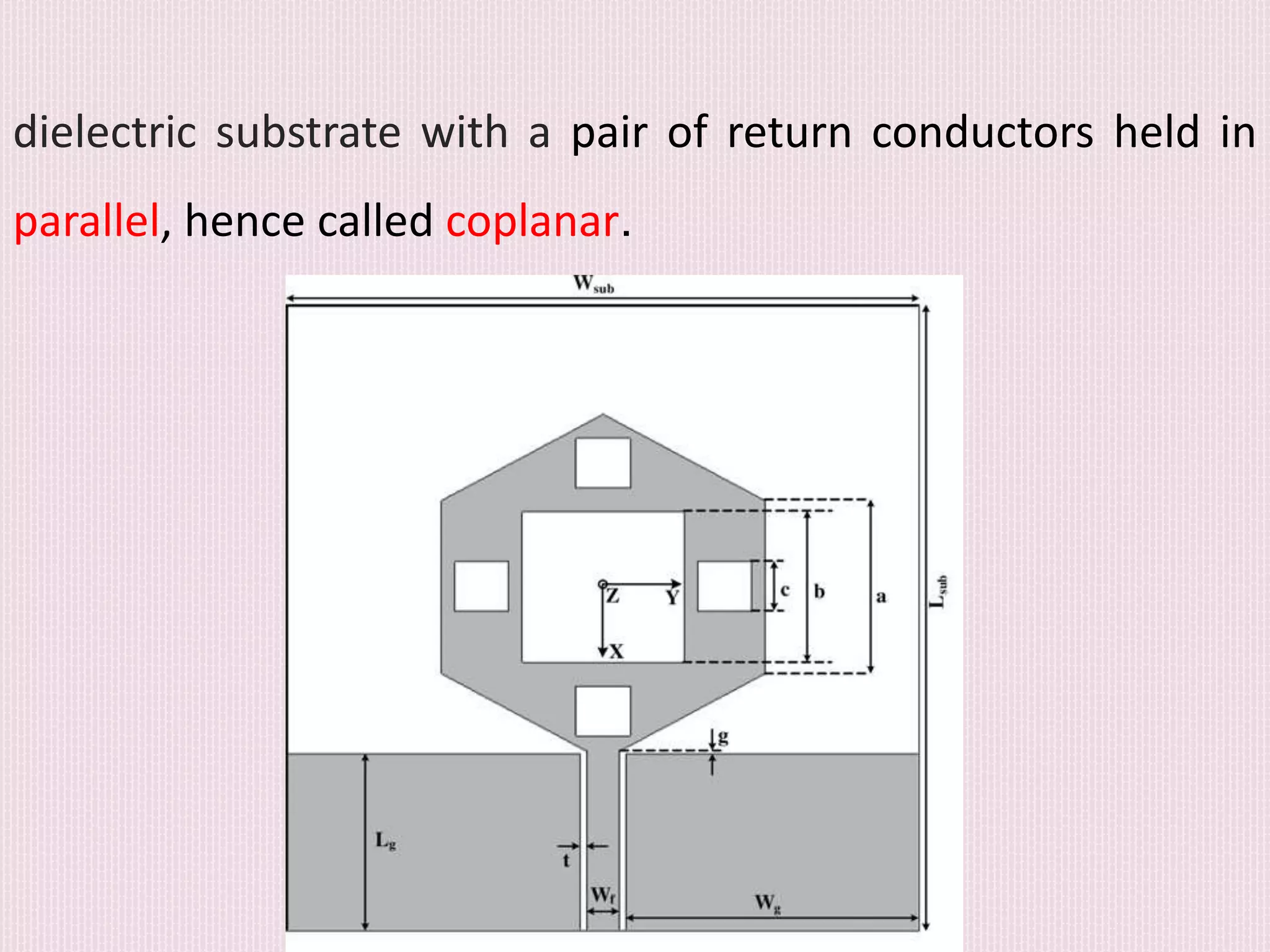
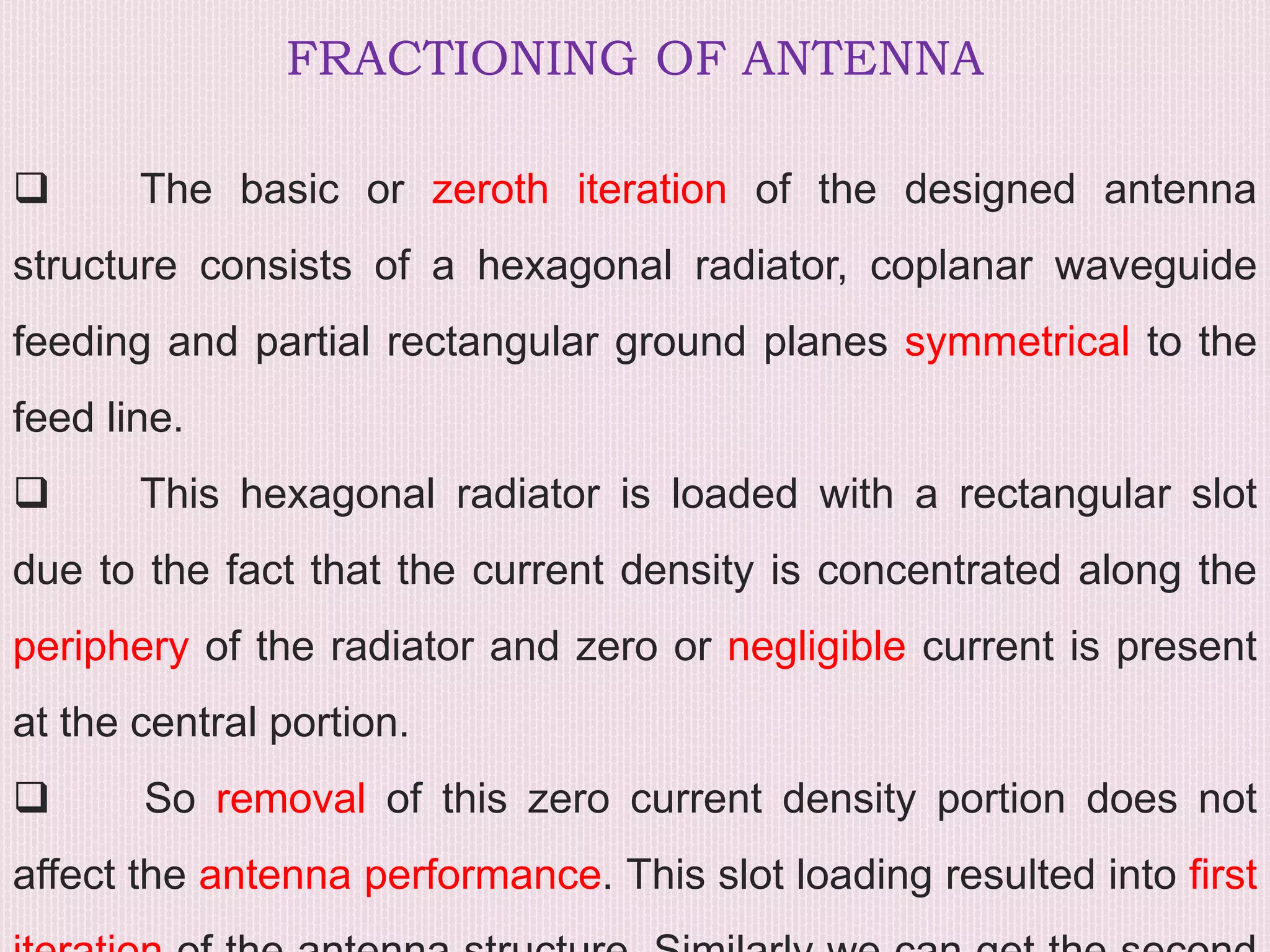
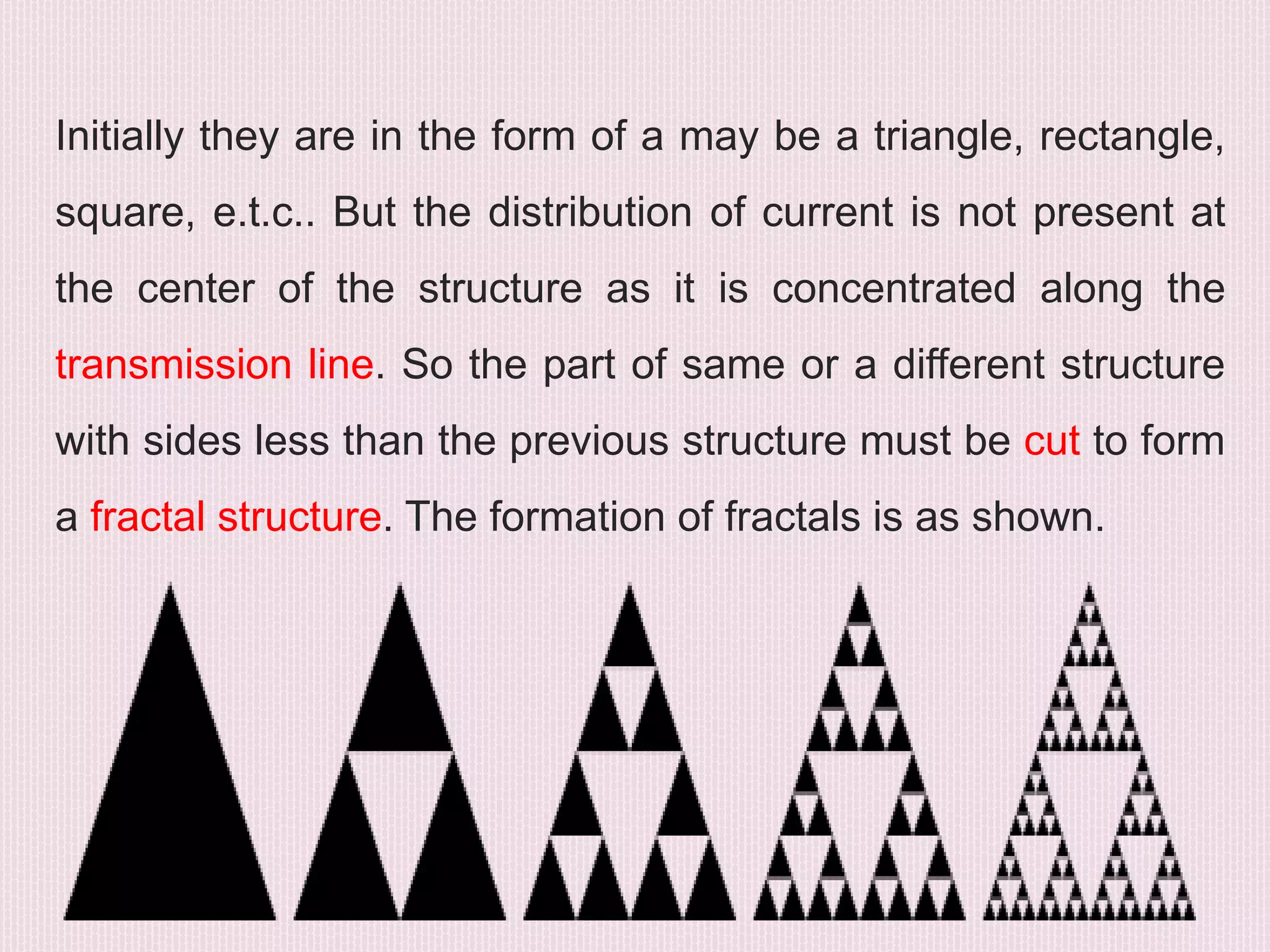
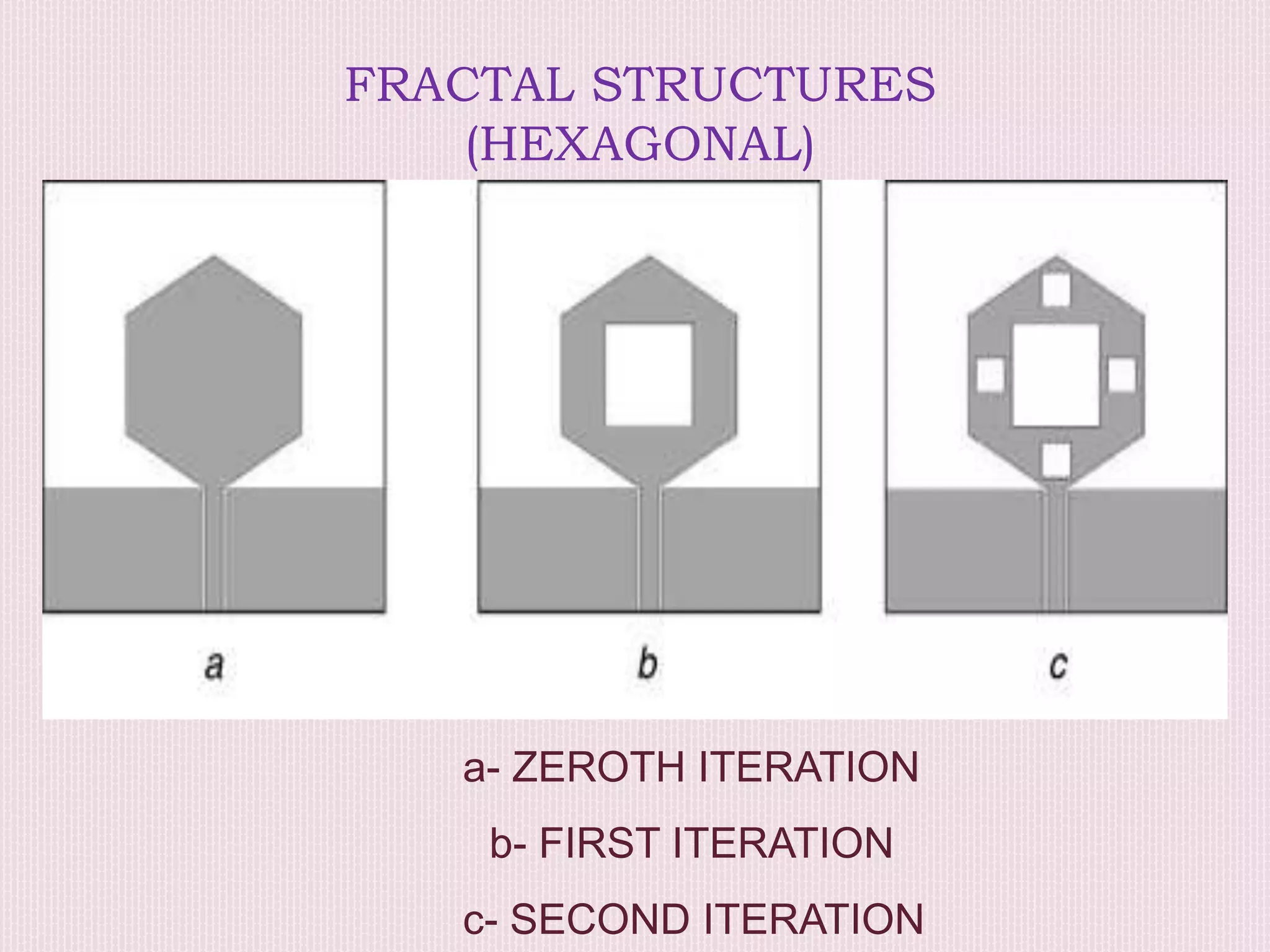
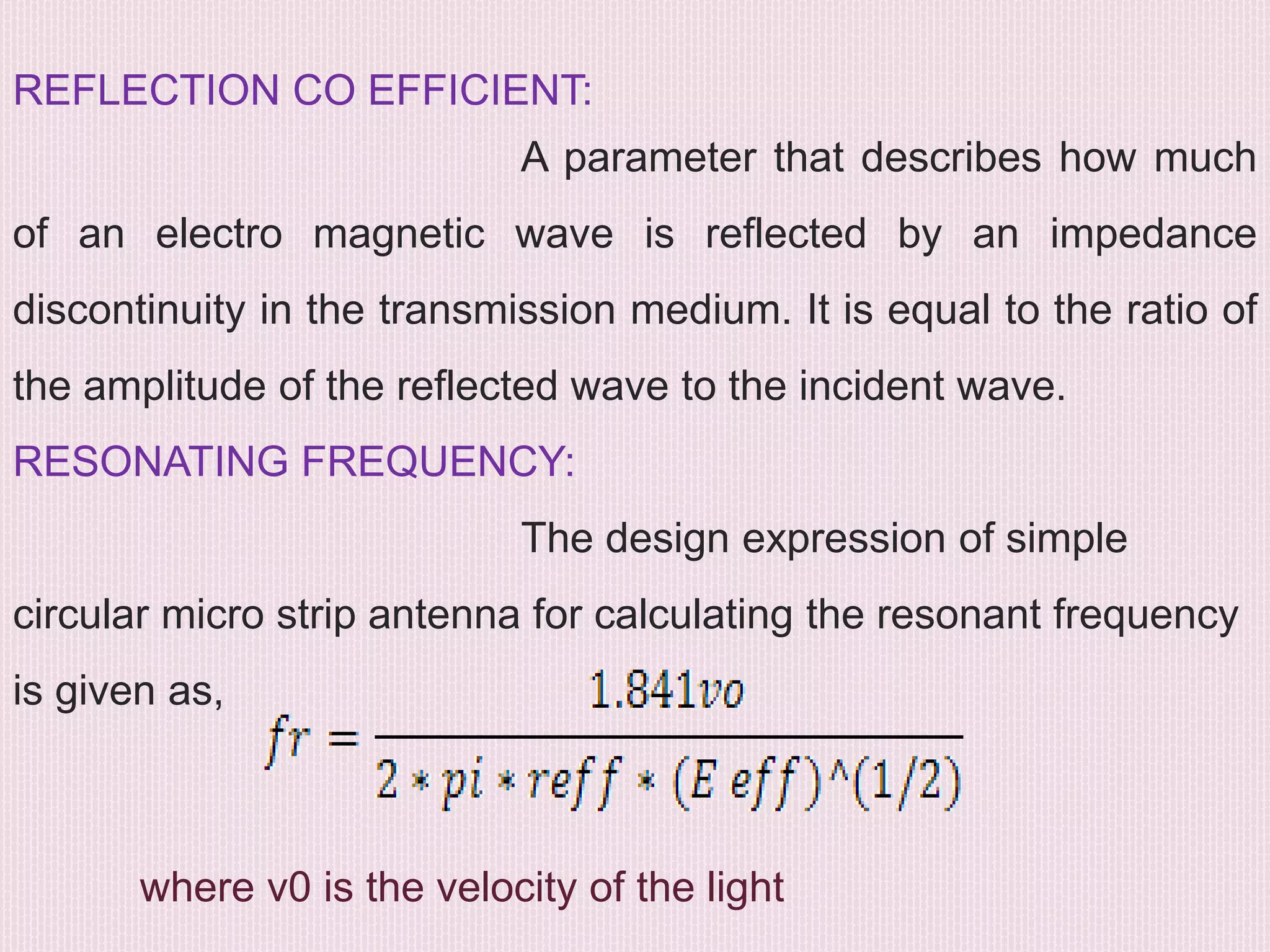
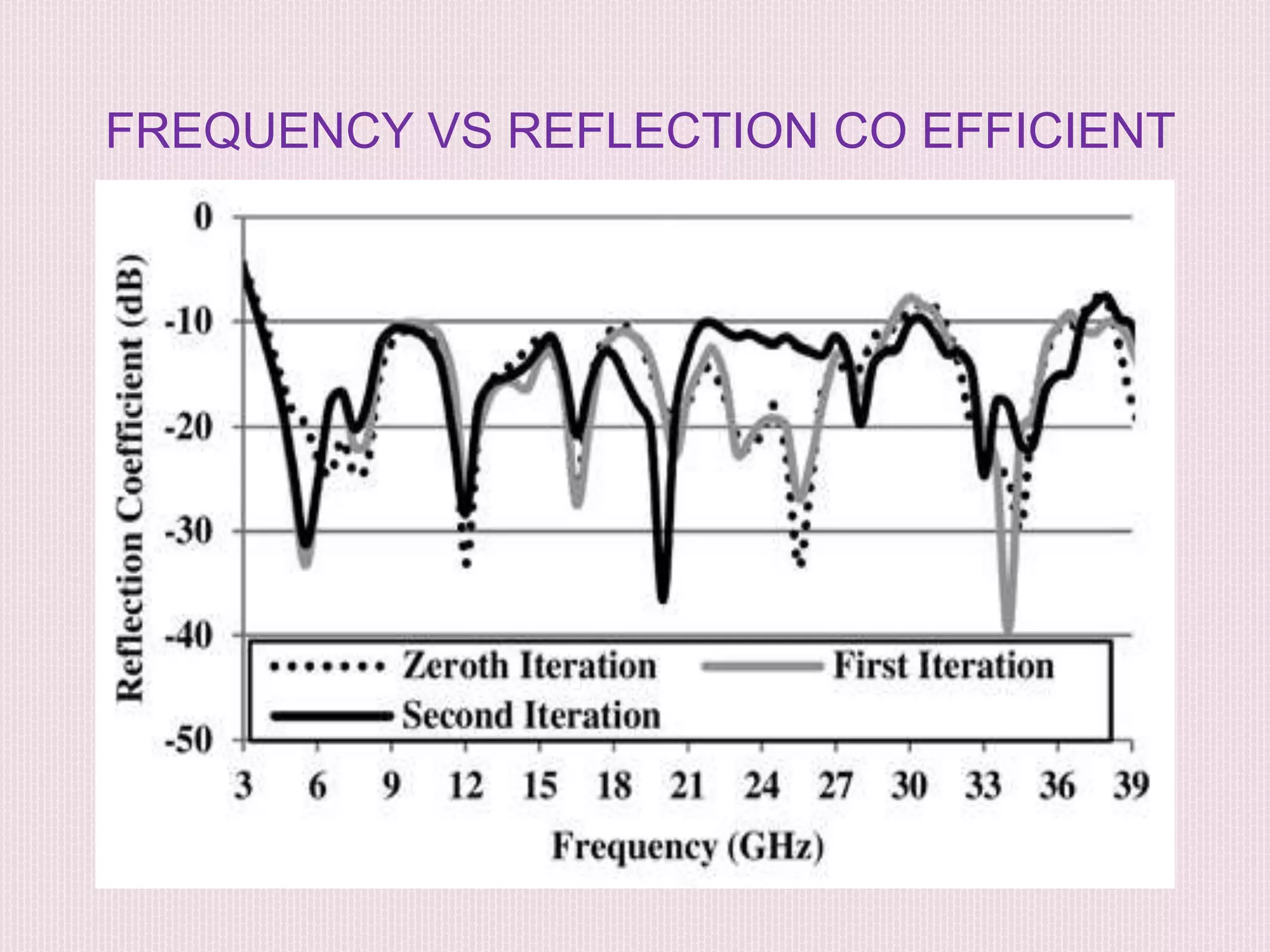
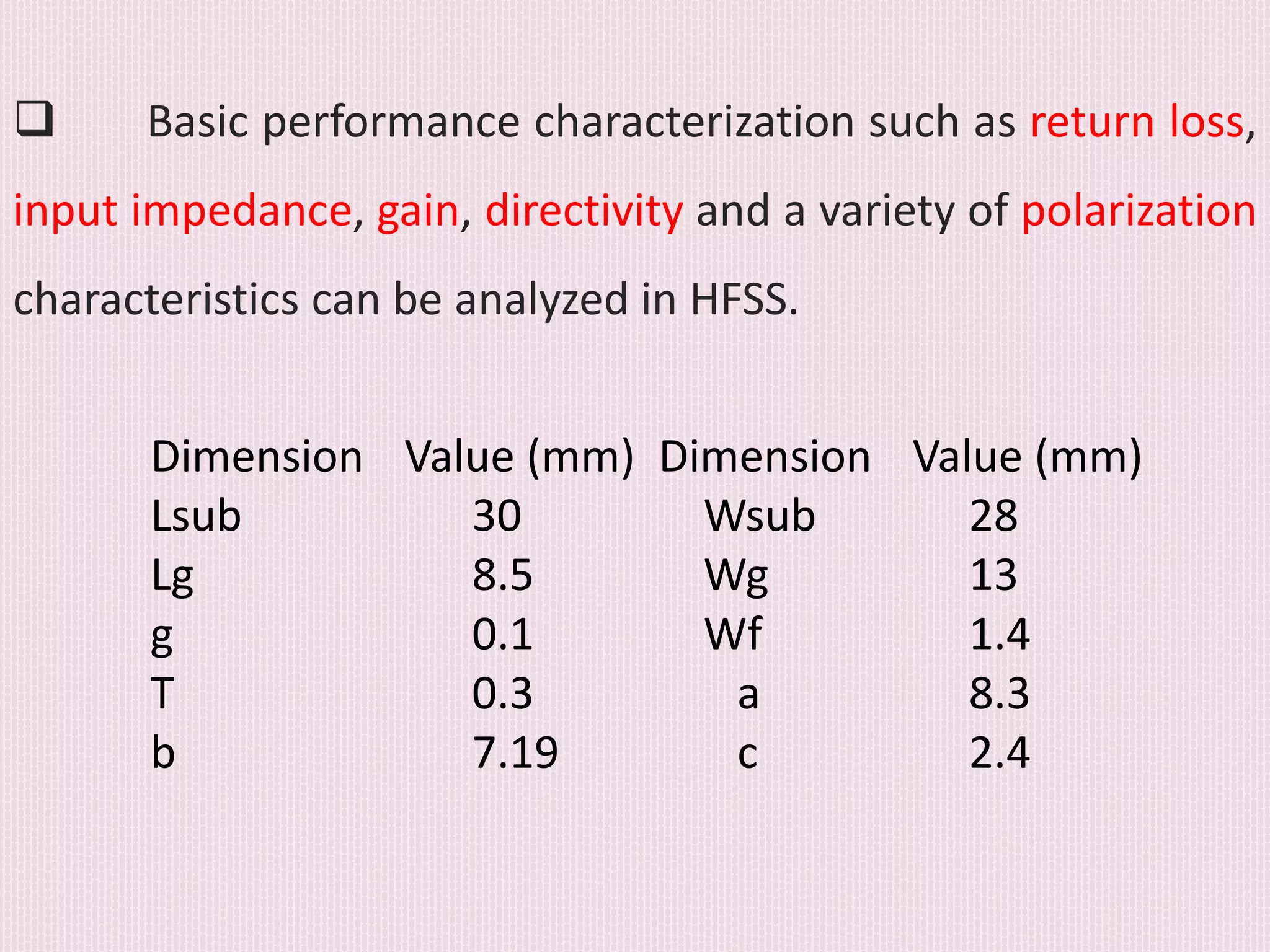
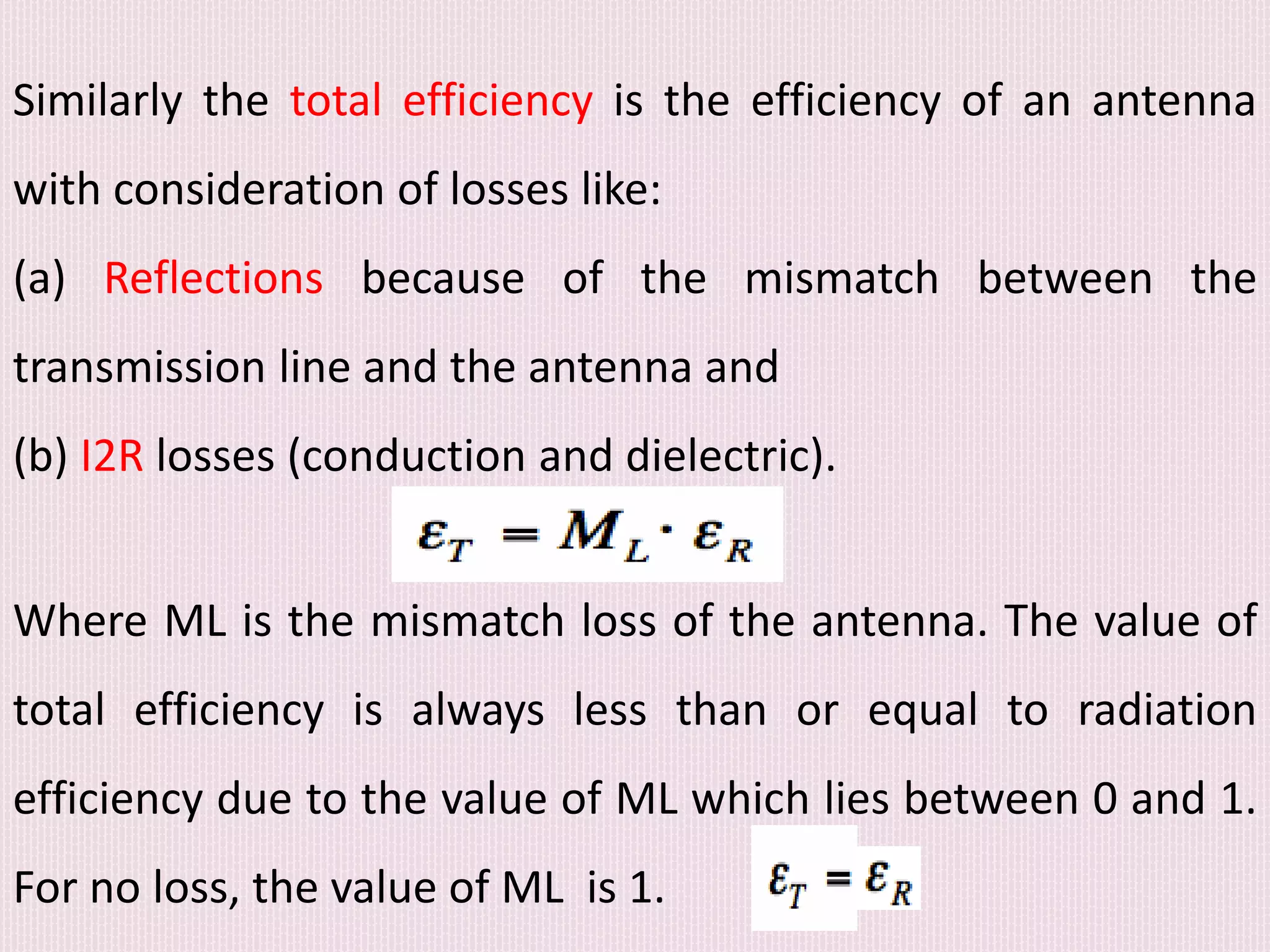
The document discusses the design and application of a cpw-fed hexagonal Sierpinski super wide band fractal antenna, which addresses the need for compact antenna sizes while maintaining efficiency and bandwidth. Key concepts include antennal fractioning, performance parameters, and applications across various fields, including wireless communication and defense systems. Ultimately, the design enhances bandwidth and reduces size, making the antenna suitable for a range of modern technology applications.