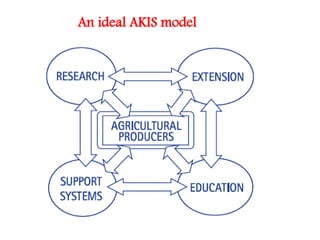
An agricultural knowledge and information system (AKIS) links people and institutions to promote sharing of agricultural knowledge and information. It integrates farmers, educators, researchers, and extensionists. The goals are to develop new technologies, increase production, solve on-farm problems, and improve delivery of services.
Key components of an ideal AKIS include knowledge generators like universities, knowledge sharers like extension services, and knowledge users like farmers. In India, examples of AKIS initiatives include government programs like AGMARKNET and Kisan Call Centres, as well as private sector programs from ITC e-Choupal and Tata Kisan Sansaar.
AKIS provides benefits like responding to farmers' technology



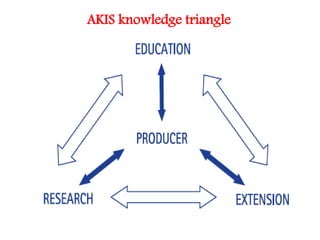

![AGMARKNET
Crops Directorates (8) [Wheat,
Jute, Cotton, Rice, Sugarcane,
Millets, Pulses, Tobacco]
Technology Mission on
Horticulture
Coconut Development Board
IFFCO
Network
Area
Office
Area
Office Kiosk
DMI
Hqs.
AGMAKRNET
http://agmarknet.ni
c.in
Area
Office Farmers
Markets
DMI State
Offices
IFFCO
Local
News
papers
Notice
Board /
Electroni
c Board
CDB
Farmer
s
Call Centres
Agri-clinics
Mobile
Operators
farmers
State Mkts./
Directorates
Regional
Portals
Public Access
Mobil
e
users
http://agmarknet.nic.in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/akis-150822030653-lva1-app6892/85/Akis-7-320.jpg)