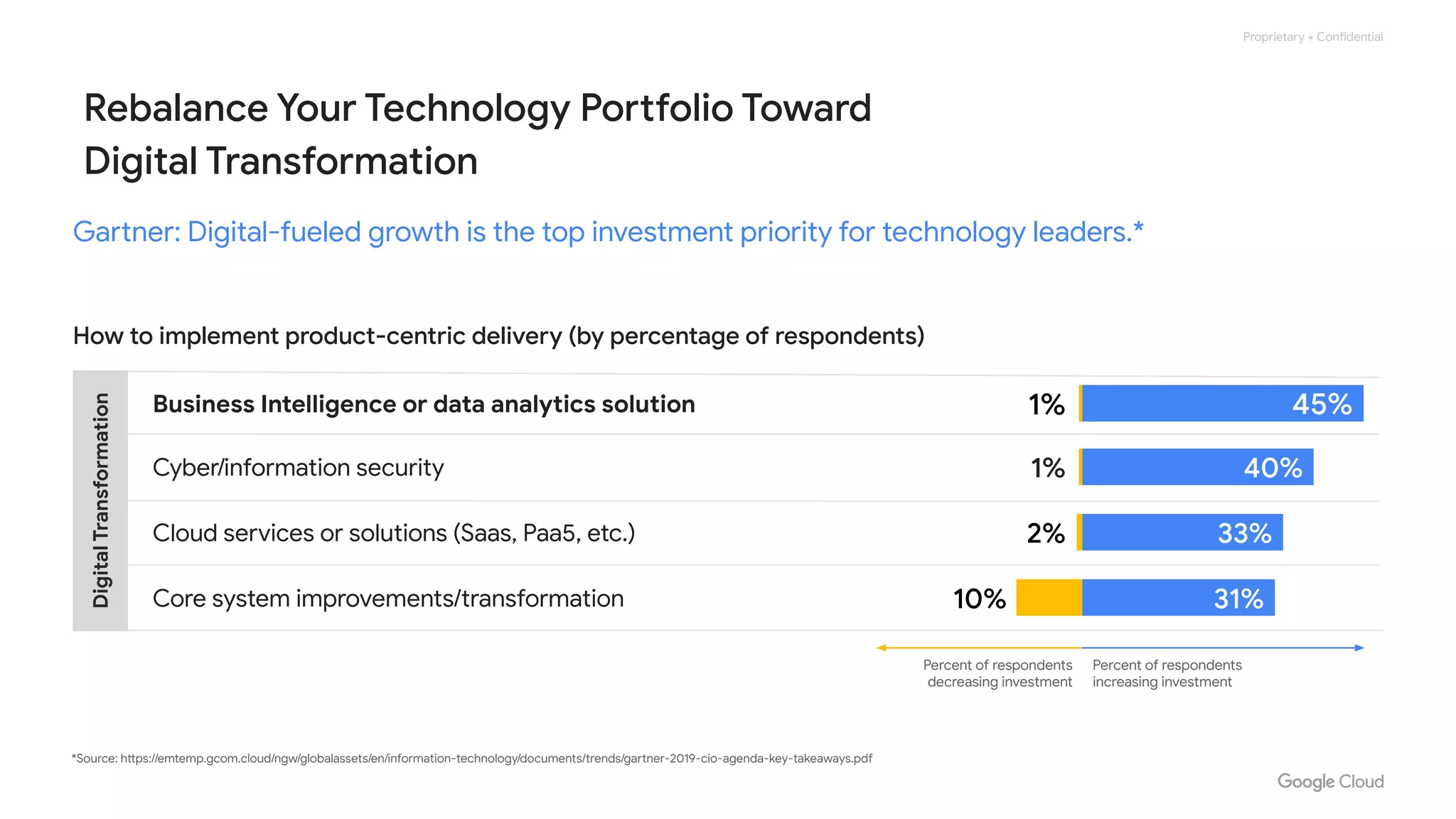
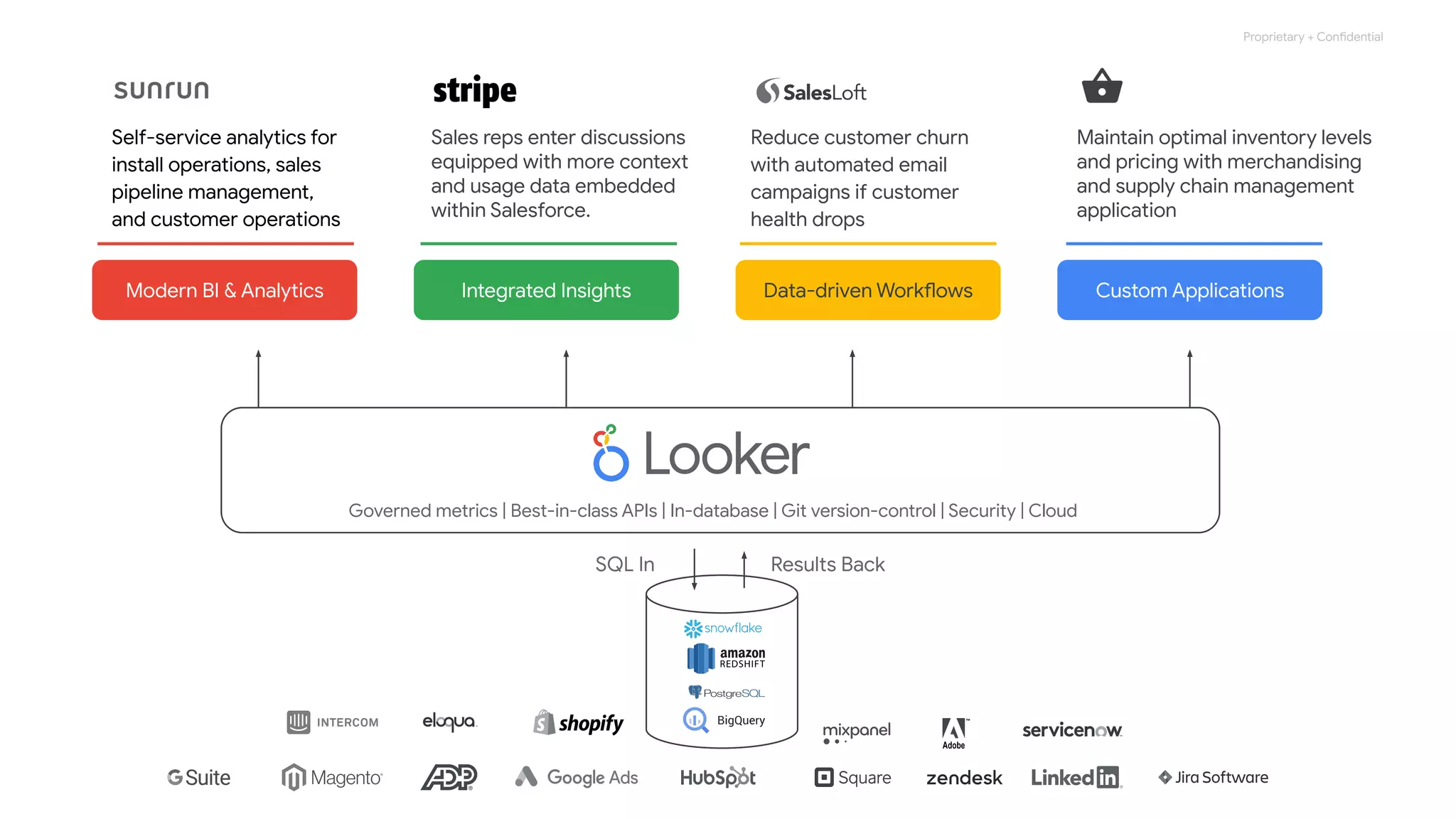
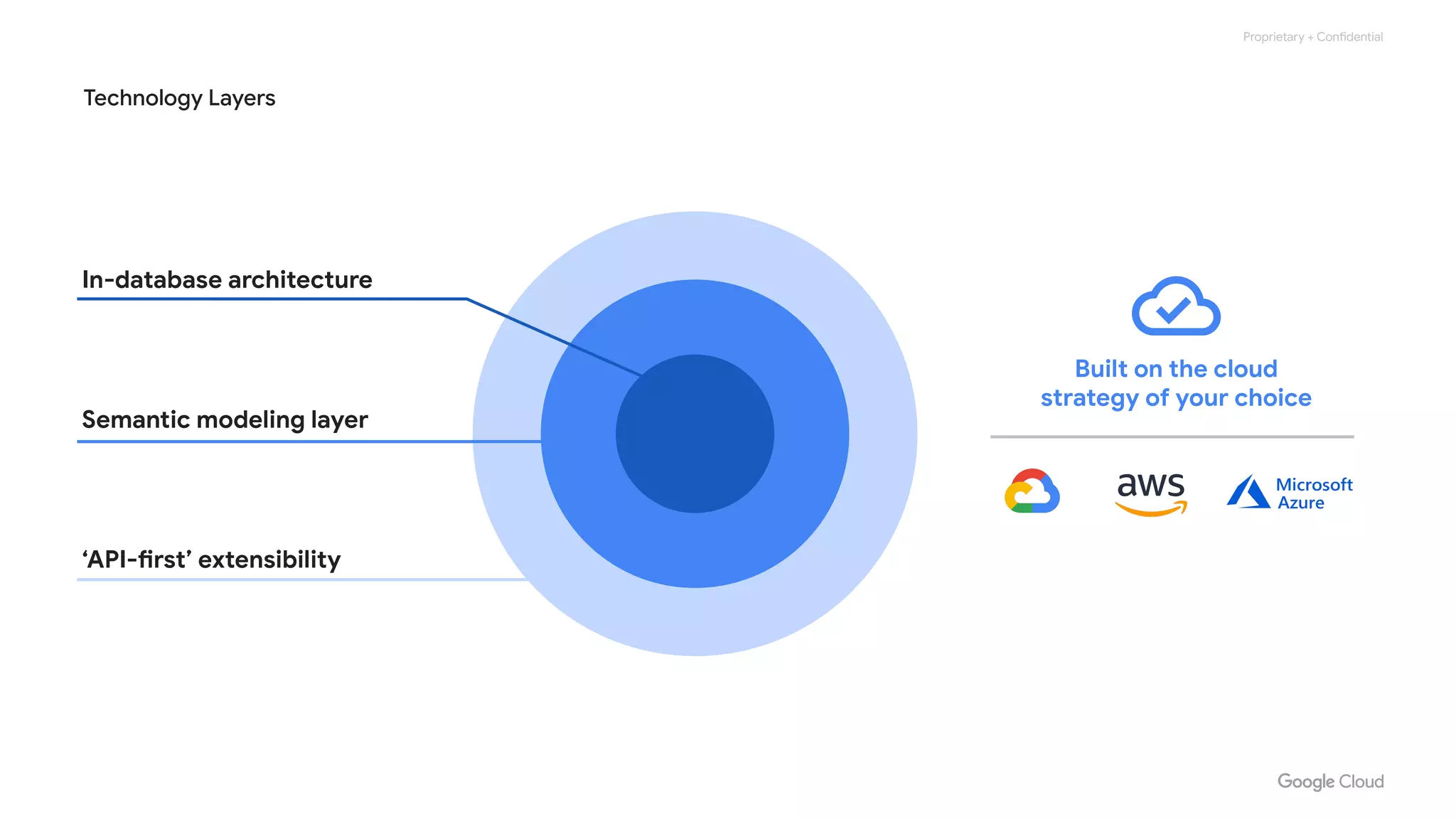
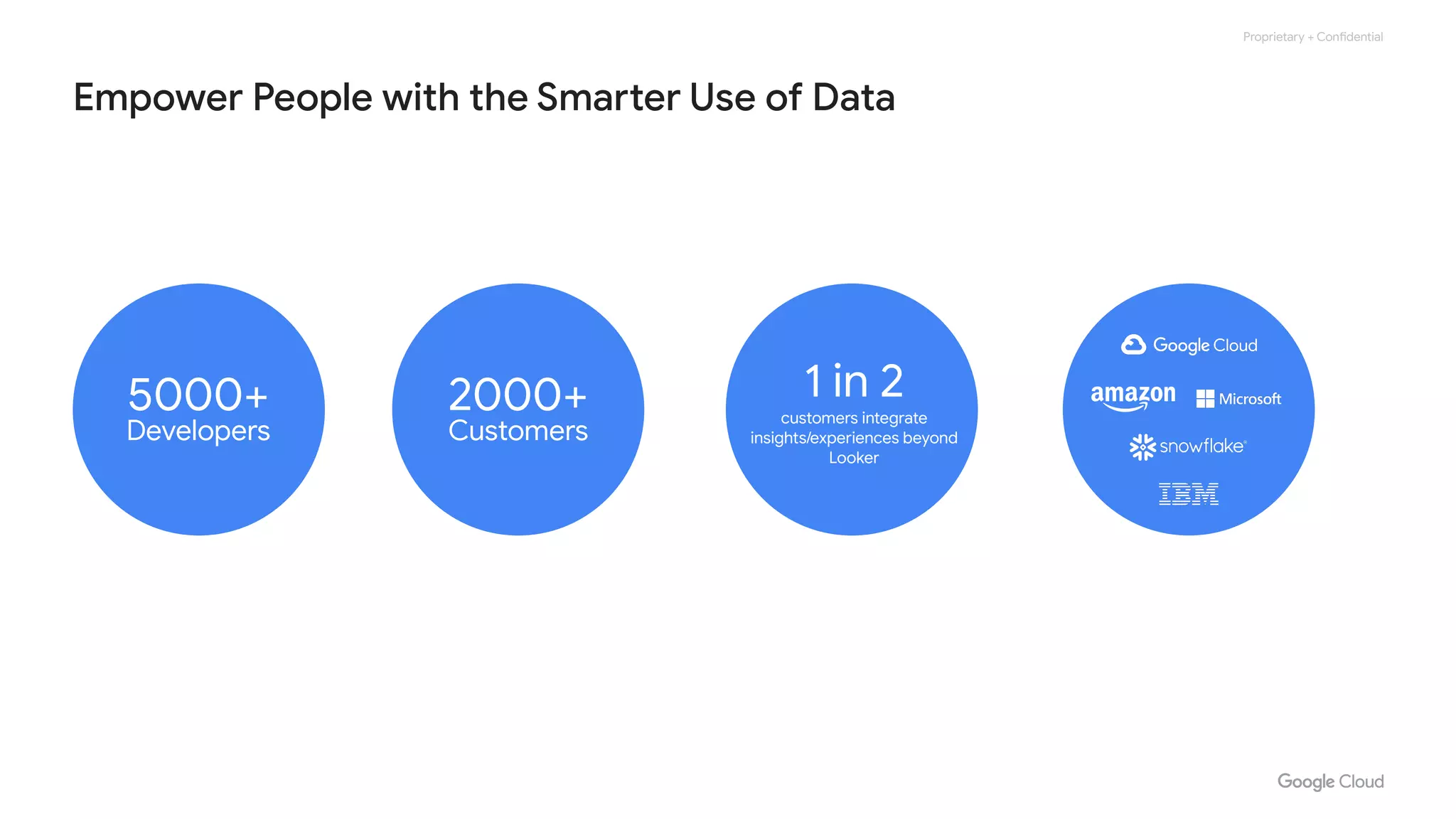
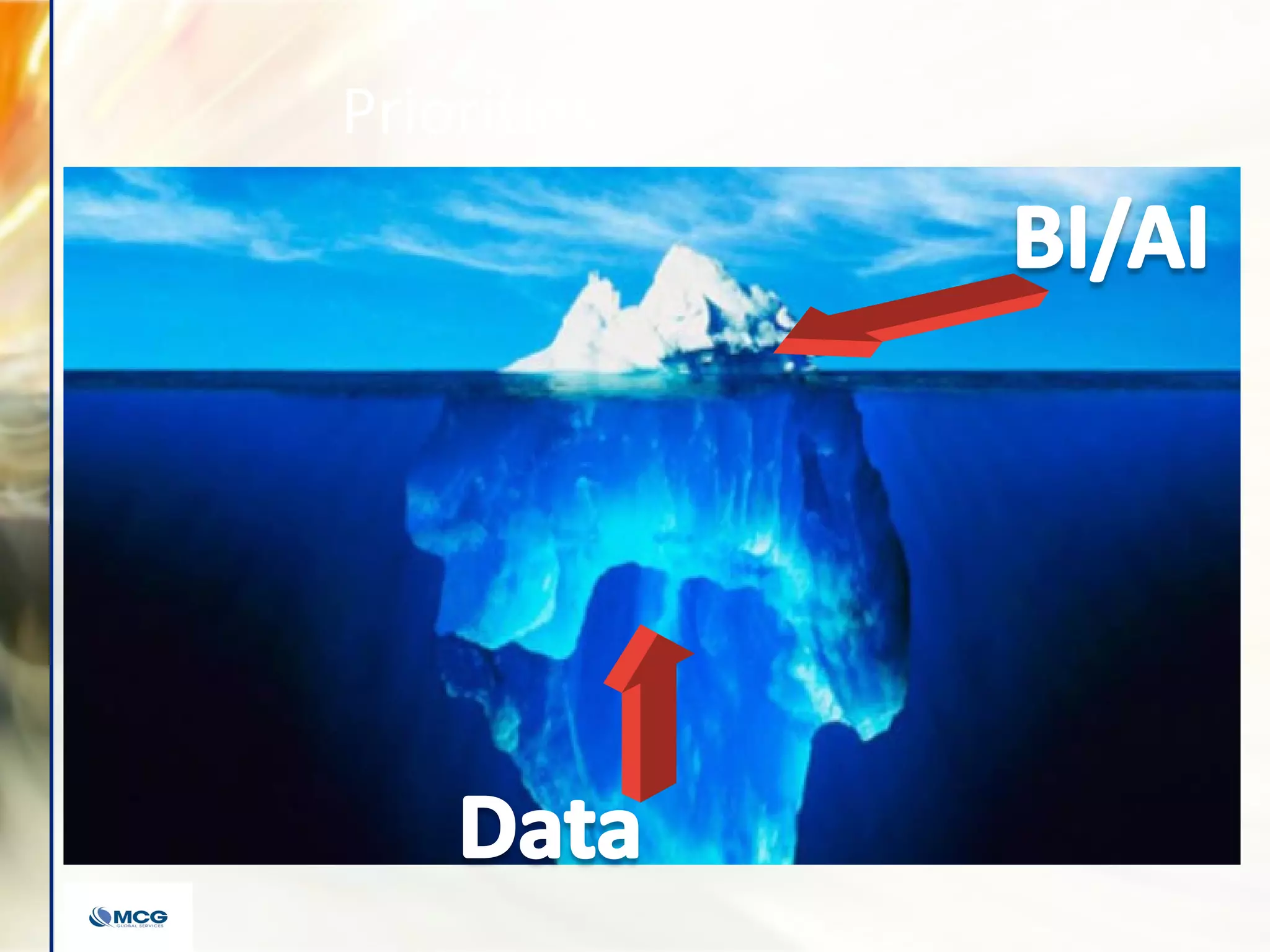
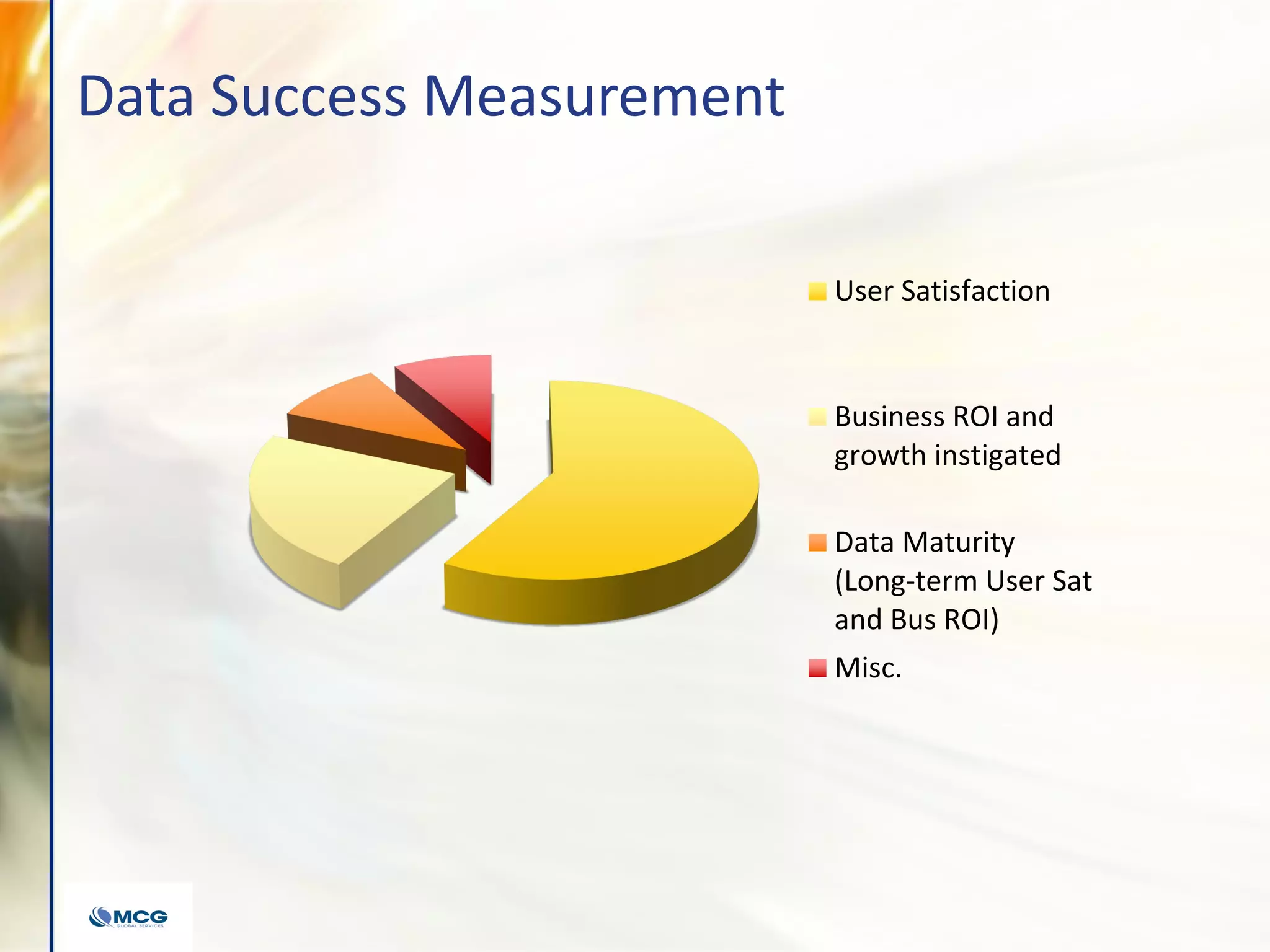
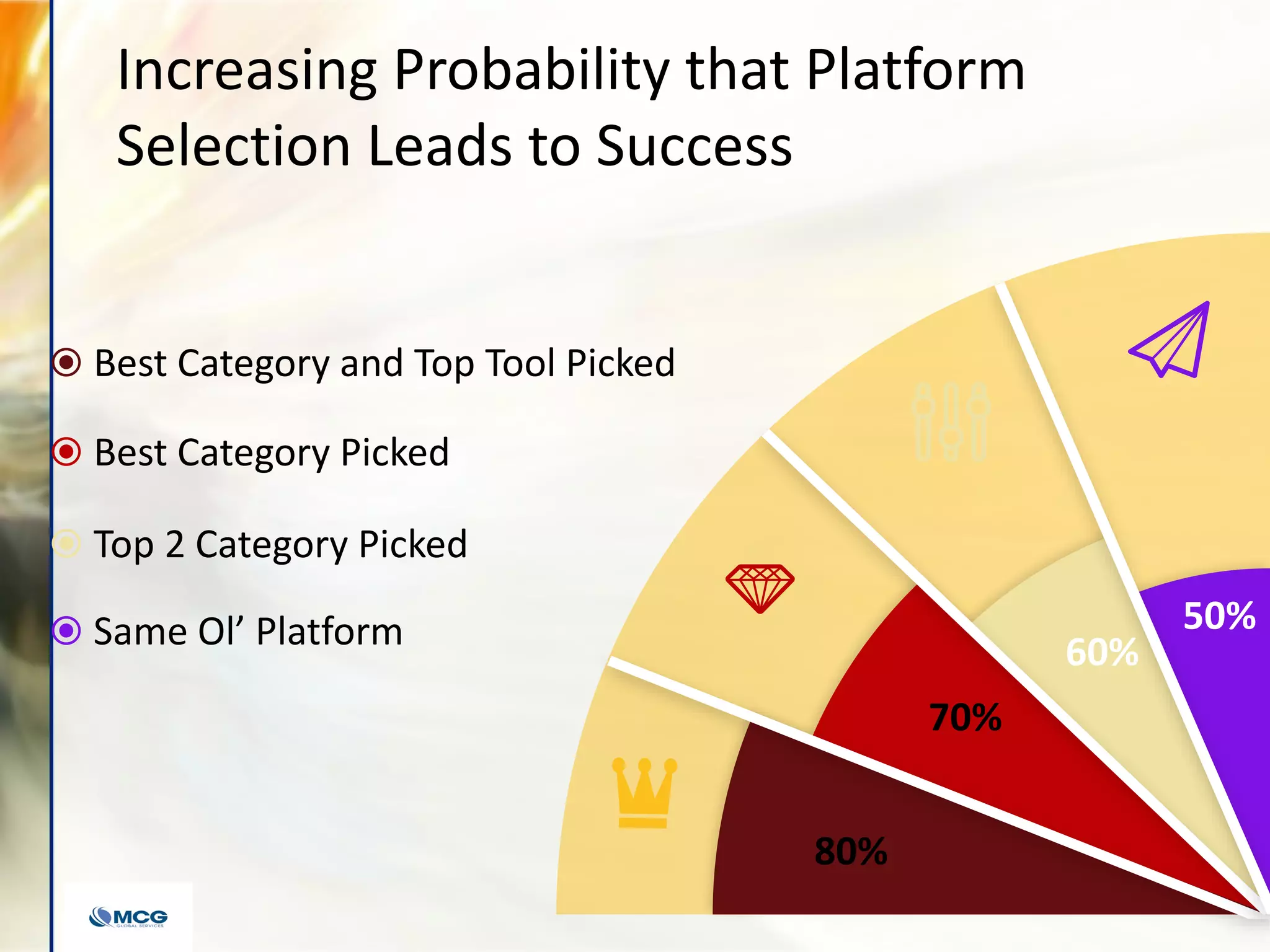
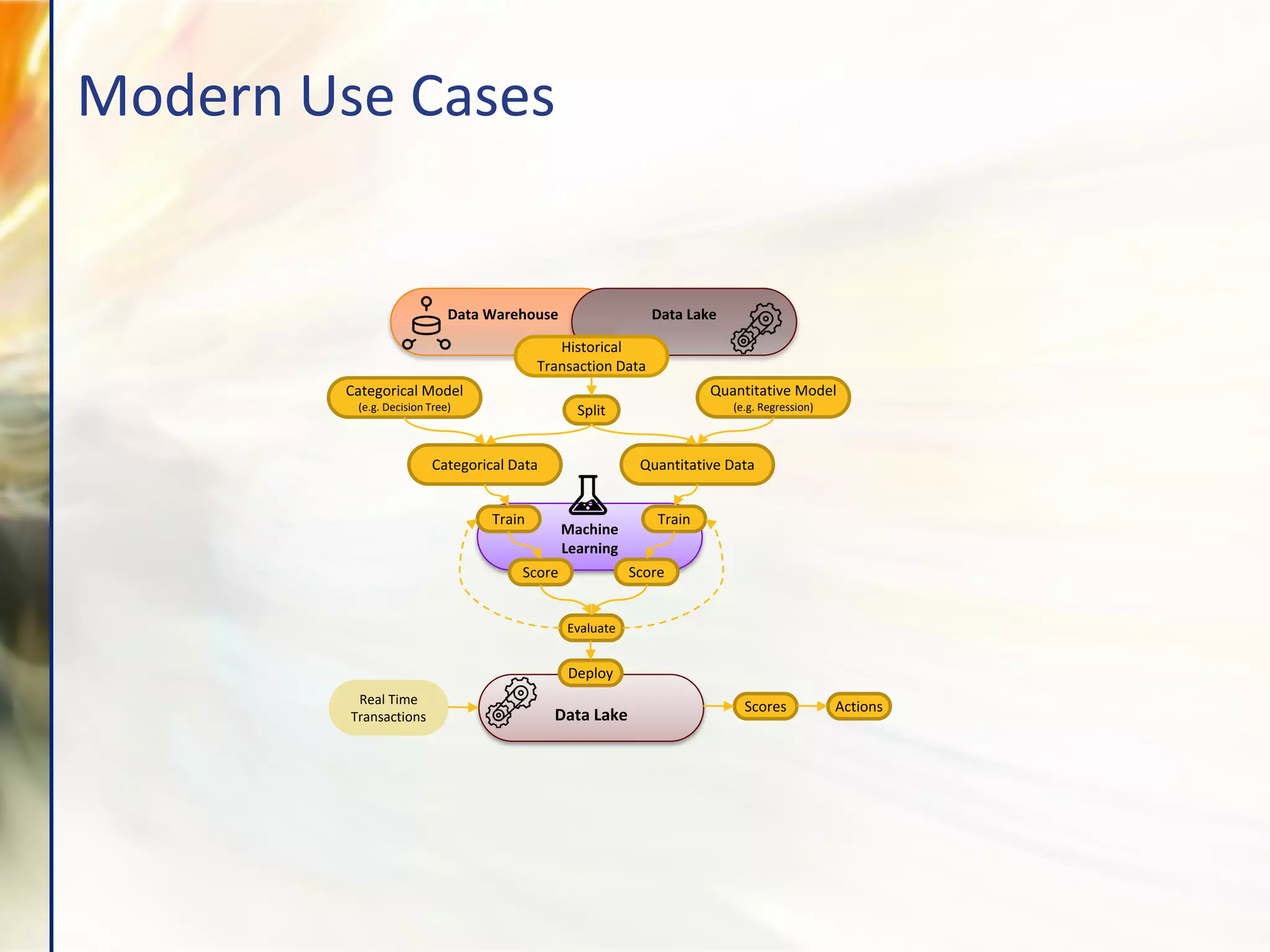
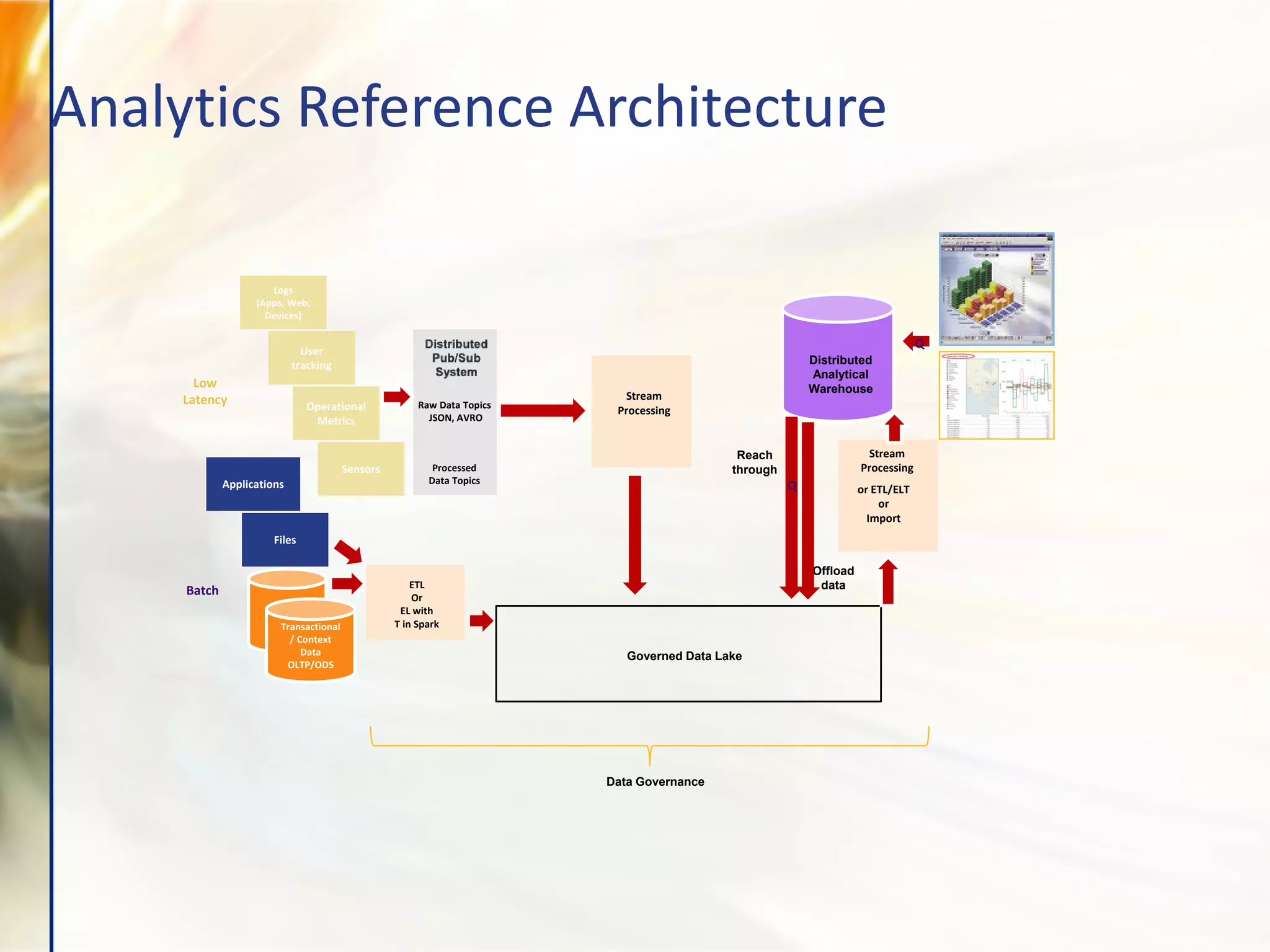
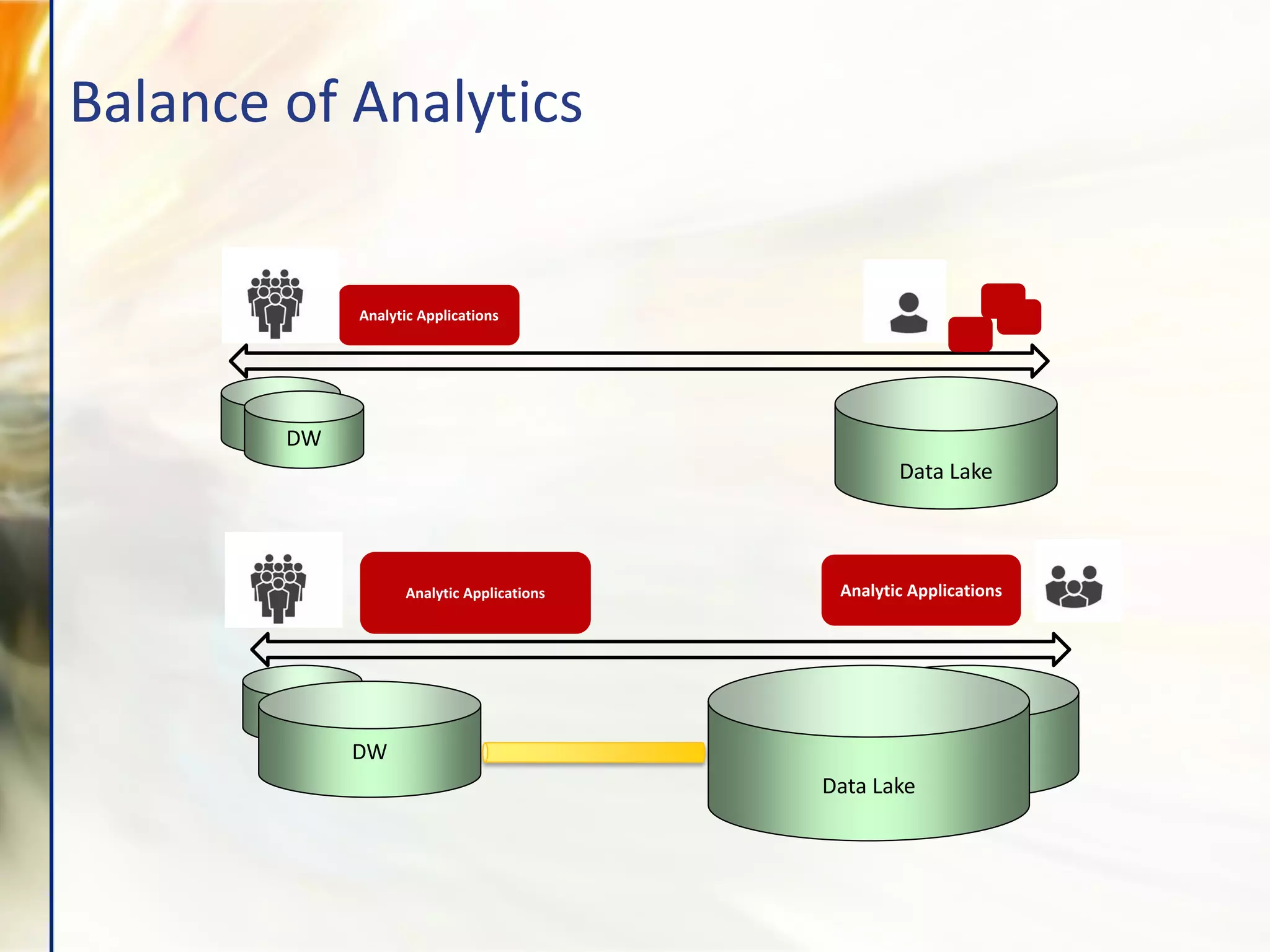
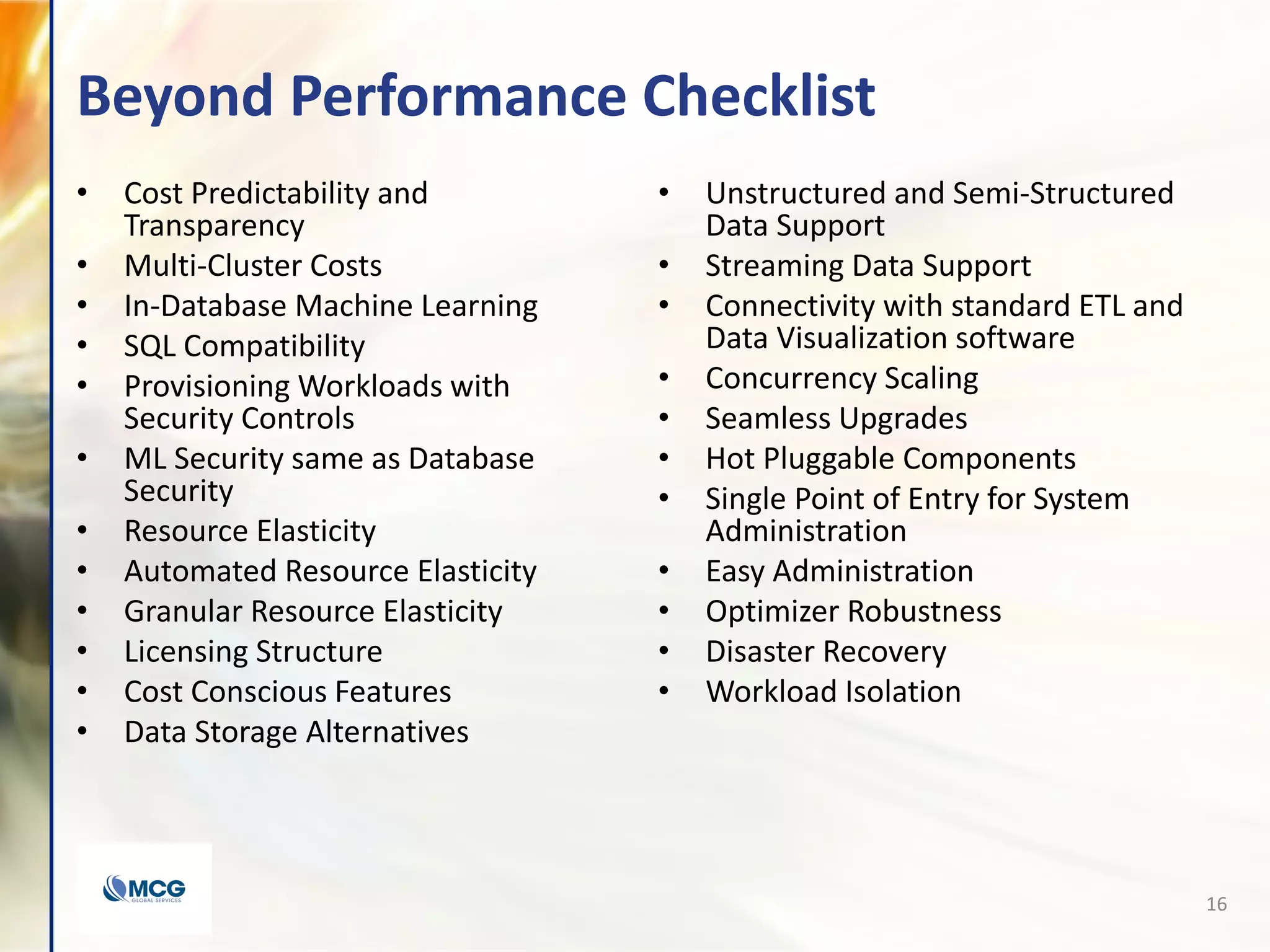
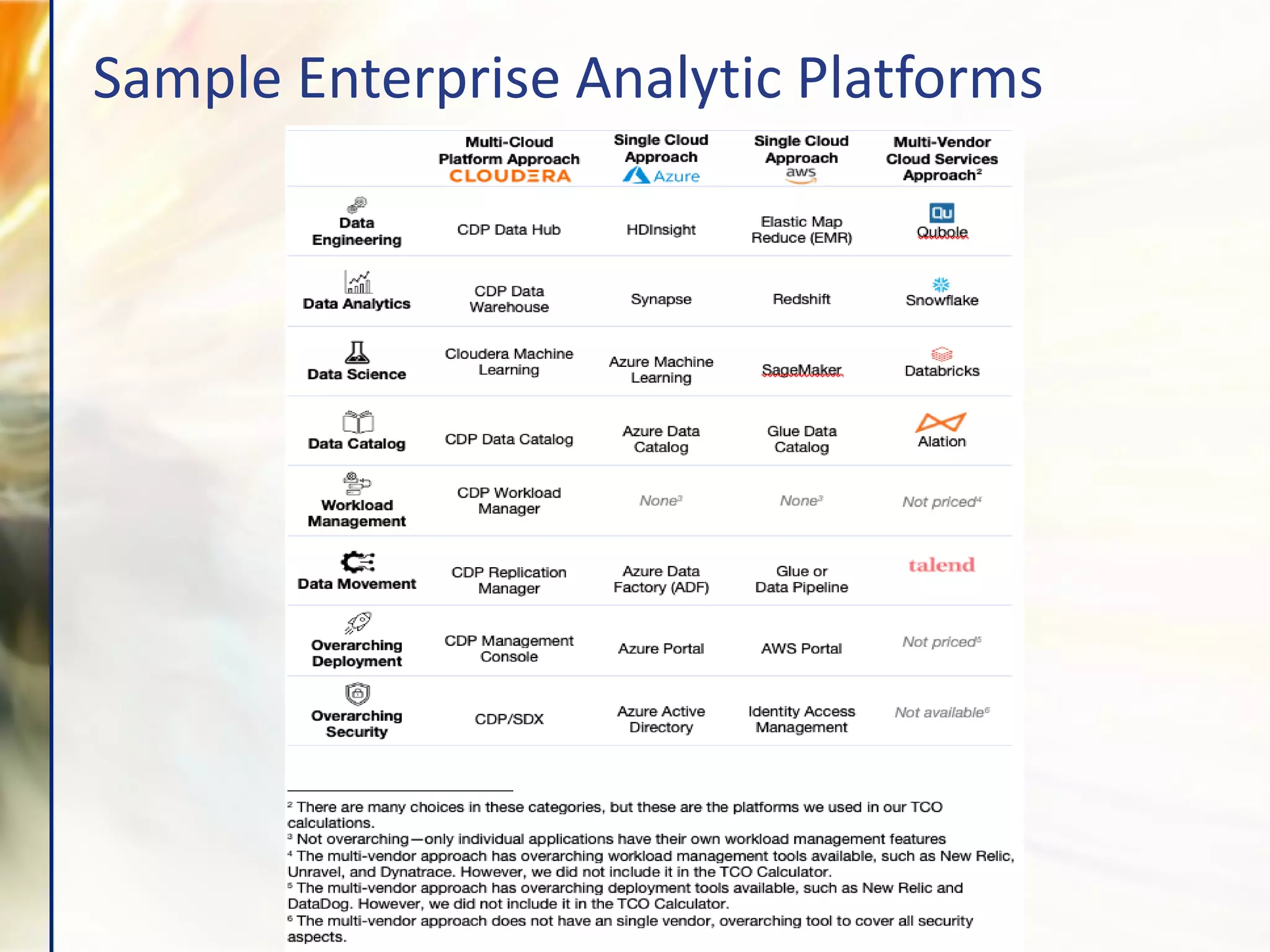
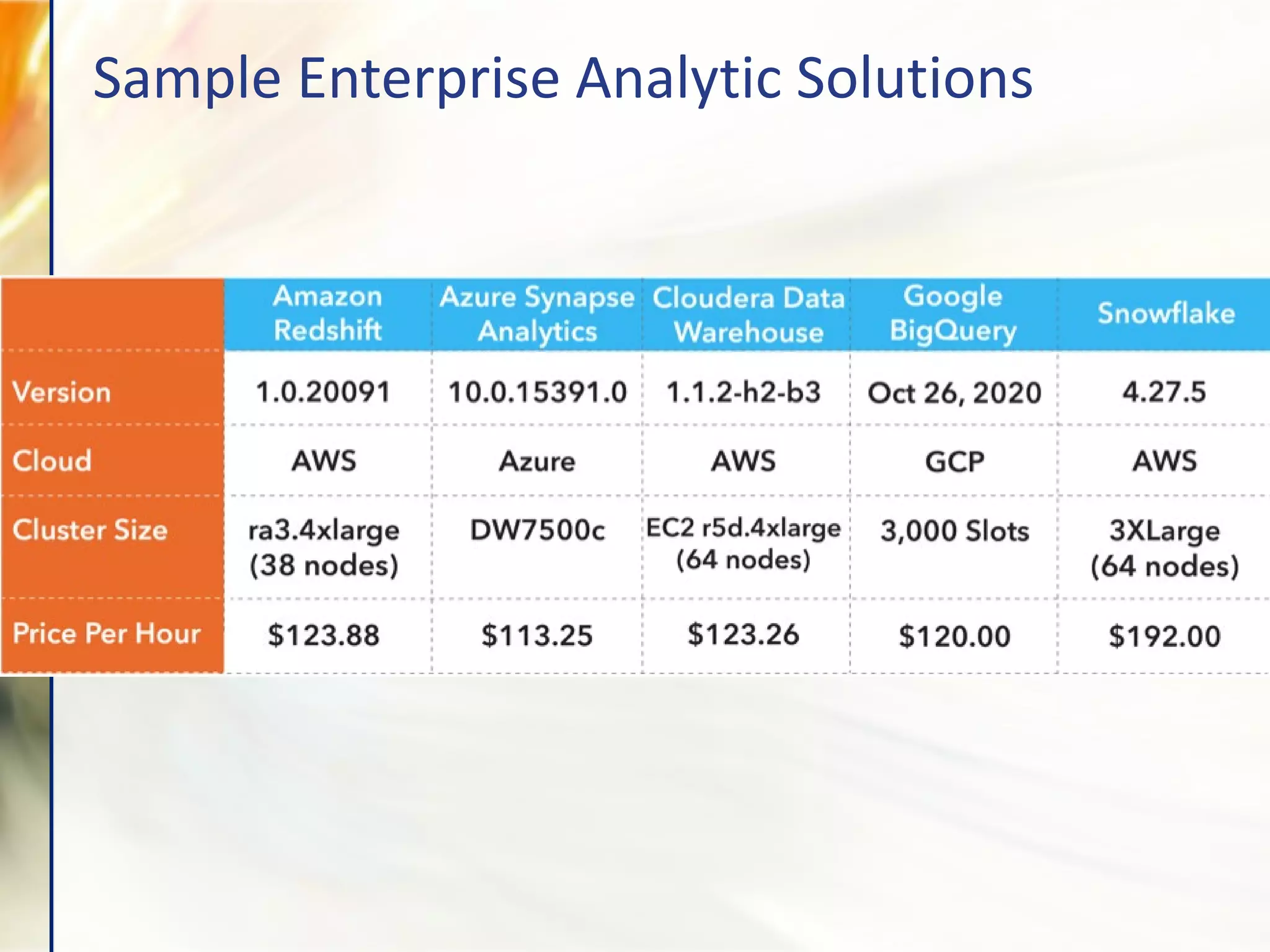
The document compares various enterprise analytic solutions, highlighting their capabilities and implementation strategies to drive growth through data-driven insights. It discusses the importance of digital transformation and advanced analytics in achieving significant business growth and better decision-making. The analysis includes detailed descriptions of specific platforms like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake, focusing on their features, performance, and pricing structures.