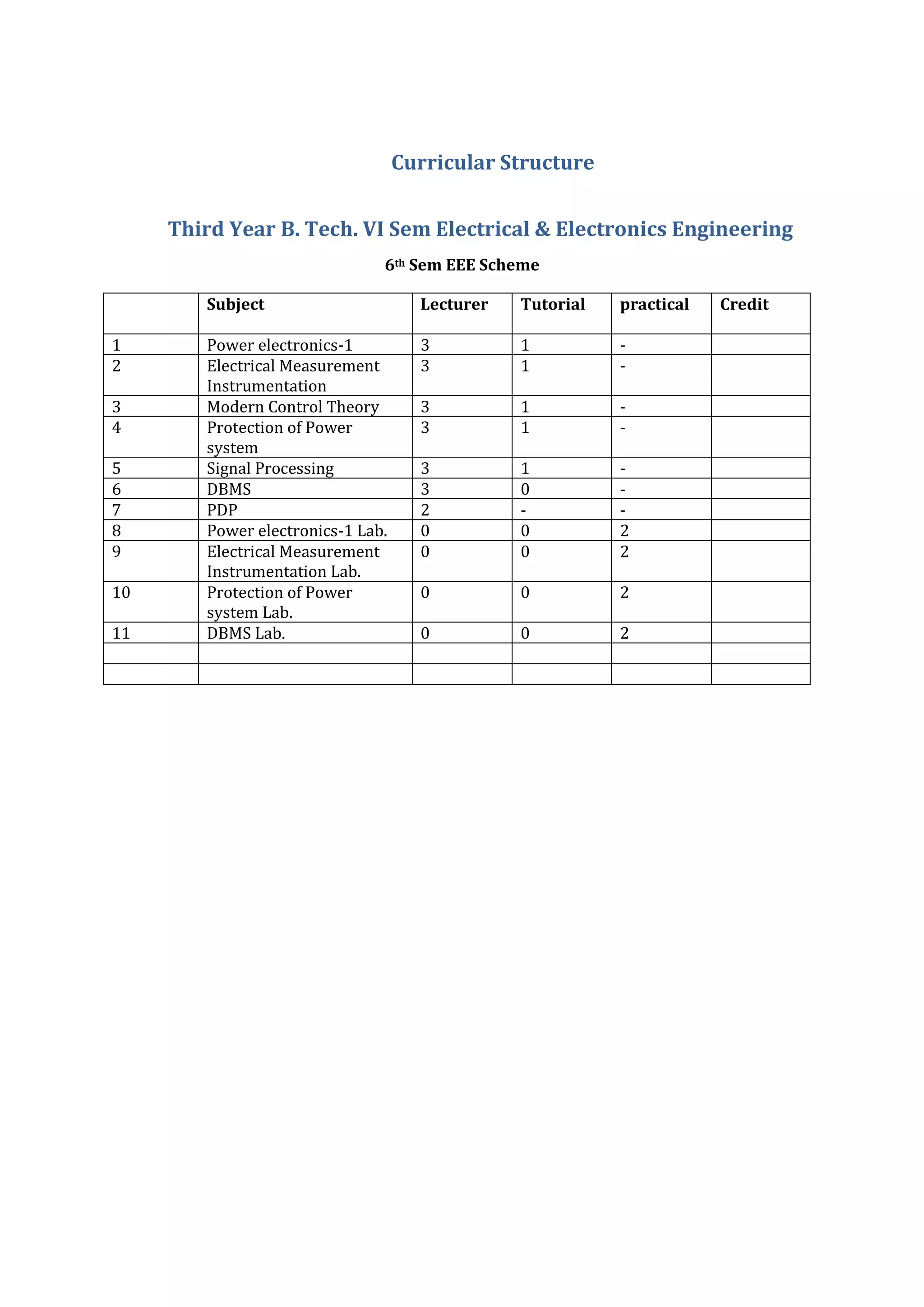
The document provides details of the curriculum structure for the 6th semester of the B.Tech Electrical and Electronics Engineering program. It includes:
1. A list of 11 subjects being offered in the 6th semester along with their credit hours and distribution of lectures, tutorials and practical sessions. Power Electronics-1, Electrical Measurement Instrumentation, Modern Control Theory, Protection of Power System, Signal Processing and DBMS are some of the major subjects.
2. Syllabus outlines for some of the subjects including Power Electronics-1, Electrical Measurement Instrumentation, Modern Control Theory, Protection of Power System and Signal Processing.
3. Lists of practical experiments for subjects with a lab component, such as Power Electronics-