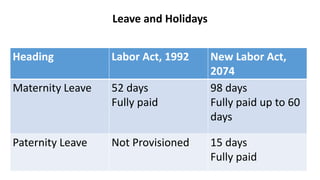
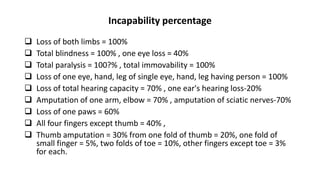
The document discusses various aspects of employment relations in the hospitality industry. It covers intake processes for permanent and temporary workers, benefits like leave policies, bonuses, and insurance. It also addresses issues like misconduct, punishments, gender discrimination and remedies, and processes for settling individual and collective labor disputes. Maintaining good employee relations through fair treatment, competitive benefits, and resolving issues are emphasized as important for business success.