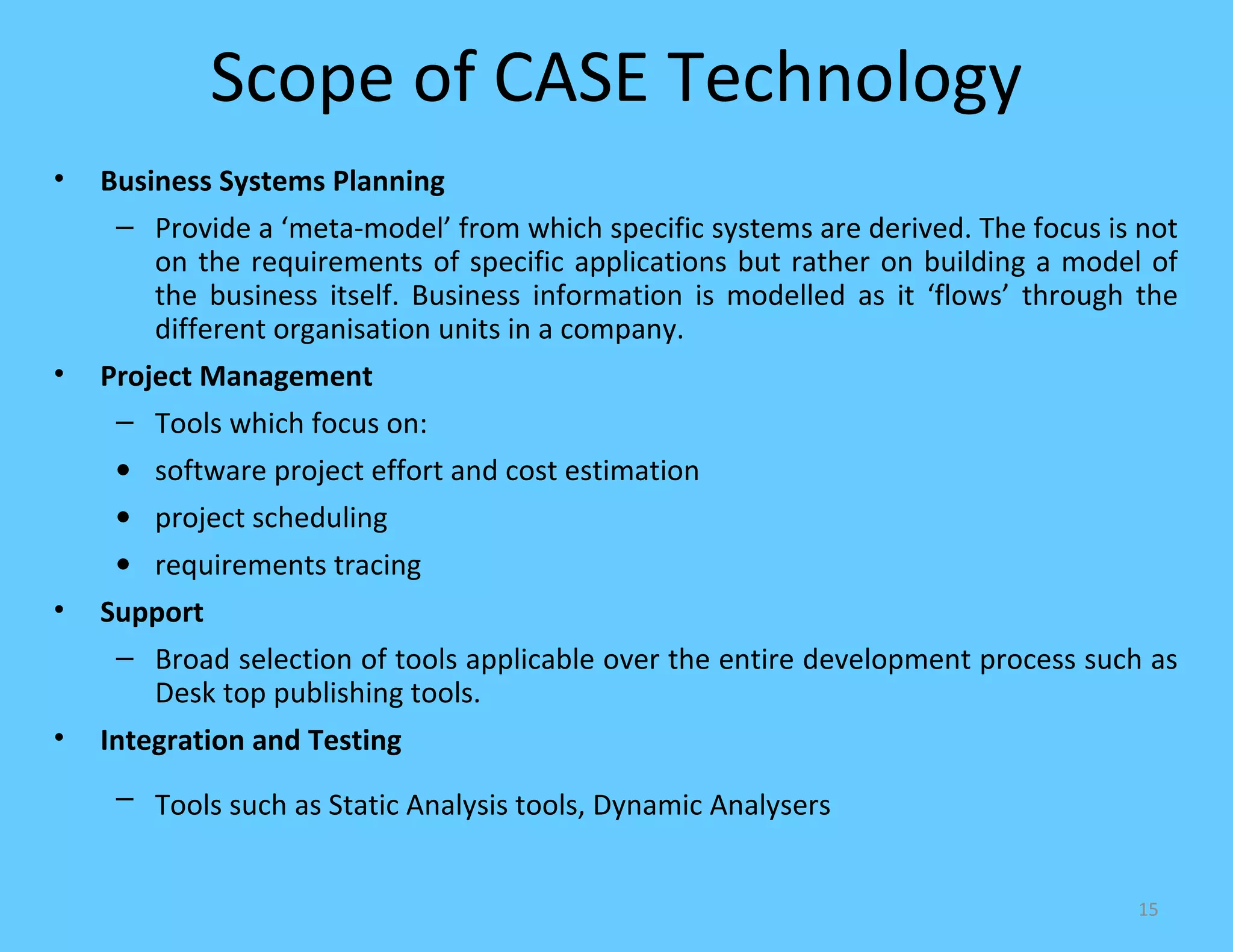
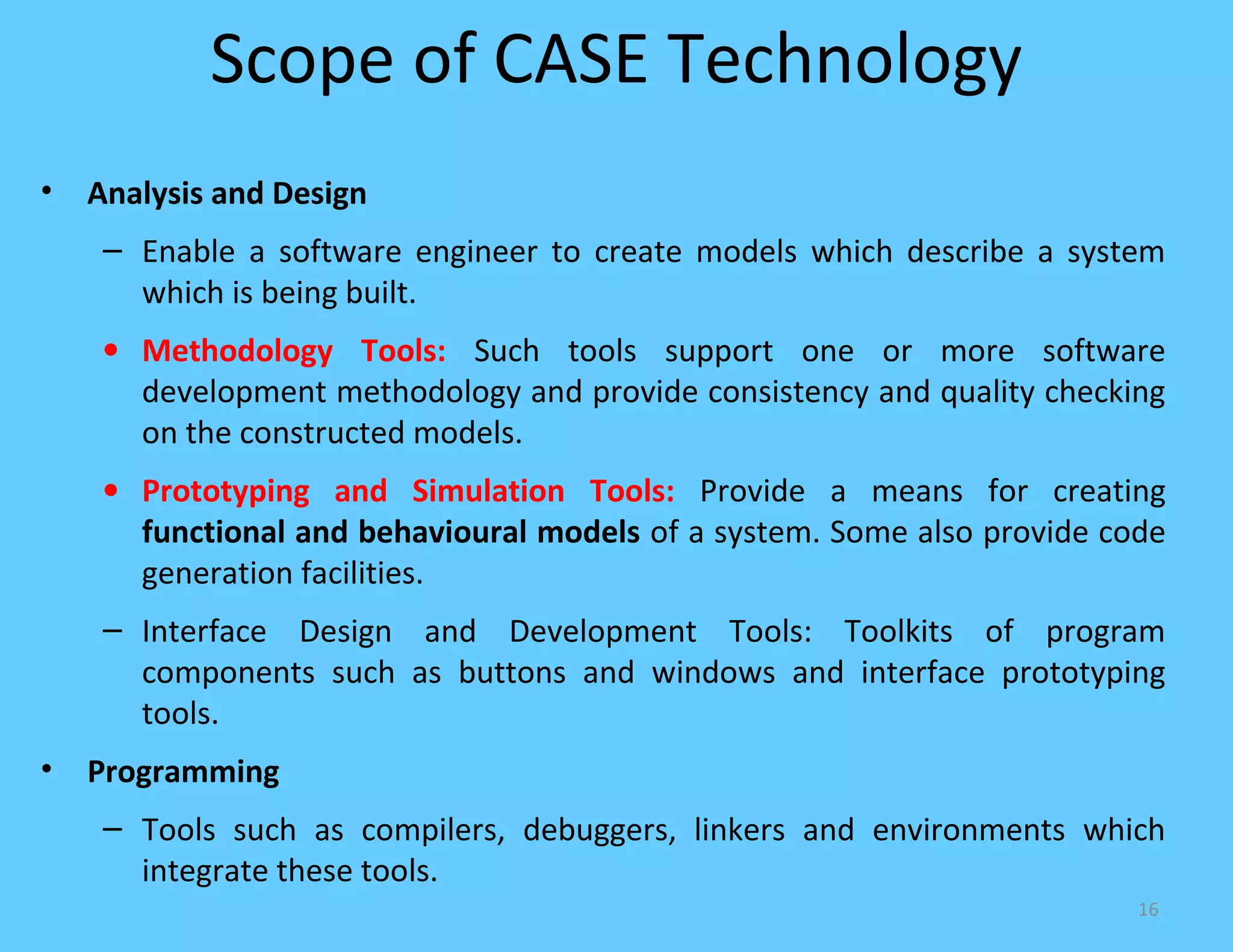
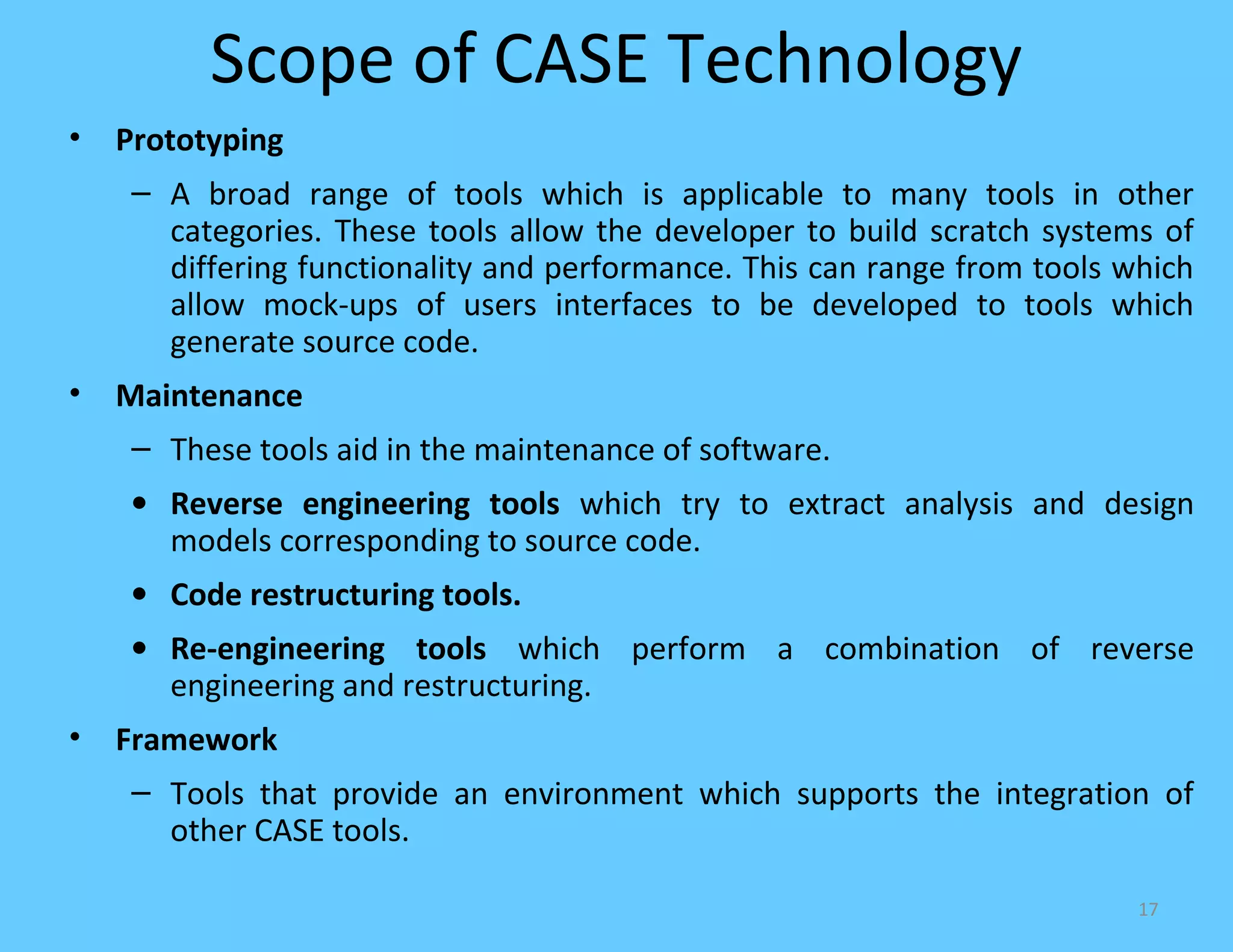
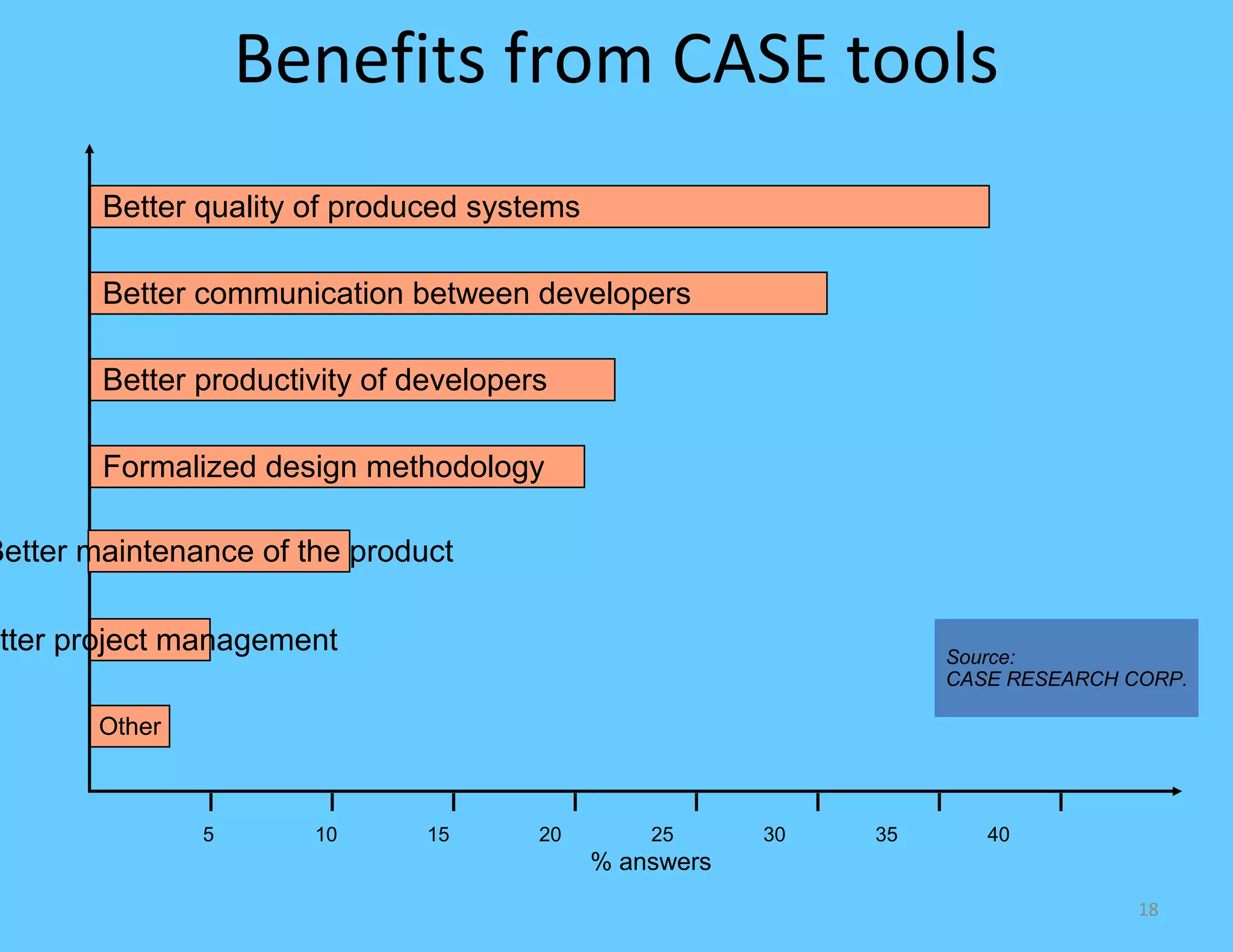
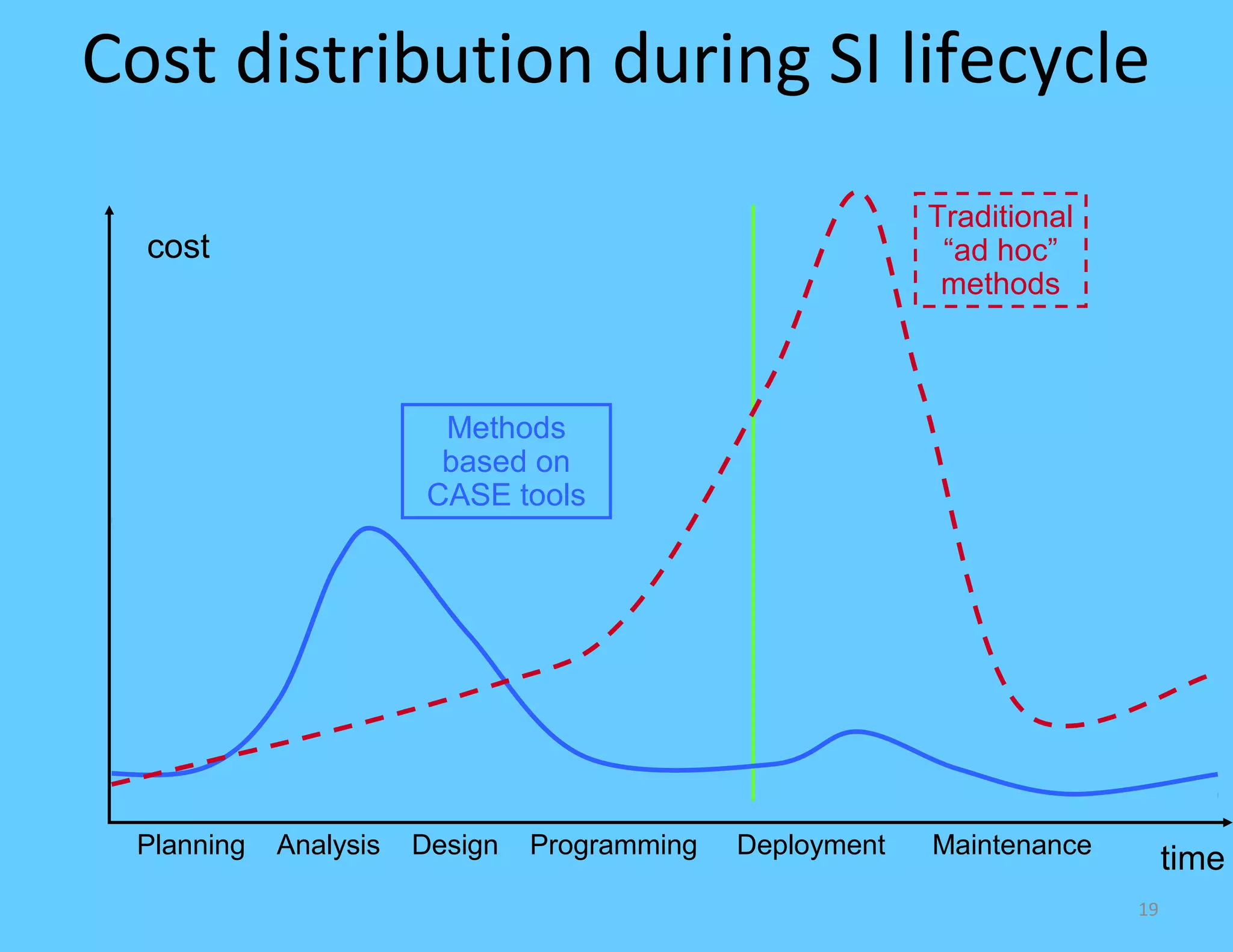
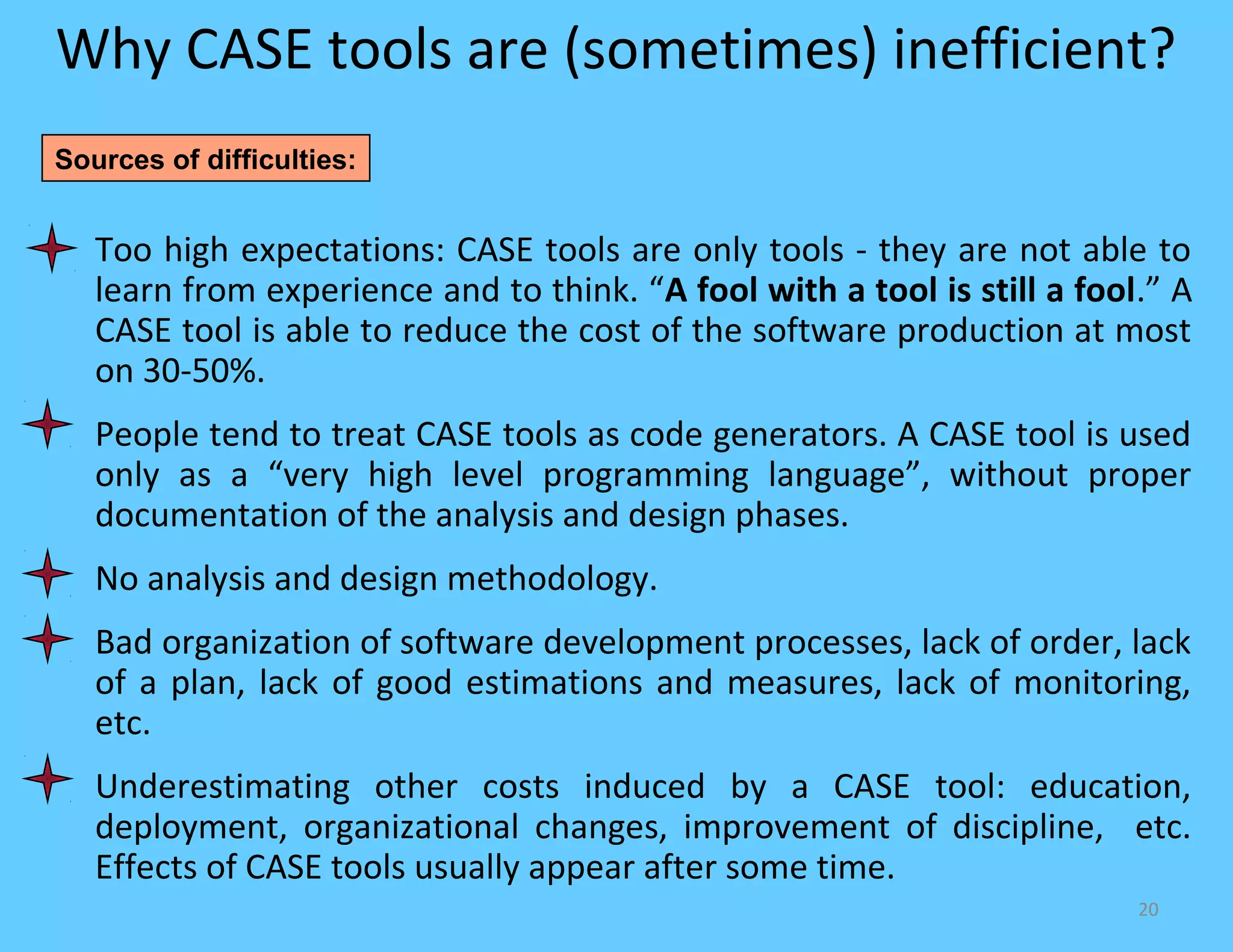
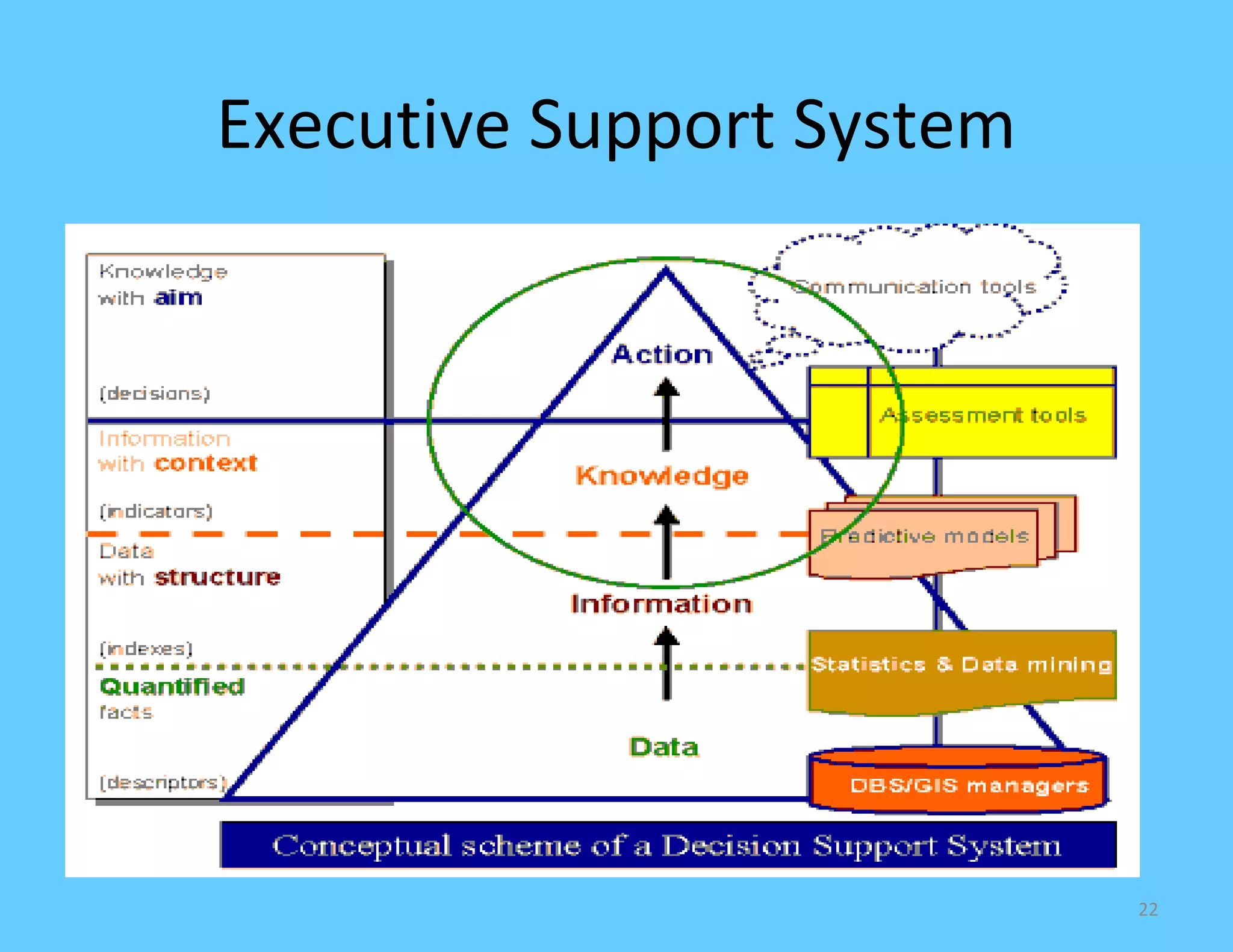
CASE tools are computer-based tools that support various stages of the software development lifecycle. They allow for modeling systems using diagrams, documentation generation, code production, and more. Popular CASE tools support requirements analysis, design, programming, project management, testing and maintenance. While CASE tools aim to improve quality, productivity and standardization, their success depends on proper methodology, organization, goals, and integration into the development process. Benefits include faster development times, increased documentation and quality, and reduced maintenance costs over the long term.