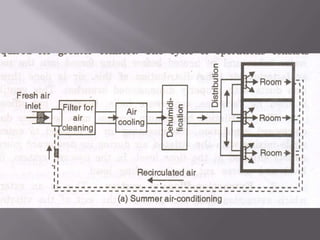
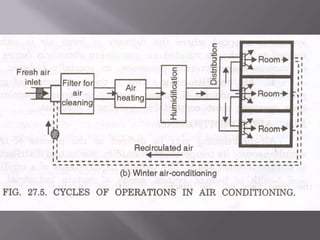
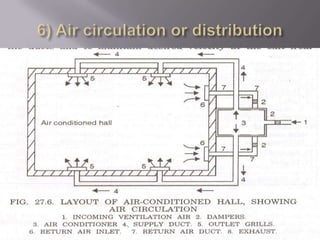
The document discusses air conditioning, defining it as the process of controlling temperature, humidity, purity, and distribution of air in an enclosed space. It describes the requirements of conditioned spaces, including comfort, industrial processes, and efficient work environments. It classifies air conditioning based on its purpose (comfort vs industrial) and based on season (summer cooling vs winter heating). The essential elements of an air conditioning system are controlling temperature, humidity, air velocity, and air quality through filtration, heating, cooling, humidification, dehumidification, and air circulation/distribution.