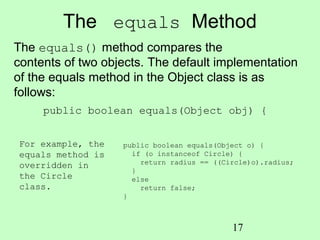
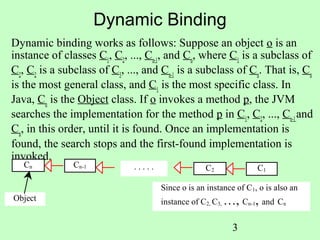
Polymorphism allows methods to be used generically for a wide range of object arguments, known as generic programming. When a method takes a superclass as a parameter, any subclass of that parameter can be passed to the method. At runtime, the specific implementation of the method invoked is determined dynamically based on the actual object passed. This capability is known as dynamic binding. Casting may be needed when assigning an object to a variable of a superclass or subclass in the inheritance hierarchy.

![Polymorphism, Dynamic Binding and Generic Programming
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
m(new GraduateStudent()); Method m takes a parameter
m(new Student());
m(new Person());
of the Object type. You can
m(new Object()); invoke it with any object.
}
public static void m(Object x) { An object of a subtype can be used wherever its
System.out.println(x.toString());
} supertype value is required. This feature is
}
known as polymorphism.
class GraduateStudent extends Student {
}
class Student extends Person { When the method m(Object x) is executed, the
public String toString() {
return "Student";
argument x’s toString method is invoked. x
} may be an instance of GraduateStudent,
}
Student, Person, or Object. Classes
class Person extends Object { GraduateStudent, Student, Person, and Object
public String toString() {
return "Person"; have their own implementation of the toString
}
} method. Which implementation is used will be
determined dynamically by the Java Virtual
Machine at runtime. This capability is known
as dynamic binding.
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8polymorphism-130324221924-phpapp01/85/8-polymorphism-2-320.jpg)

![Generic Programming
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) { Polymorphism allows methods to be used
m(new GraduateStudent()); generically for a wide range of object
m(new Student());
m(new Person());
arguments. This is known as generic
m(new Object()); programming.
} If a method’s parameter type is a
public static void m(Object x) { superclass (e.g., Object), you may pass an
System.out.println(x.toString()); object to this method of any of the
} parameter’s subclasses (e.g., Student or
}
GraduateStudent).
class GraduateStudent extends Student { When an object (e.g., a Student object or
}
a GraduateStudent object) is used in the
class Student extends Person { method, the particular implementation of
public String toString() { the method of the object that is invoked
}
return "Student"; (e.g., toString) is determined dynamically.
}
class Person extends Object {
public String toString() {
return "Person";
}
}
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8polymorphism-130324221924-phpapp01/85/8-polymorphism-5-320.jpg)