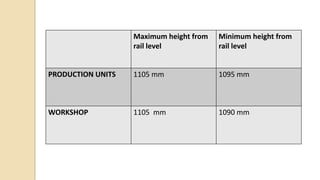
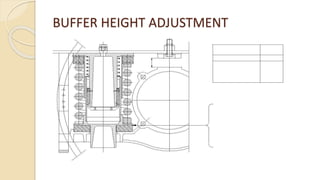
The document summarizes the maintenance of buffers in coaches for the Danapur division of the East Central Railway in India. It discusses the importance of buffers for absorbing shocks and providing safety. It outlines maintenance schedules for coaches, including intermediate overhauling every 9 months and periodic overhauling every 18 months. It describes the components of buffers and issues encountered, such as cracked buffer casings and worn rubber pads. Proper maintenance of buffers is necessary to provide a comfortable ride for passengers.