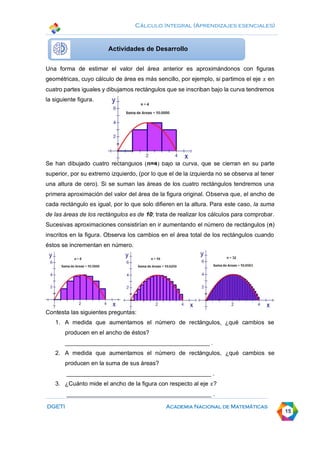
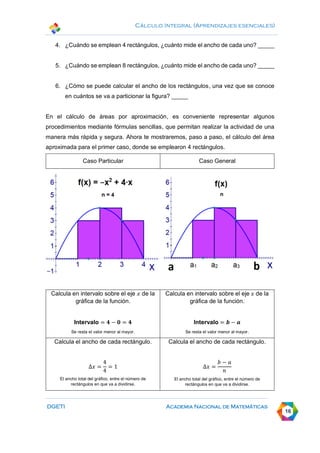
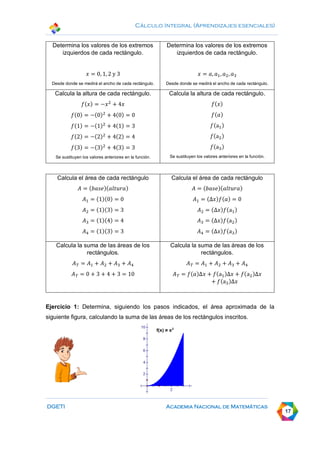
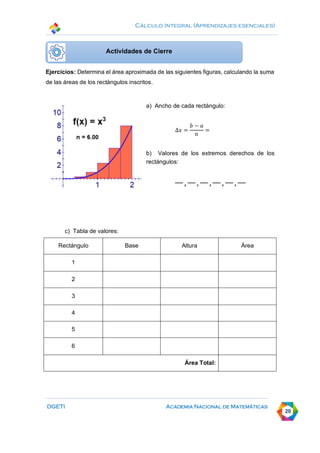
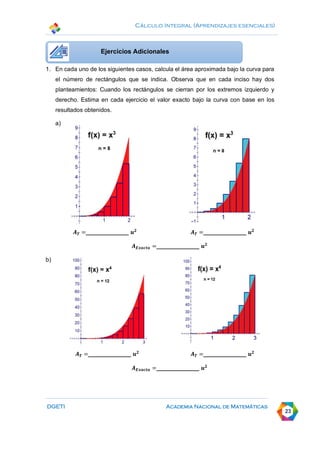
This document discusses calculating areas by approximation using integral calculus. It provides examples of approximating the area under a curve by dividing it into rectangles and summing the areas. Students are guided through examples of approximating areas by partitioning the x-axis into different numbers of equal widths and calculating the area of each corresponding rectangle. The document emphasizes that increasing the number of rectangles used results in a more accurate approximation of the total area under the curve.