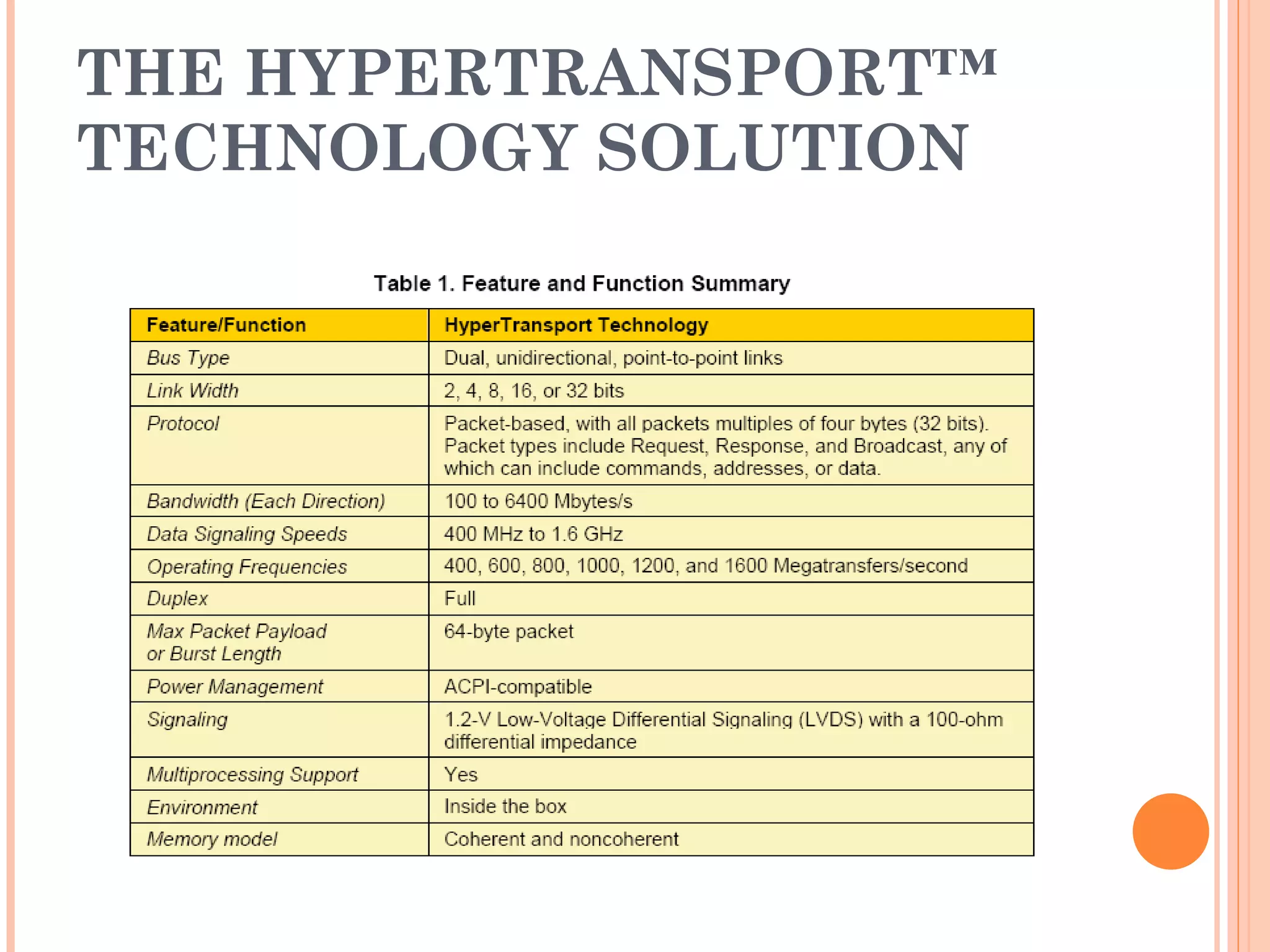
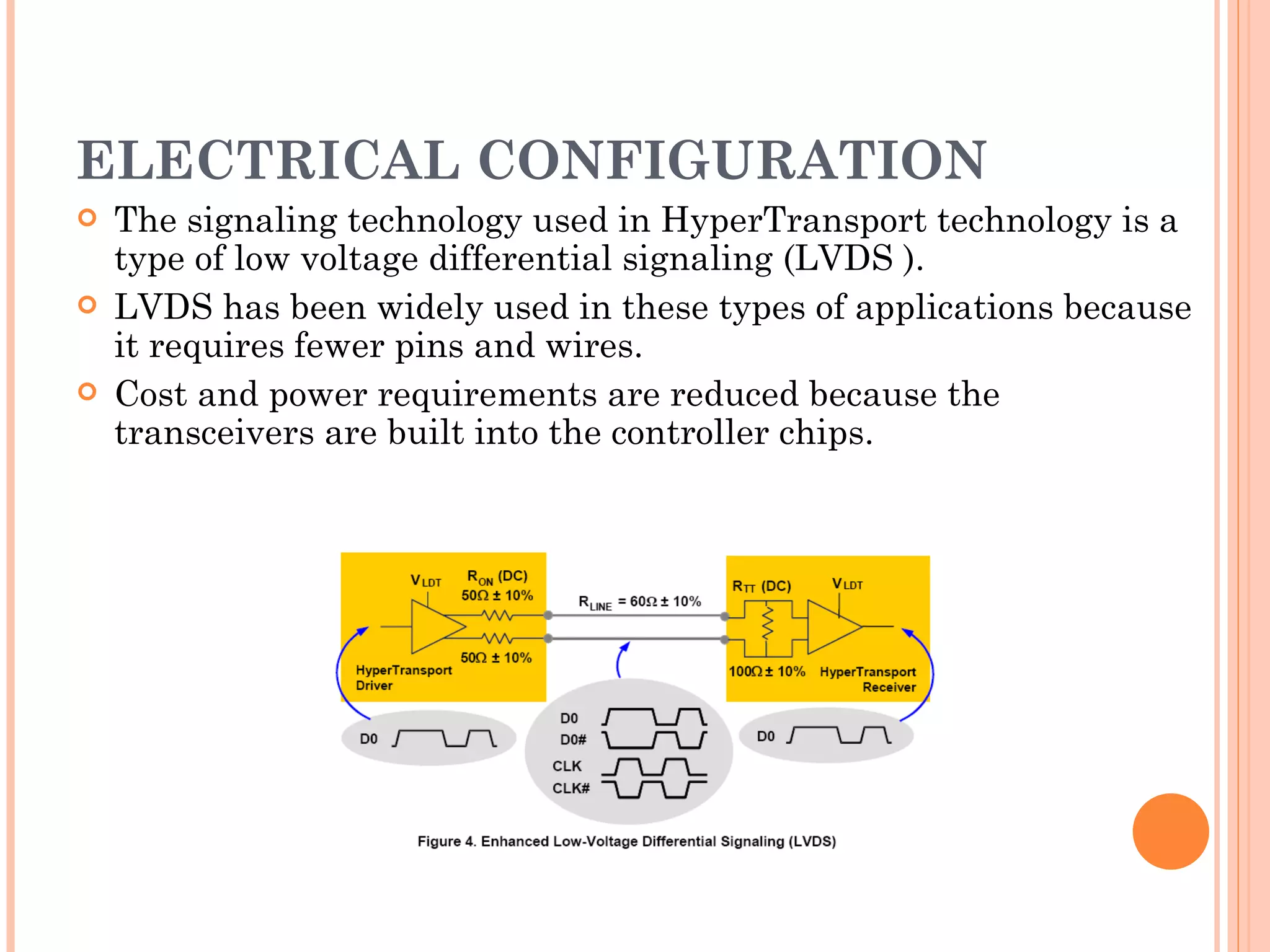
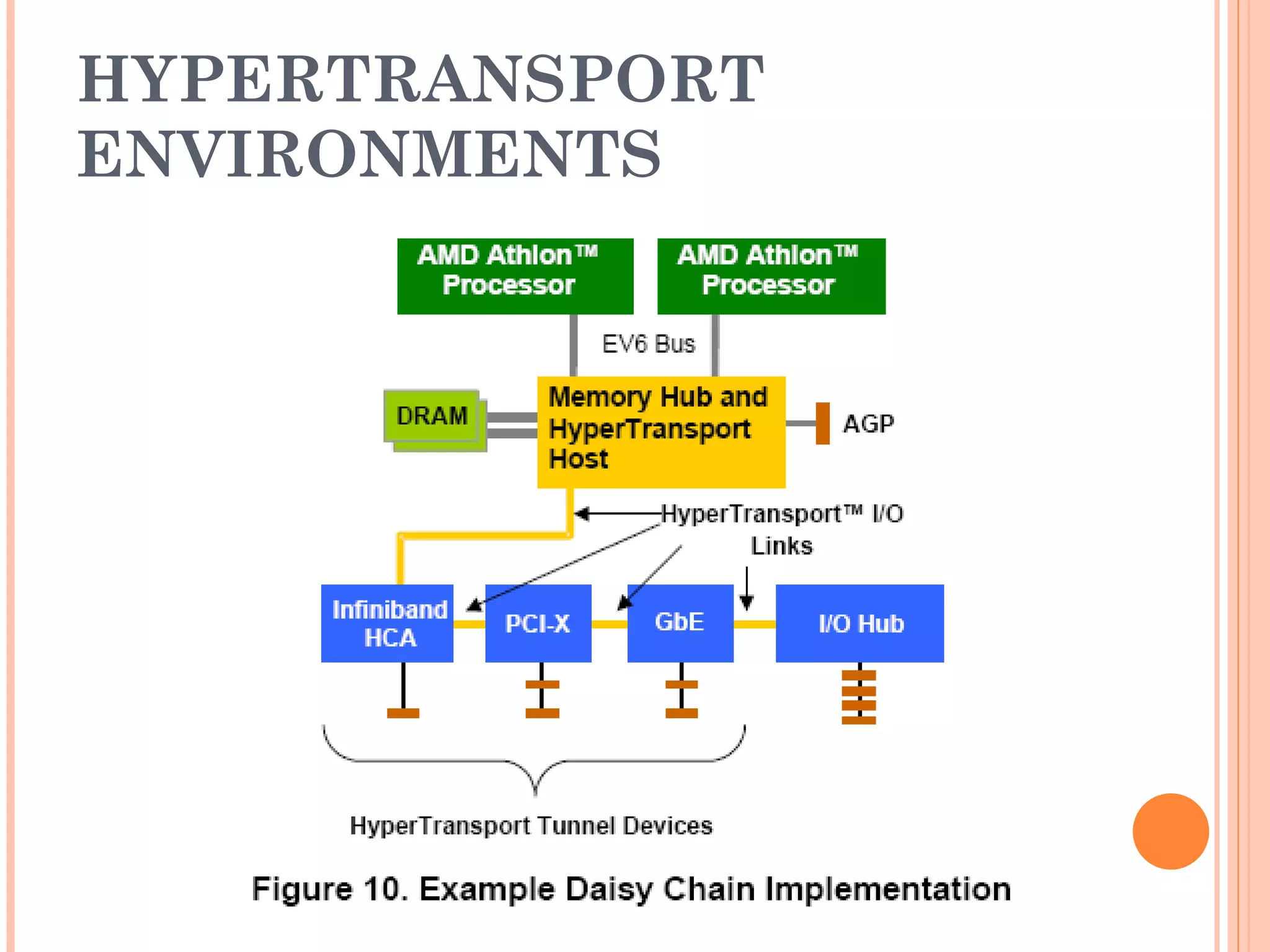
Hyper Transport (HT) is an open standard interconnect technology that provides high-bandwidth communication between processors, GPUs, and I/O devices. It was developed to address the growing performance gap between rising processor speeds and slower I/O buses. HT uses low-voltage differential signaling and a packet-based protocol to provide low latency, scalable connections at speeds up to 1.6GHz per channel for aggregate bandwidths over 12.8GB/s. The technology simplifies system design, improves performance, and aims to be compatible with legacy systems while enabling continued improvements.