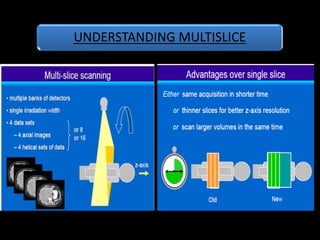
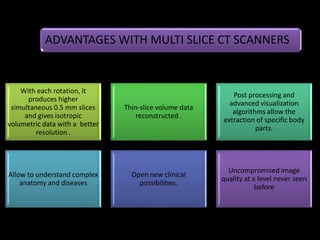
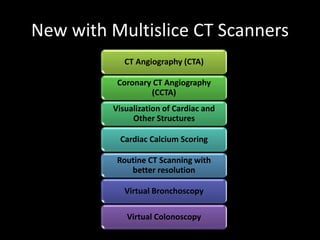
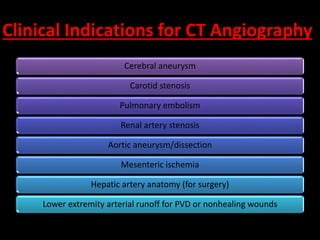
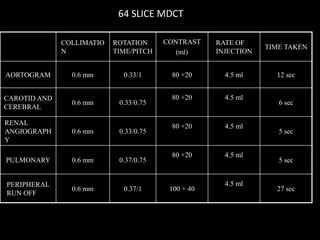
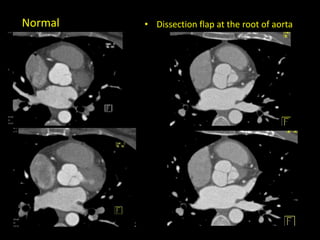
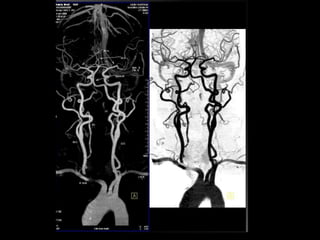
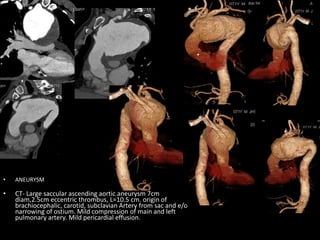
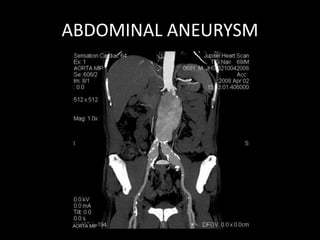
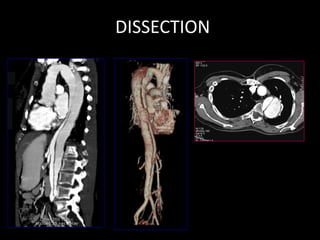
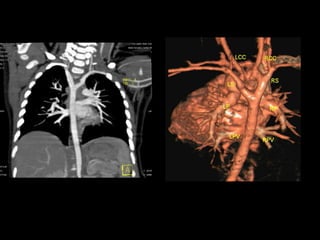
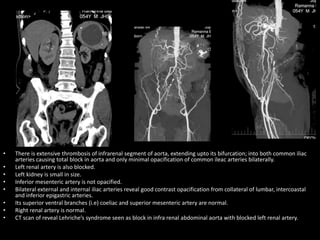
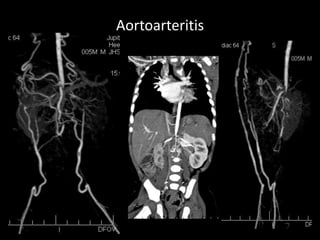
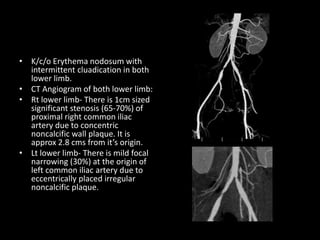
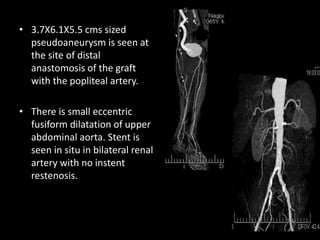
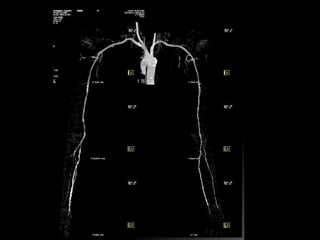
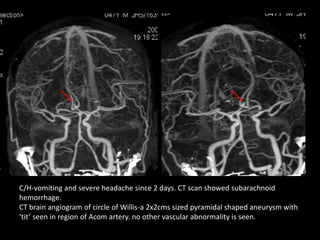
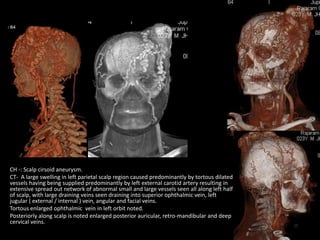
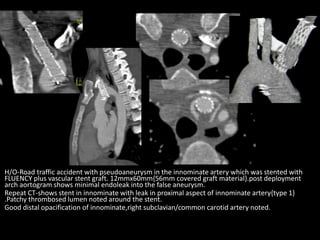
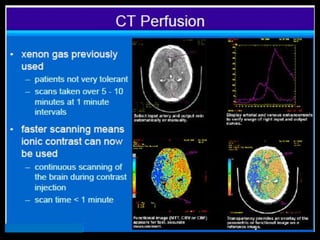
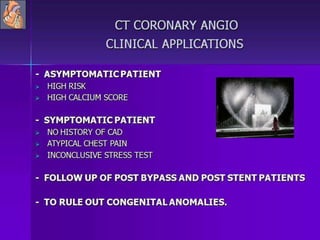
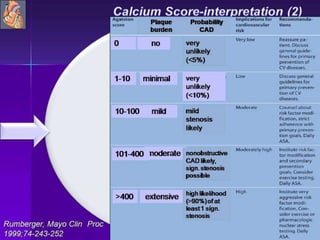
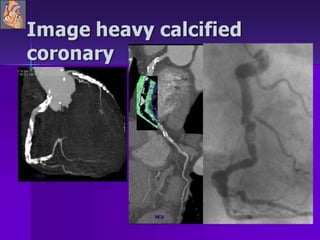
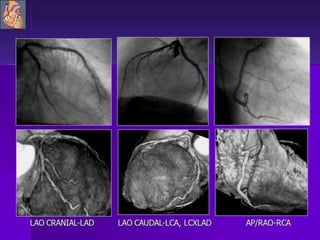
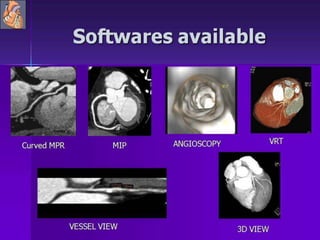
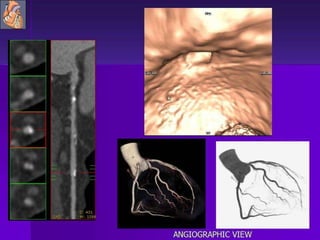
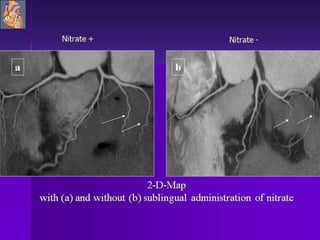
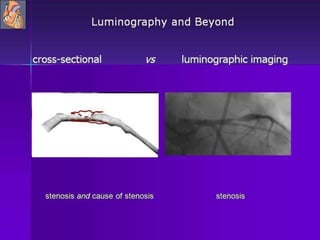
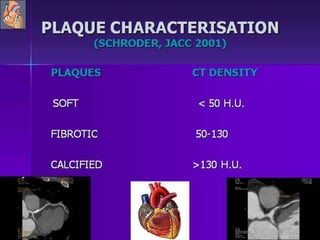
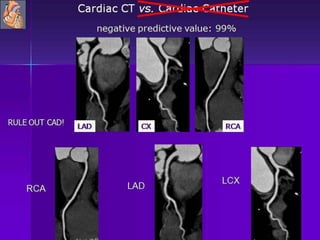
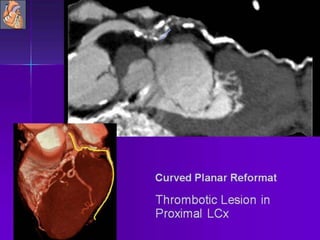
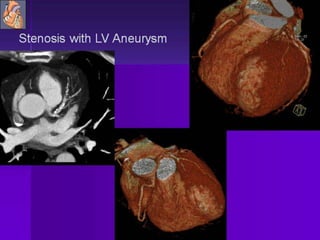
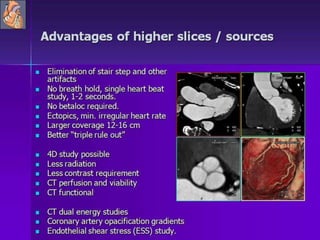
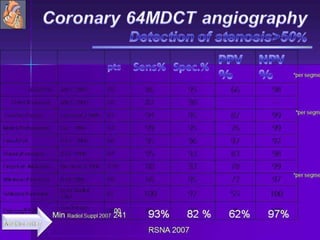
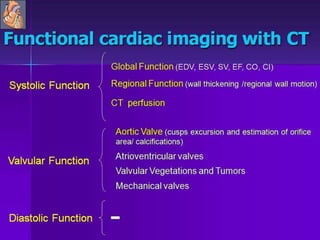
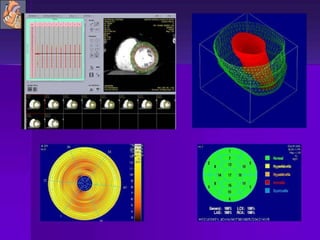
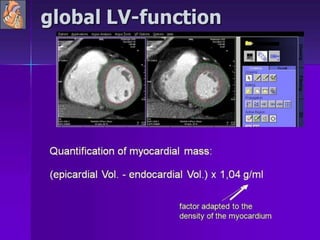
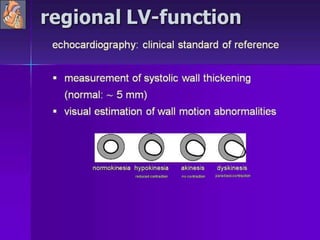
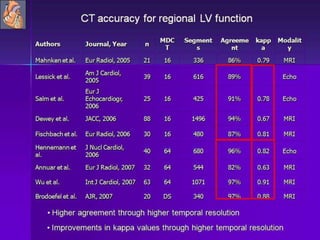
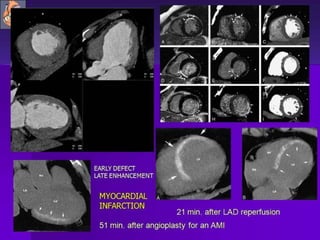
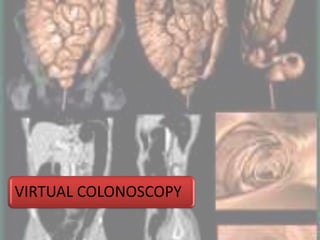
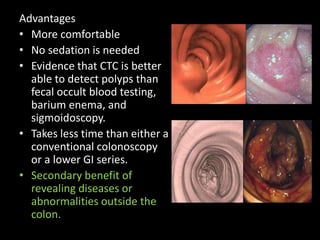
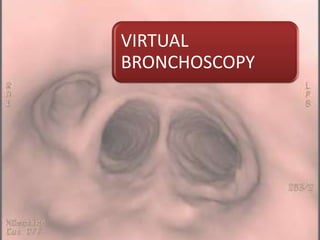
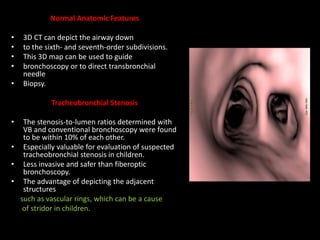
Advances in CT technology allow for higher resolution imaging with multi-slice CT scanners. This provides benefits for visualizing complex anatomy, diseases, and evaluating vasculature non-invasively with techniques like CT angiography. Additional applications enabled by high resolution volumetric data include virtual bronchoscopy and colonoscopy which provide endoluminal views to evaluate airways and the colon with benefits over conventional scopes. While CT involves ionizing radiation, doses are addressed with new technologies and some procedures may replace more invasive options, proving new CT applications are of increasing clinical value.