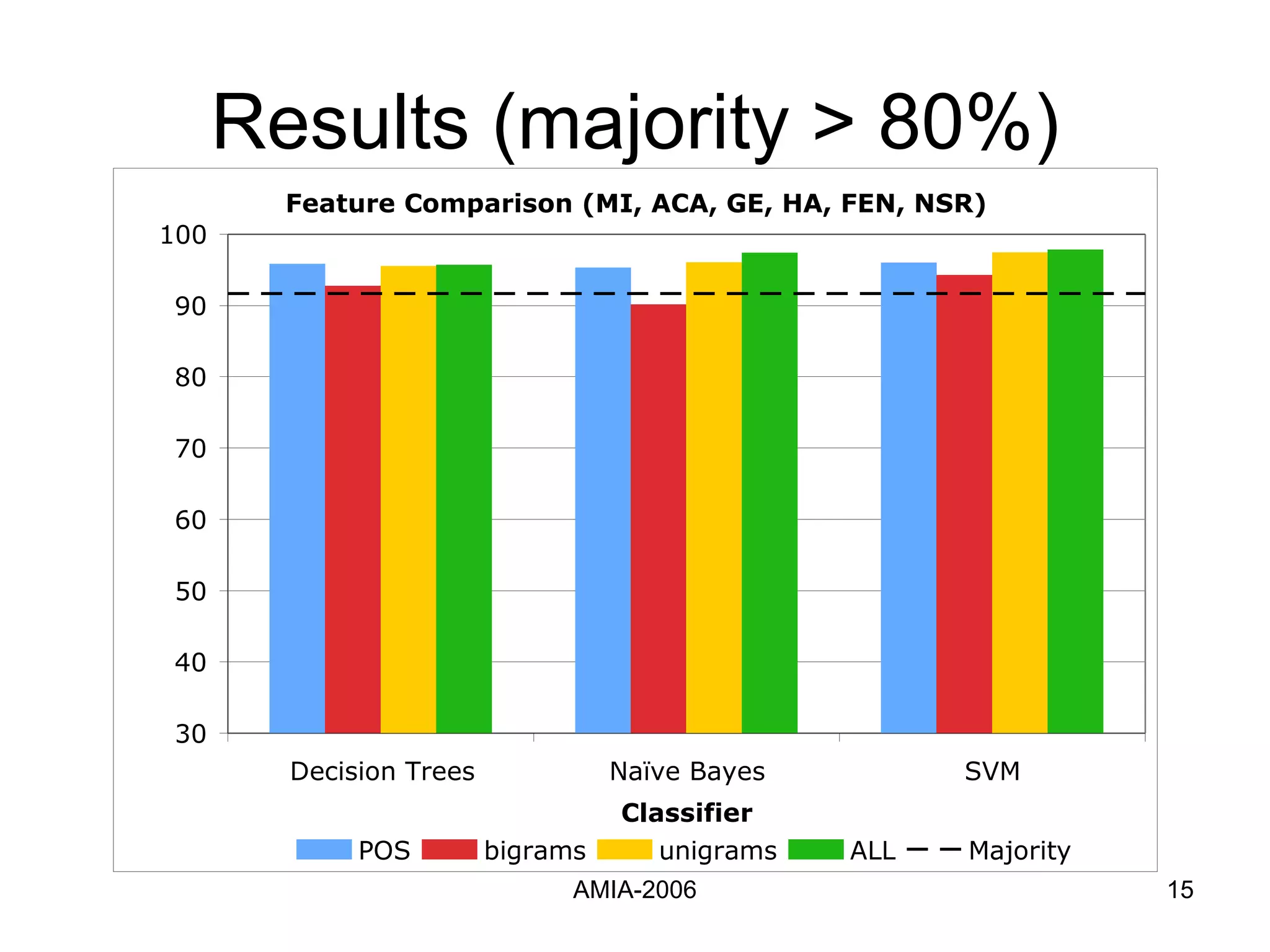
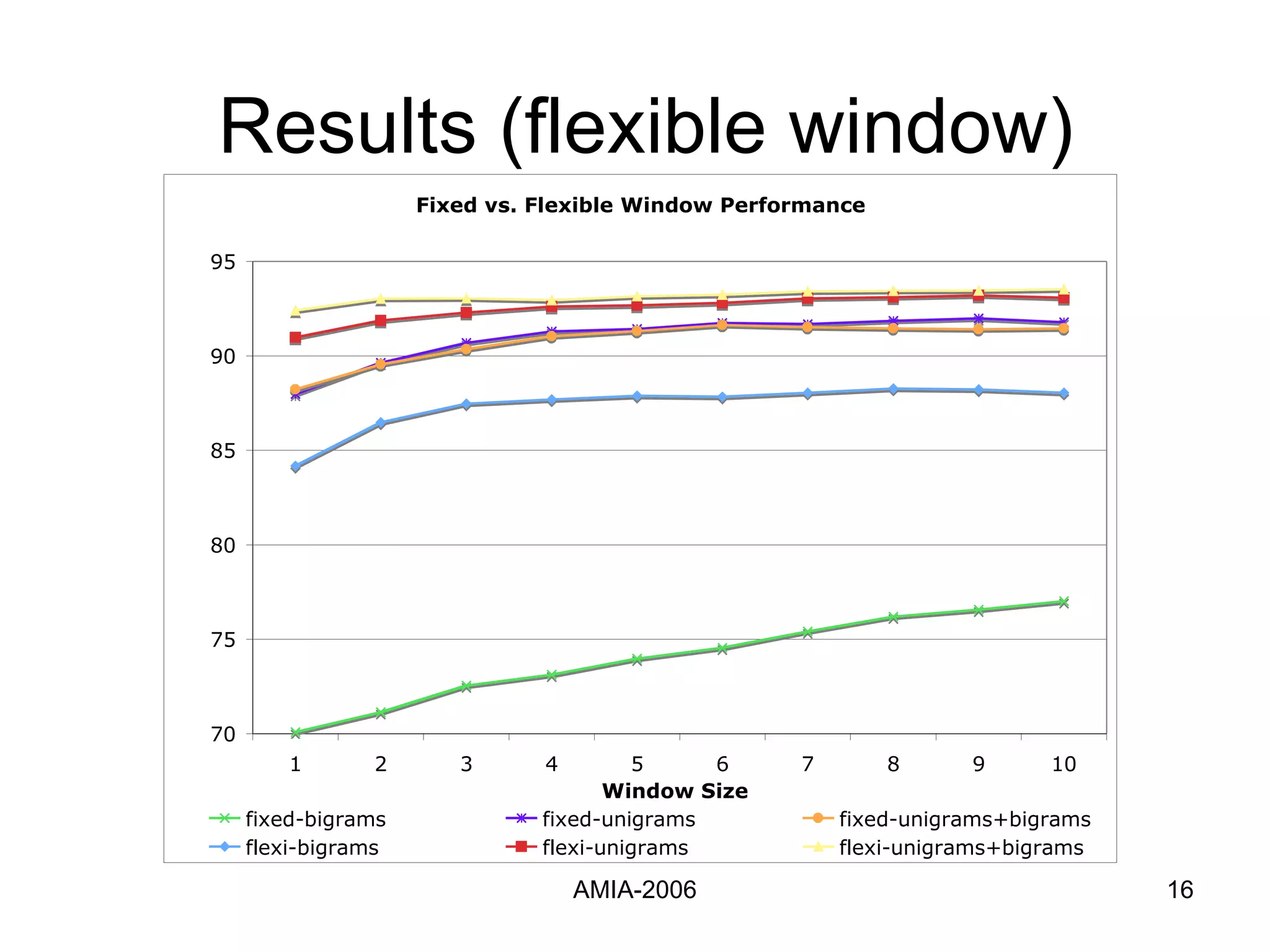
The document summarizes a study that compares supervised learning methods for expanding acronyms in clinical reports. It finds that naïve Bayesian classifiers, decision trees, and support vector machines can expand acronyms with over 90% accuracy. Unigrams are the most important features for the task. Considering a flexible window of text around acronyms improves performance over a fixed window.