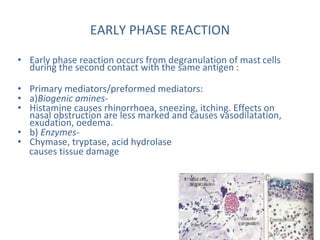
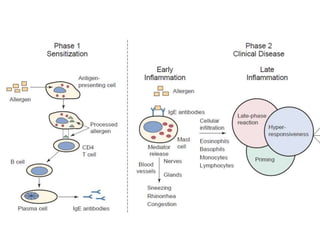
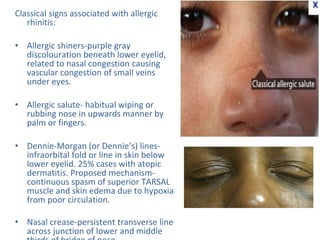
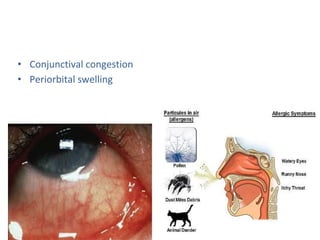
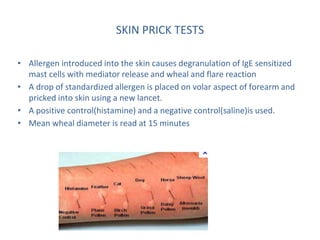
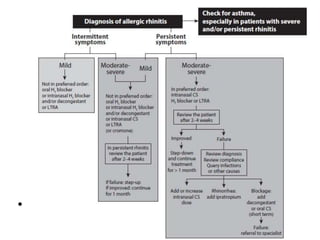
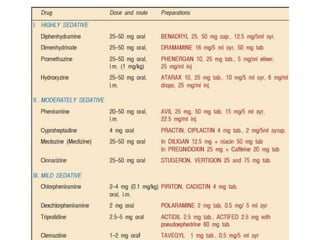
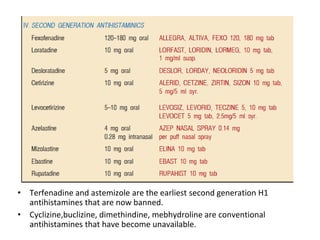
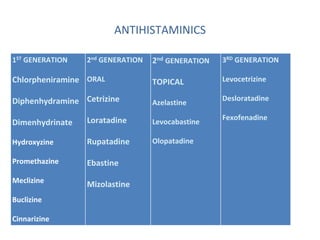
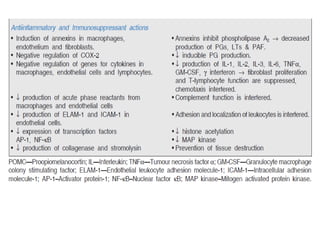
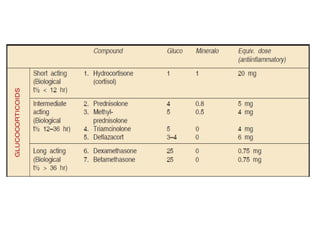
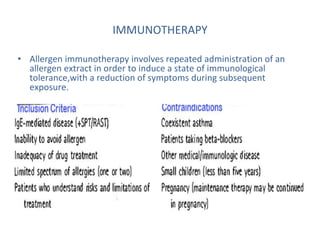
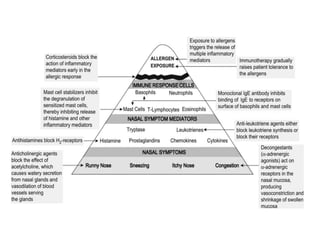
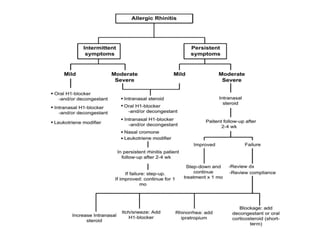
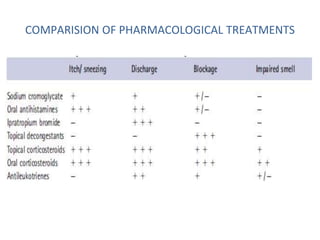
Allergic rhinitis is an inflammatory condition of the nasal mucosa caused by an IgE-mediated immune response to inhaled allergens. It is characterized by symptoms such as sneezing, rhinorrhea, nasal itching and congestion. The condition results from sensitization followed by exposure to an allergen, leading to mast cell degranulation and release of inflammatory mediators. This causes early phase symptoms, followed by late phase cellular infiltration and chronic inflammation. Diagnosis involves assessing symptoms and exposure history, with confirmation using skin prick tests or serum IgE tests. Treatment focuses on allergen avoidance, pharmacotherapy with antihistamines and intranasal corticosteroids, and immunotherapy for persistent