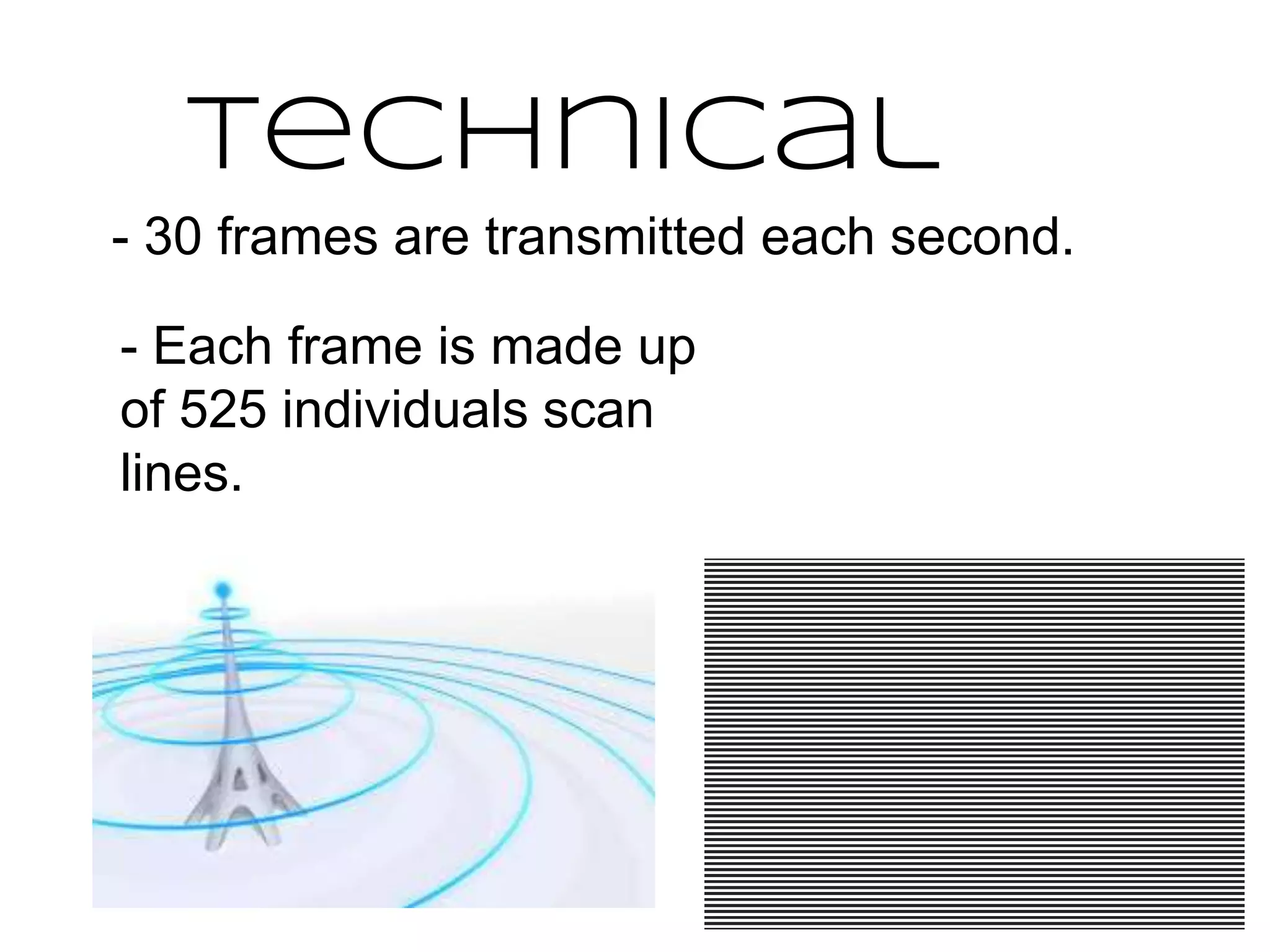
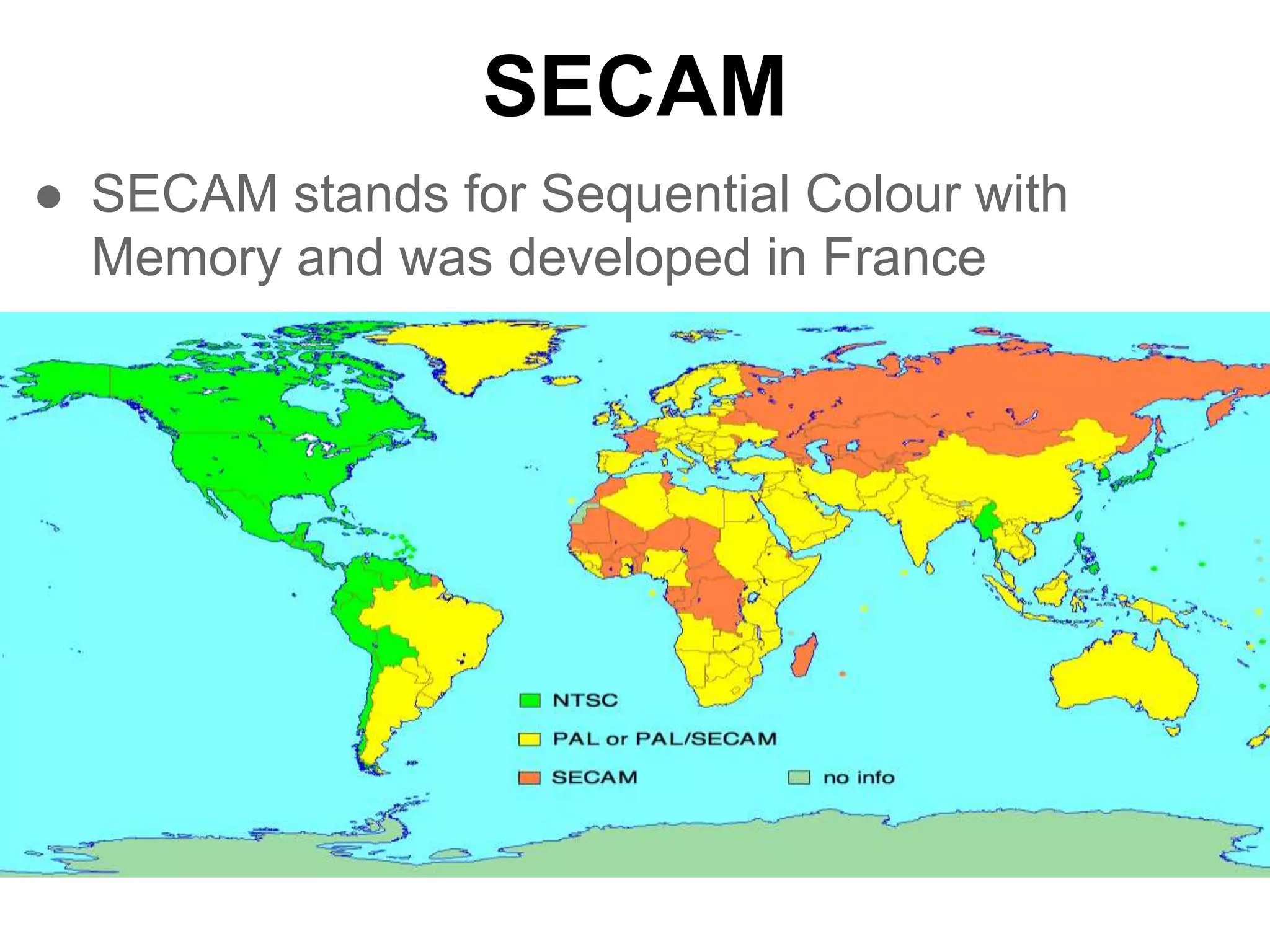
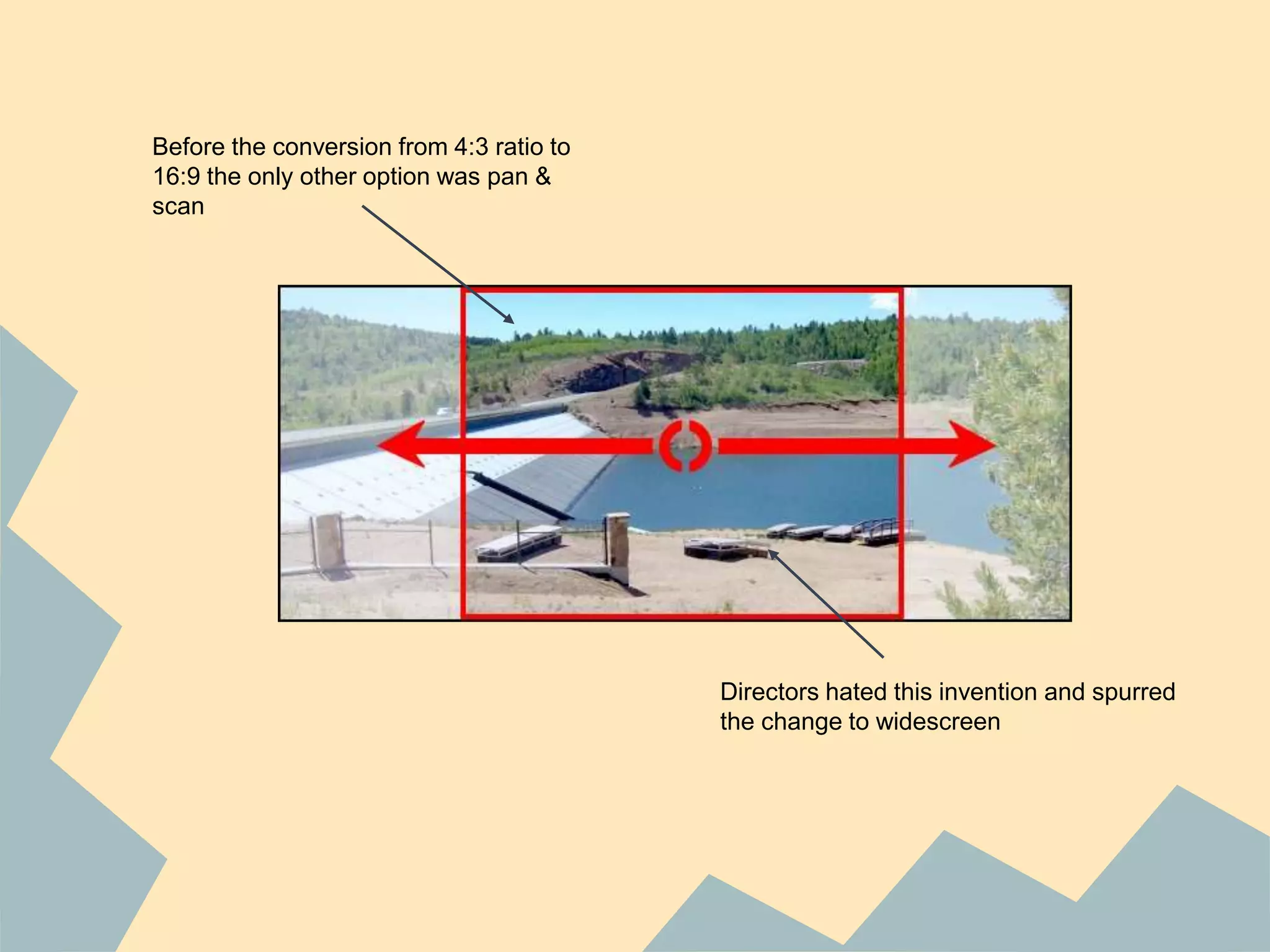
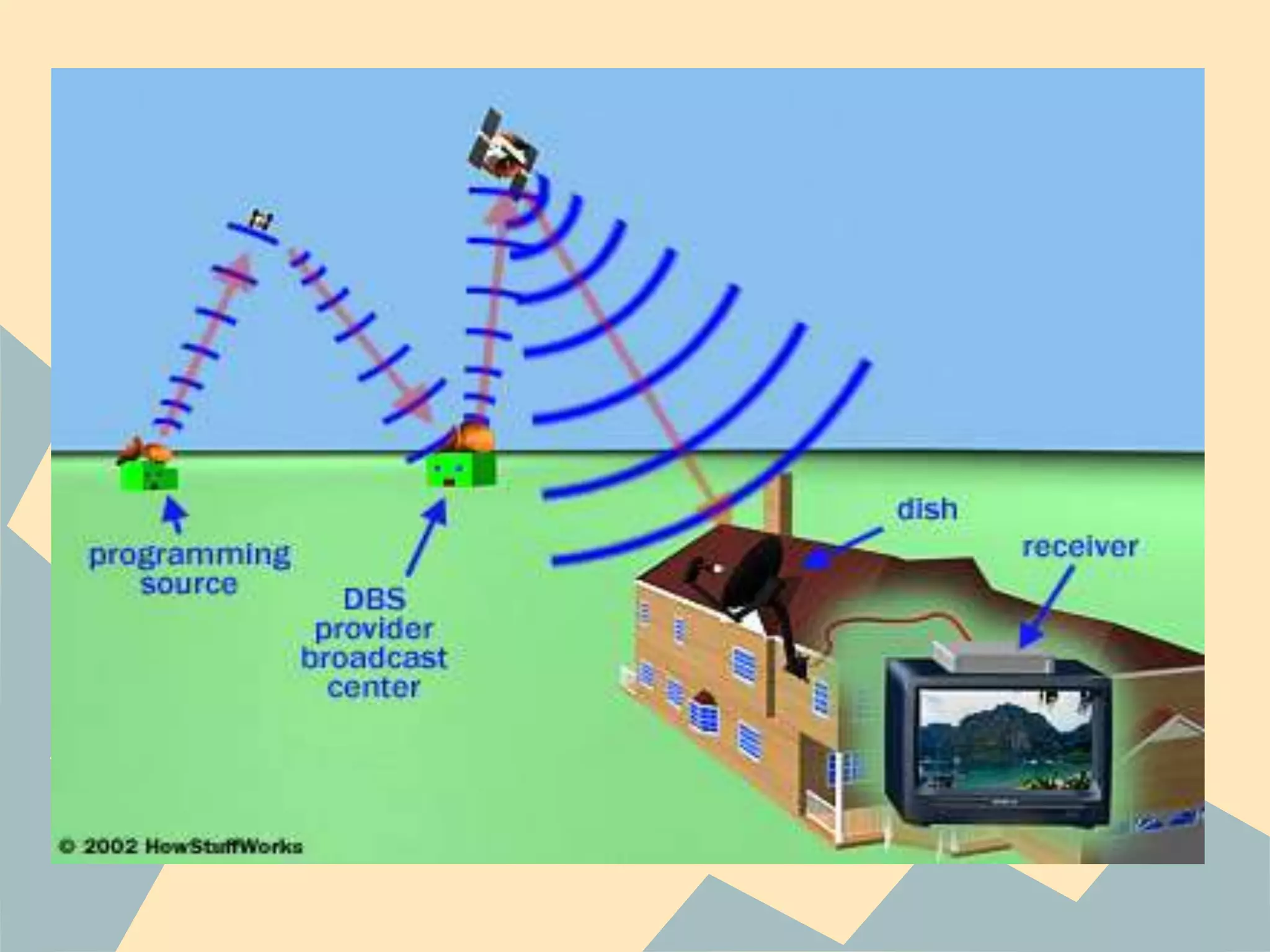
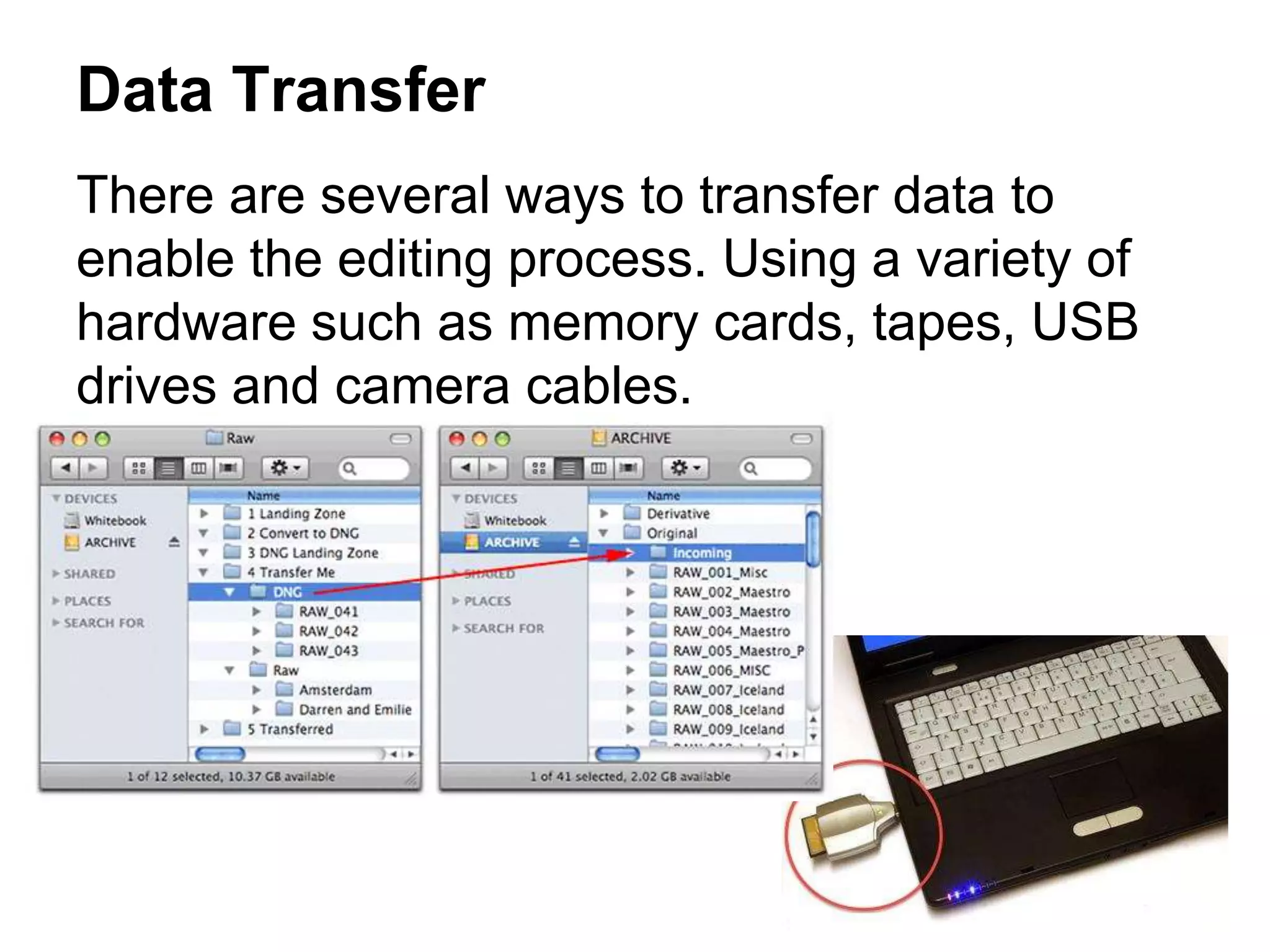
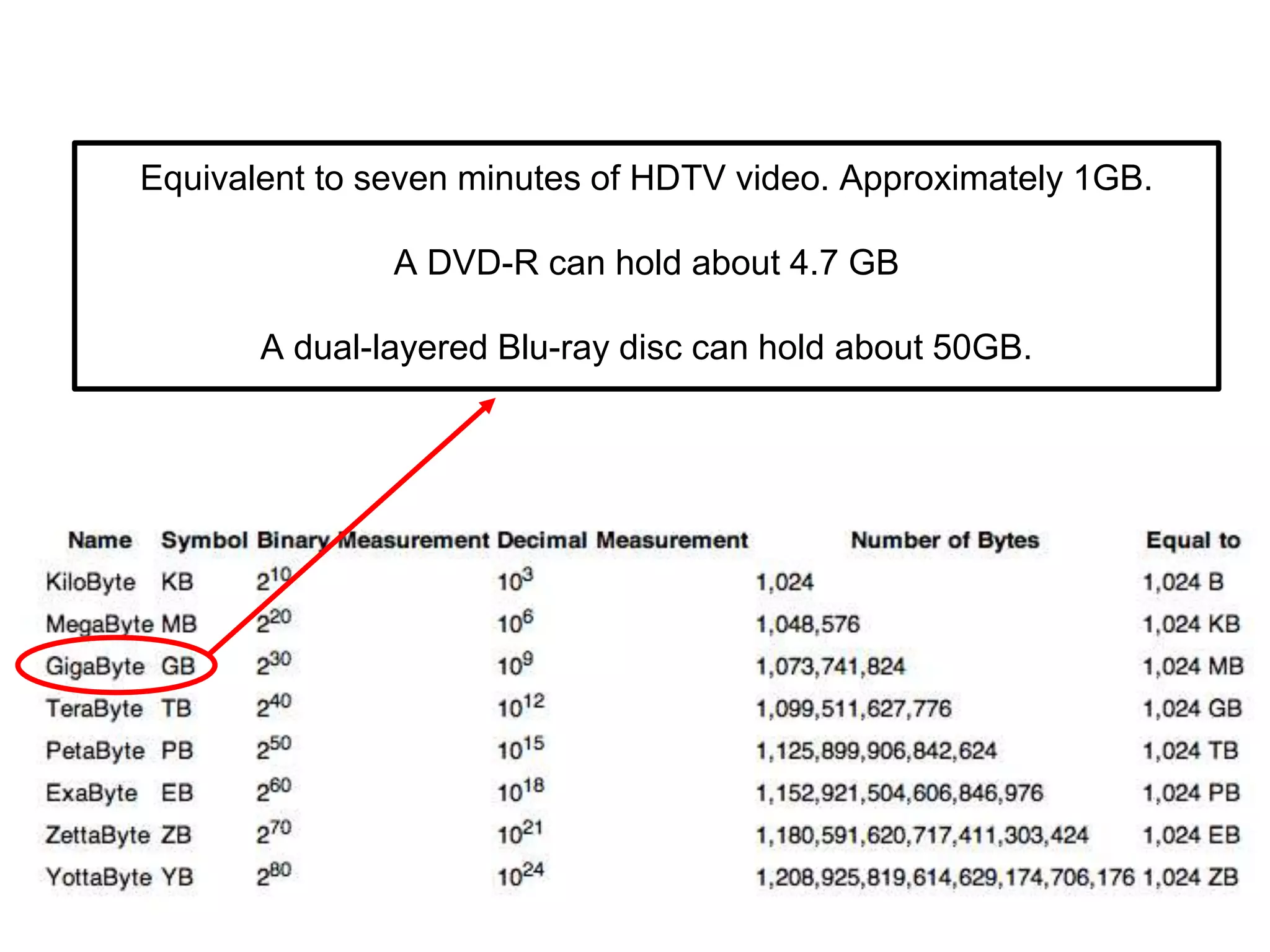
PAL was invented by Walter Bruch in Germany in 1963 and the first broadcasts using the PAL format occurred in 1967 in the UK and Germany. PAL provides a better image than NTSC but is seen as inferior to France's SECAM format. NTSC was developed in 1941 for use in North America, parts of South America, and Asia. It uses 30 frames per second with 525 scan lines per frame. SECAM was developed in France in 1956 and was introduced there in 1967. It has the advantage of transmitting colors one at a time to avoid artificial colors but has the disadvantage of being harder to edit than PAL or NTSC.