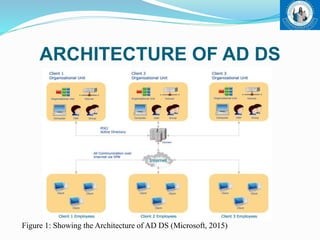
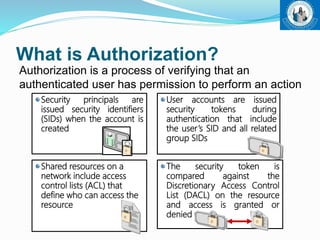
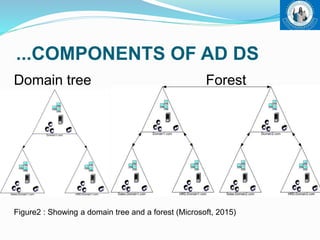
This document outlines Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), including its introduction as a centralized directory service for Windows networks, architecture using LDAP protocol, components like domains and forests, and authentication and authorization processes. It also discusses benefits like single sign-on access and centralized management, limitations such as costs, and concludes that AD DS enables centralized network management compared to workgroup networks.