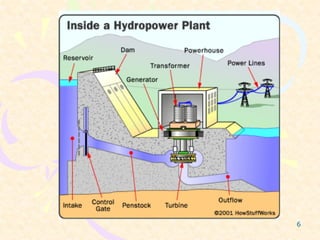
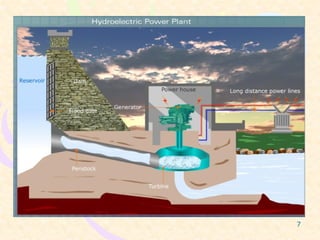
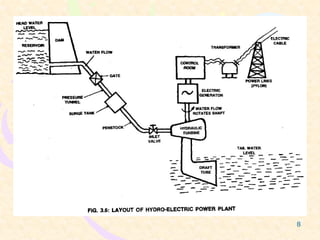
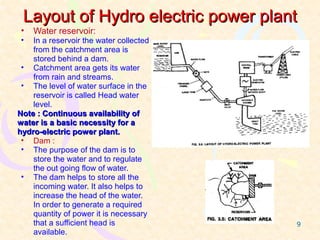
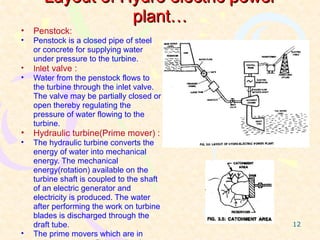
This document provides an overview of hydel power plants. It begins with an introduction explaining how hydel power plants convert the kinetic energy of falling water into electricity. It then discusses the history of hydel power, from ancient water wheels to modern hydroelectric plants. The working principles and typical layout of a hydel plant are explained, including components like the reservoir, dam, penstock, turbine, generator and tailrace. Hydel plants are classified based on head of water. The main turbines - Pelton, Francis and Kaplan - are depicted in diagrams. Advantages include renewability while disadvantages include high initial costs and variable power production. In conclusion, hydel power is encouraged with environmental impacts weighed against development needs.