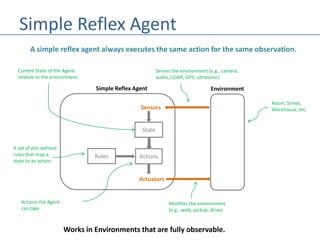
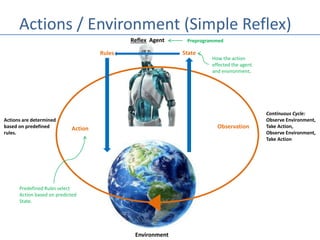
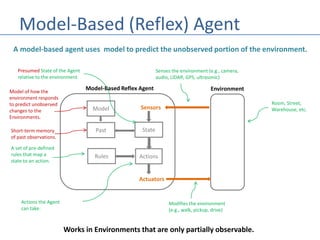
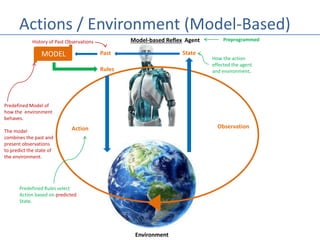
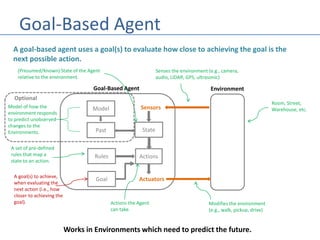
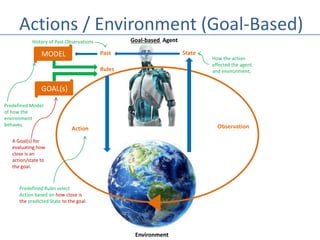
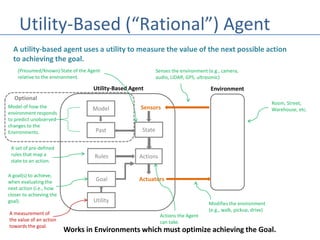
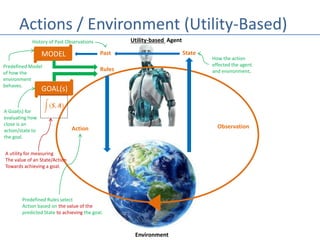
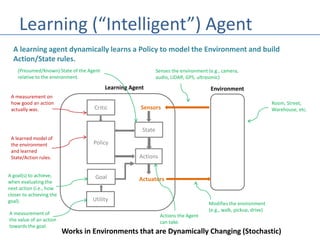
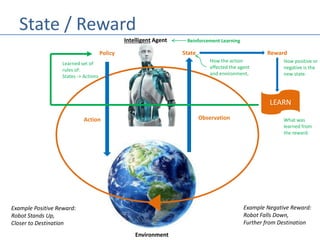
This document discusses four types of learning agents in artificial intelligence: simple reflex agents, model-based agents, goal-based agents, and utility-based agents. A learning agent improves upon these by dynamically learning a policy to model its environment and build action-state rules based on rewards from interacting with its environment.