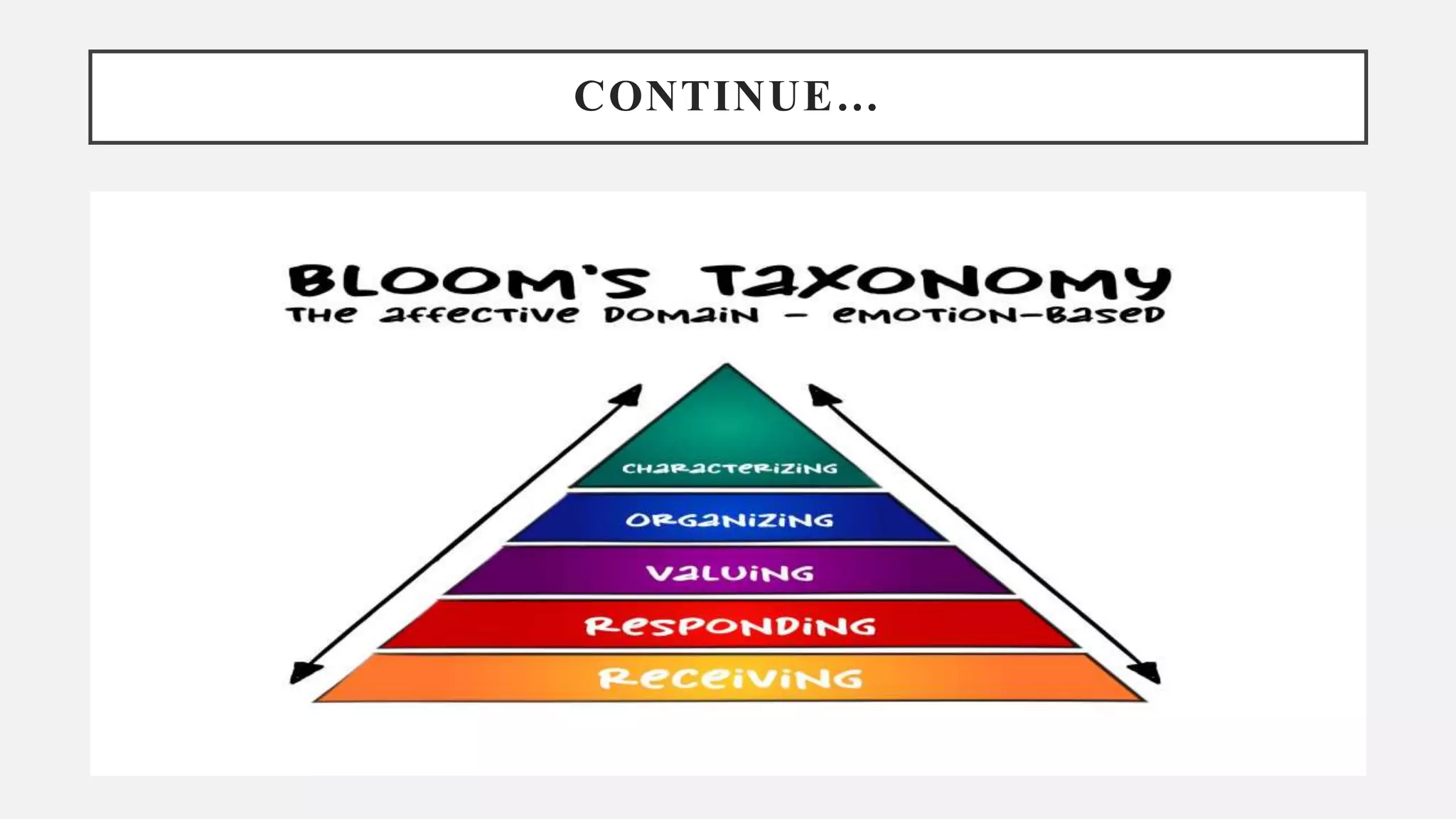
This document discusses Bloom's Taxonomy of the Affective Domain, which focuses on the development of feelings, attitudes, values, and appreciations in learning. It outlines the five levels of the Affective Domain - Receiving, Responding, Valuing, Organizing, and Characterizing - each representing a more complex level of learning in how learners feel about and are motivated towards what they are learning. The Affective Domain is important for developing positive attitudes, values, and appreciations in learners that can lead to increased engagement, good decision making, and an enriched life experience.