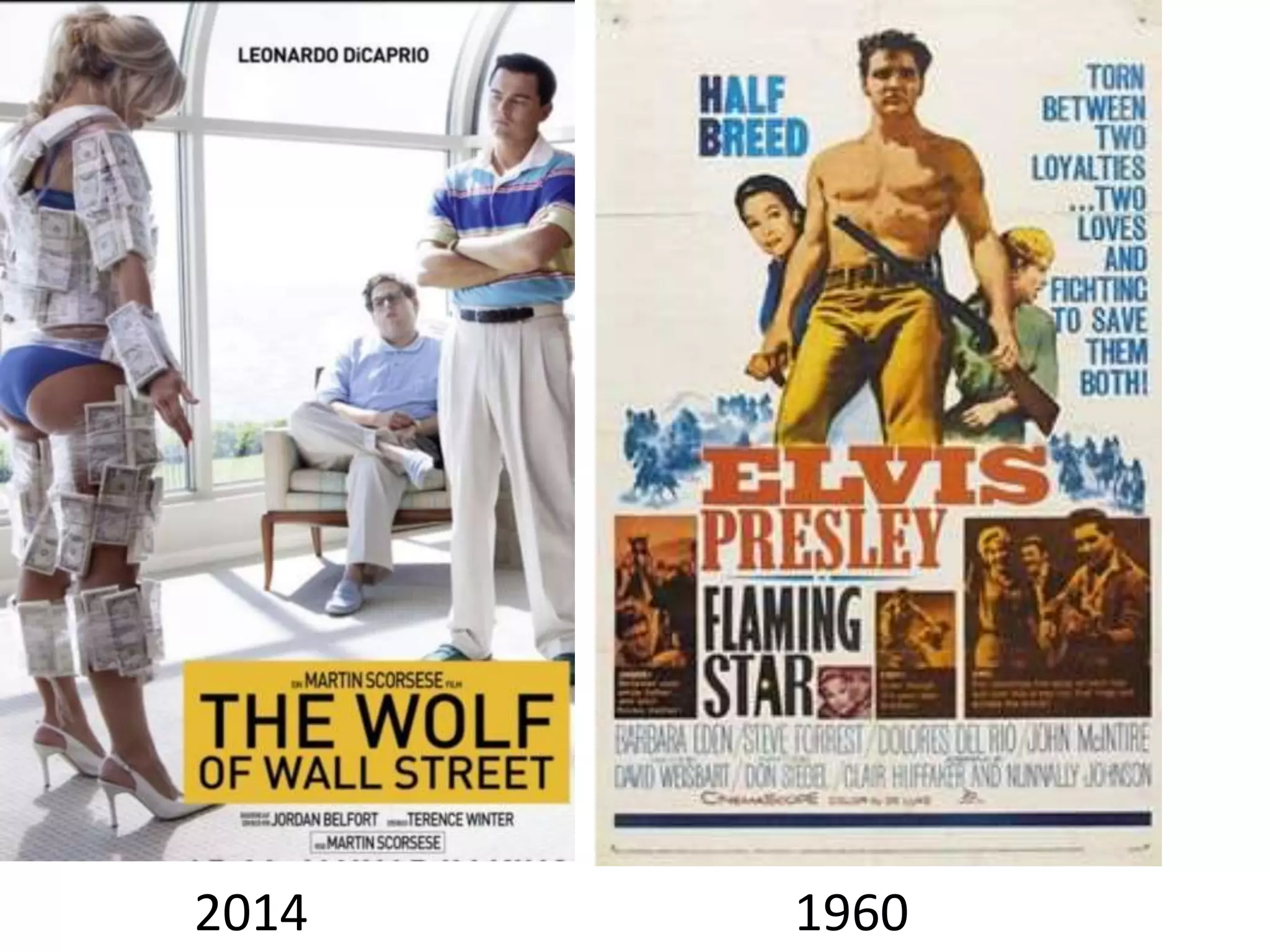
The document discusses key concepts for analyzing representations in media texts, including:
1) Who or what is being represented, how the representation is created and by whom, and why the representation is constructed in a certain way.
2) Groups that are commonly underrepresented or misrepresented, such as women, minorities, and LGBTQ individuals.
3) Theories for analyzing representations, including the male gaze, female gaze, and concepts of femininity, patriarchy, and progressive vs. regressive portrayals.