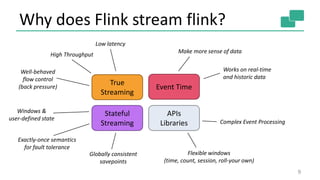
The document discusses streaming analytics using Apache Flink, highlighting its capabilities for real-time and batch processing through features like low latency, fault tolerance, and various time semantics. It covers the architecture, data flow, and examples of case classes for event processing, as well as techniques for stateful streaming and complex event processing. The document concludes with insights on future enhancements and use cases of Flink in large-scale data environments.


![Programs and Dataflows
8
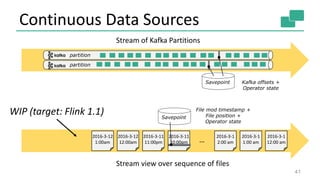
Source
Transformation
Transformation
Sink
val lines: DataStream[String] = env.addSource(new FlinkKafkaConsumer09(…))
val events: DataStream[Event] = lines.map((line) => parse(line))
val stats: DataStream[Statistic] = stream
.keyBy("sensor")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.sum(new MyAggregationFunction())
stats.addSink(new RollingSink(path))
Source
[1]
map()
[1]
keyBy()/
window()/
apply()
[1]
Sink
[1]
Source
[2]
map()
[2]
keyBy()/
window()/
apply()
[2]
Streaming
Dataflow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-8-320.jpg)

![Time-Windowed Aggregations
11
case class Event(sensor: String, measure: Double)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("sensor")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5))
.sum("measure")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-11-320.jpg)
![Time-Windowed Aggregations
12
case class Event(sensor: String, measure: Double)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("sensor")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(60), Time.seconds(5))
.sum("measure")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-12-320.jpg)
![Session-Windowed Aggregations
13
case class Event(sensor: String, measure: Double)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("sensor")
.window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.seconds(60)))
.max("measure")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-13-320.jpg)
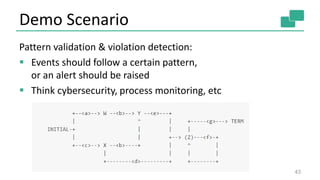
![Pattern Detection
14
case class Event(producer: String, evtType: Int, msg: String)
case class Alert(msg: String)
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("producer")
.flatMap(new RichFlatMapFuncion[Event, Alert]() {
lazy val state: ValueState[Int] = getRuntimeContext.getState(…)
def flatMap(event: Event, out: Collector[Alert]) = {
val newState = state.value() match {
case 0 if (event.evtType == 0) => 1
case 1 if (event.evtType == 1) => 0
case x => out.collect(Alert(event.msg, x)); 0
}
state.update(newState)
}
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-14-320.jpg)
![Pattern Detection
15
case class Event(producer: String, evtType: Int, msg: String)
case class Alert(msg: String)
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("producer")
.flatMap(new RichFlatMapFuncion[Event, Alert]() {
lazy val state: ValueState[Int] = getRuntimeContext.getState(…)
def flatMap(event: Event, out: Collector[Alert]) = {
val newState = state.value() match {
case 0 if (event.evtType == 0) => 1
case 1 if (event.evtType == 1) => 0
case x => out.collect(Alert(event.msg, x)); 0
}
state.update(newState)
}
})
Embedded key/value
state store](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-15-320.jpg)



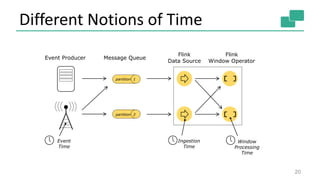
![Example: Windowing by Time
19
case class Event(id: String, measure: Double, timestamp: Long)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(15), Time.seconds(5))
.sum("measure")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-19-320.jpg)
![Processing Time
23
case class Event(id: String, measure: Double, timestamp: Long)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(ProcessingTime)
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(15), Time.seconds(5))
.sum("measure")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-23-320.jpg)
![Ingestion Time
24
case class Event(id: String, measure: Double, timestamp: Long)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(IngestionTime)
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(15), Time.seconds(5))
.sum("measure")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-24-320.jpg)
![Event Time
25
case class Event(id: String, measure: Double, timestamp: Long)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(EventTime)
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
stream
.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(15), Time.seconds(5))
.sum("measure")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-25-320.jpg)
![Event Time
26
case class Event(id: String, measure: Double, timestamp: Long)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(EventTime)
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(…)
val tsStream = stream.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
new MyTimestampsAndWatermarkGenerator())
tsStream
.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(15), Time.seconds(5))
.sum("measure")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-26-320.jpg)
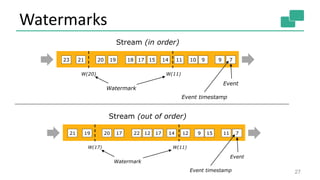
![Watermarks in Parallel
28
Source
(1)
Source
(2)
map
(1)
map
(2)
window
(1)
window
(2)
29
29
17
14
14
29
14
14
W(33)
W(17)
W(17)
A|30B|31
C|30
D|15
E|30
F|15G|18H|20
K|35
Watermark
Event Time
at the operator
Event
[id|timestamp]
Event Time
at input streams
Watermark
Generation
M|39N|39Q|44
L|22O|23R|37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-28-320.jpg)
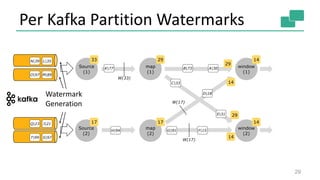

![Back to the Aggregation Example
31
case class Event(id: String, measure: Double, timestamp: Long)
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream: DataStream[Event] = env.addSource(
new FlinkKafkaConsumer09(topic, schema, properties))
stream
.keyBy("id")
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(15), Time.seconds(5))
.sum("measure")
Stateful](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streaminganalyticswithapacheflinkstephanewen-160511192751/85/Advanced-Streaming-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-and-Apache-Kafka-Stephan-Ewen-31-320.jpg)