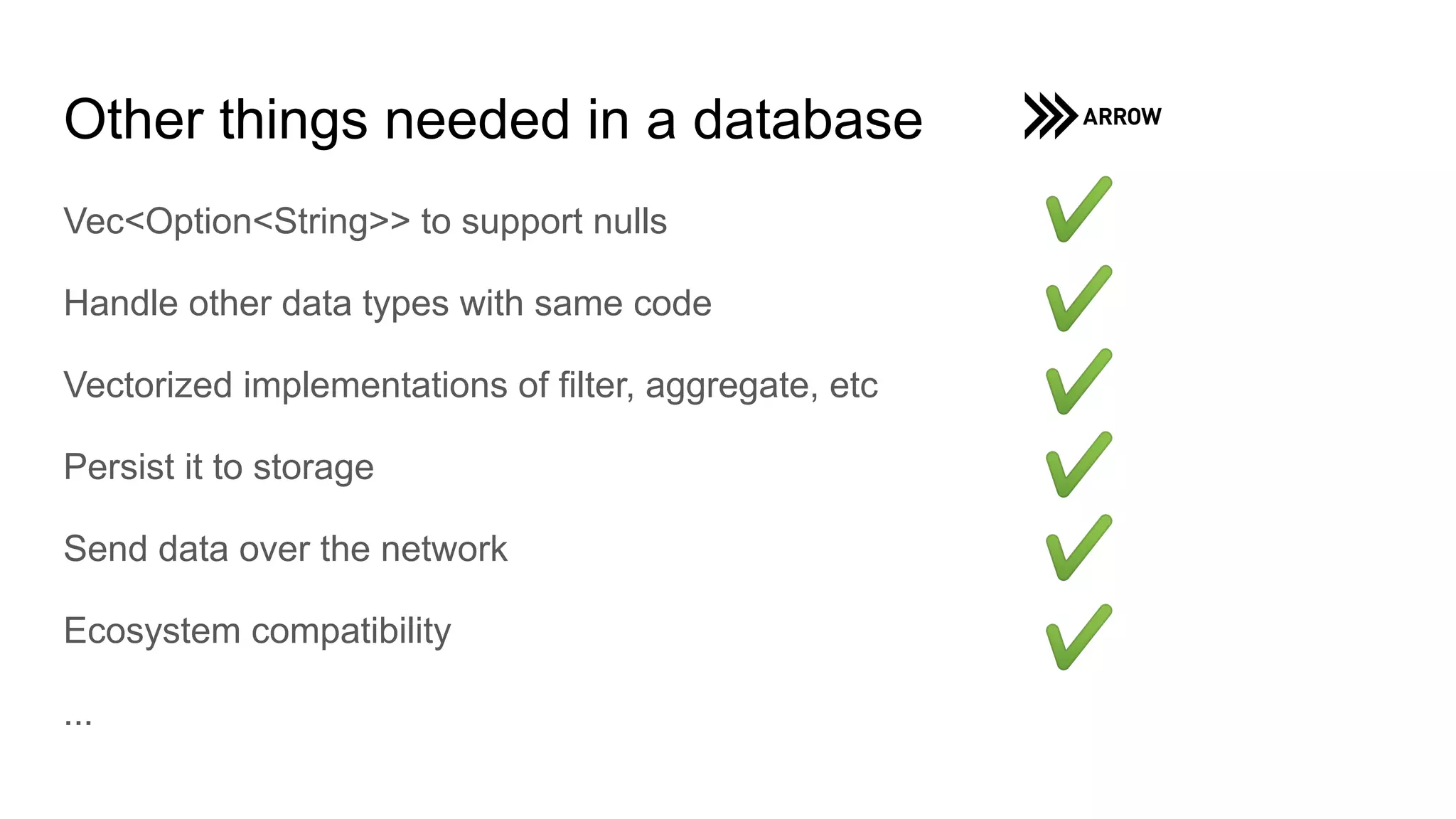
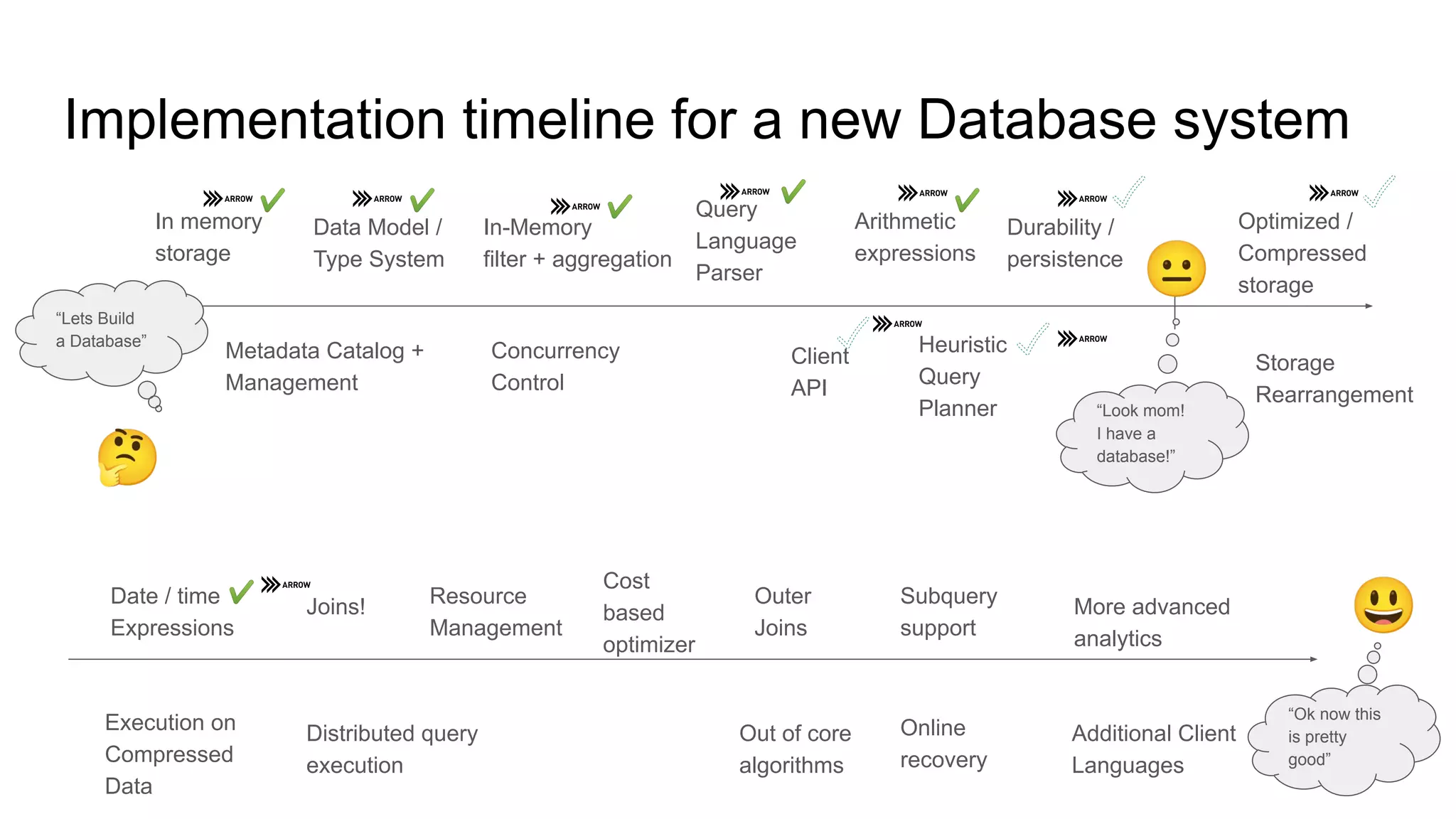
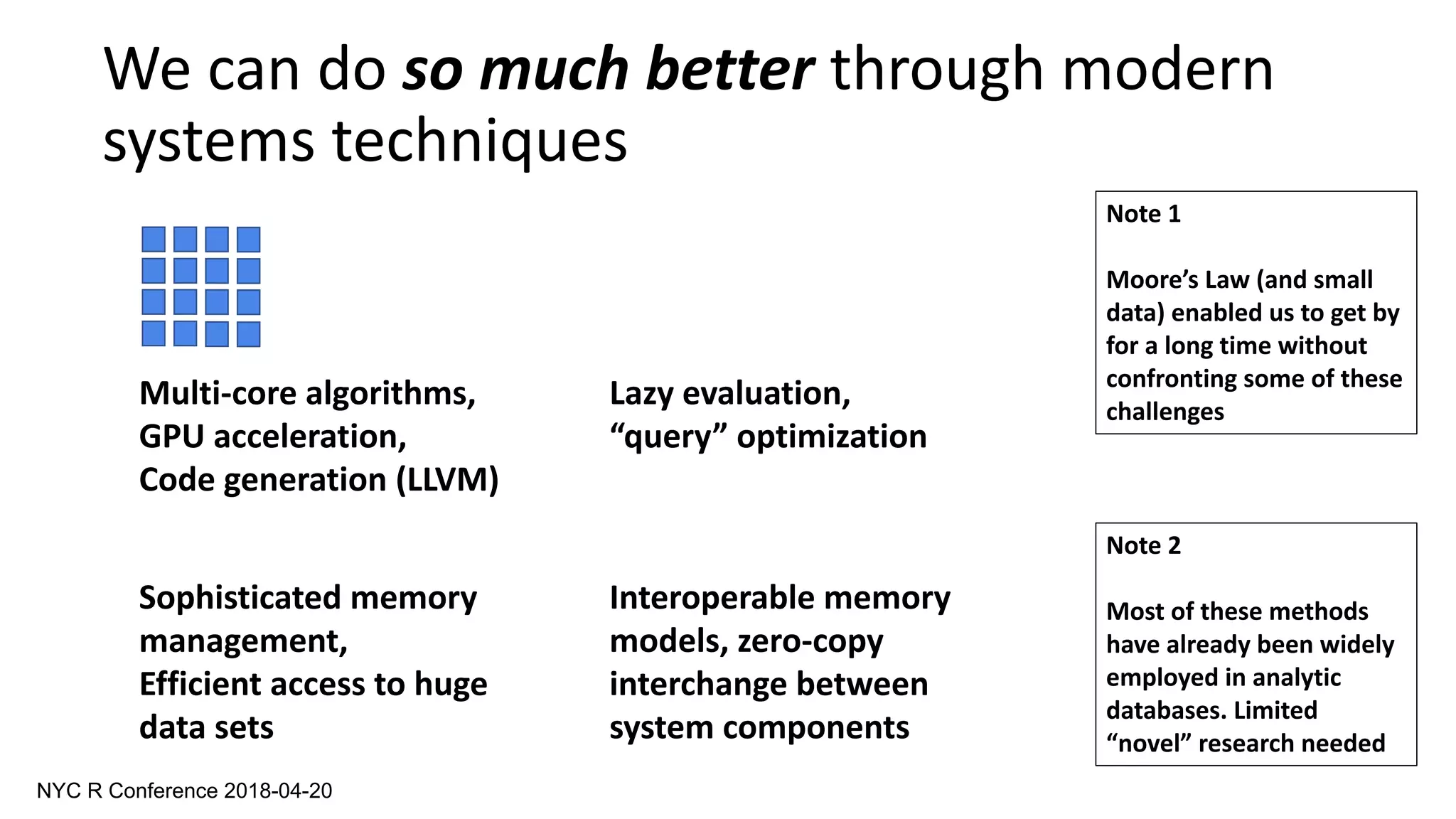
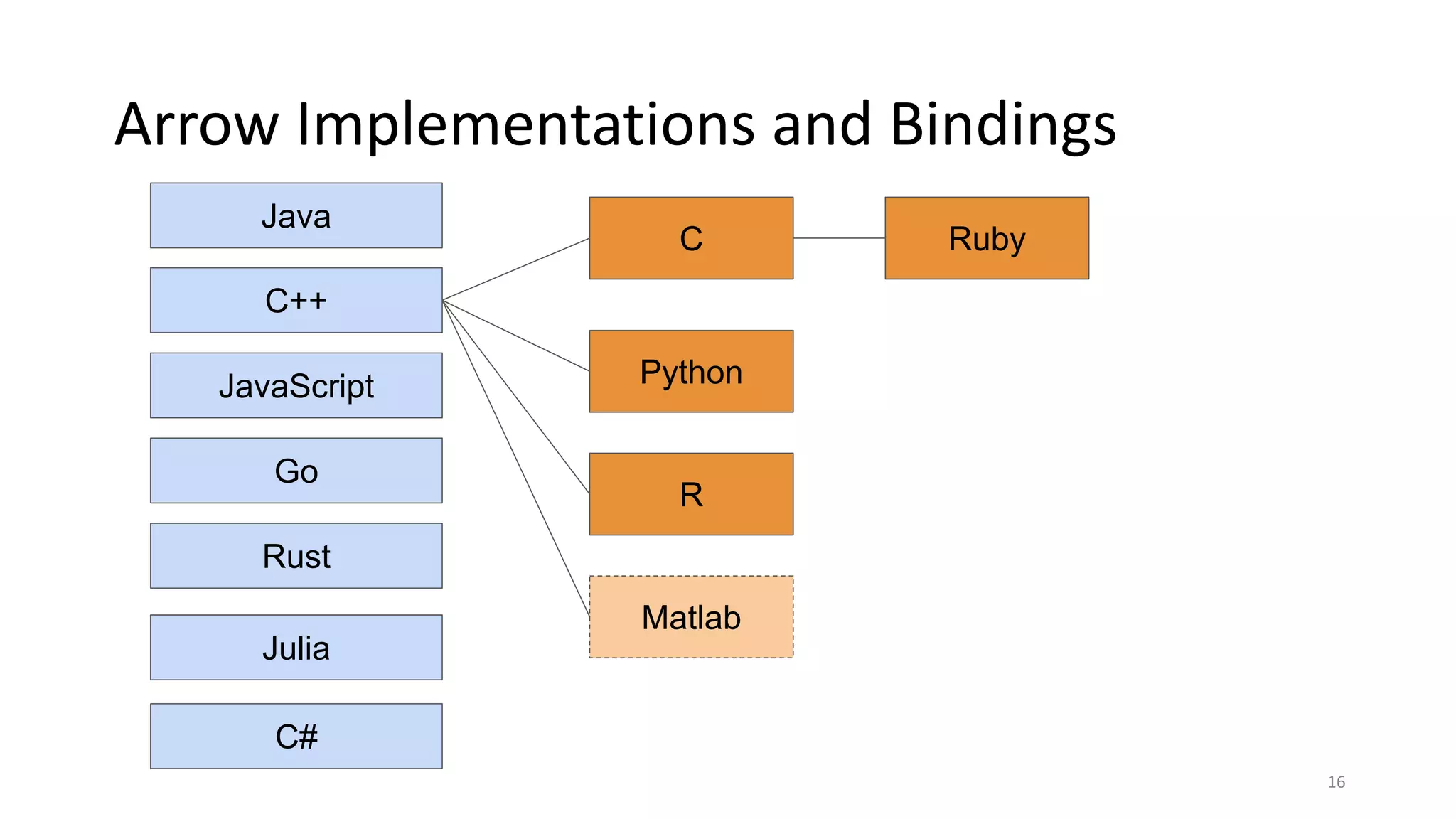
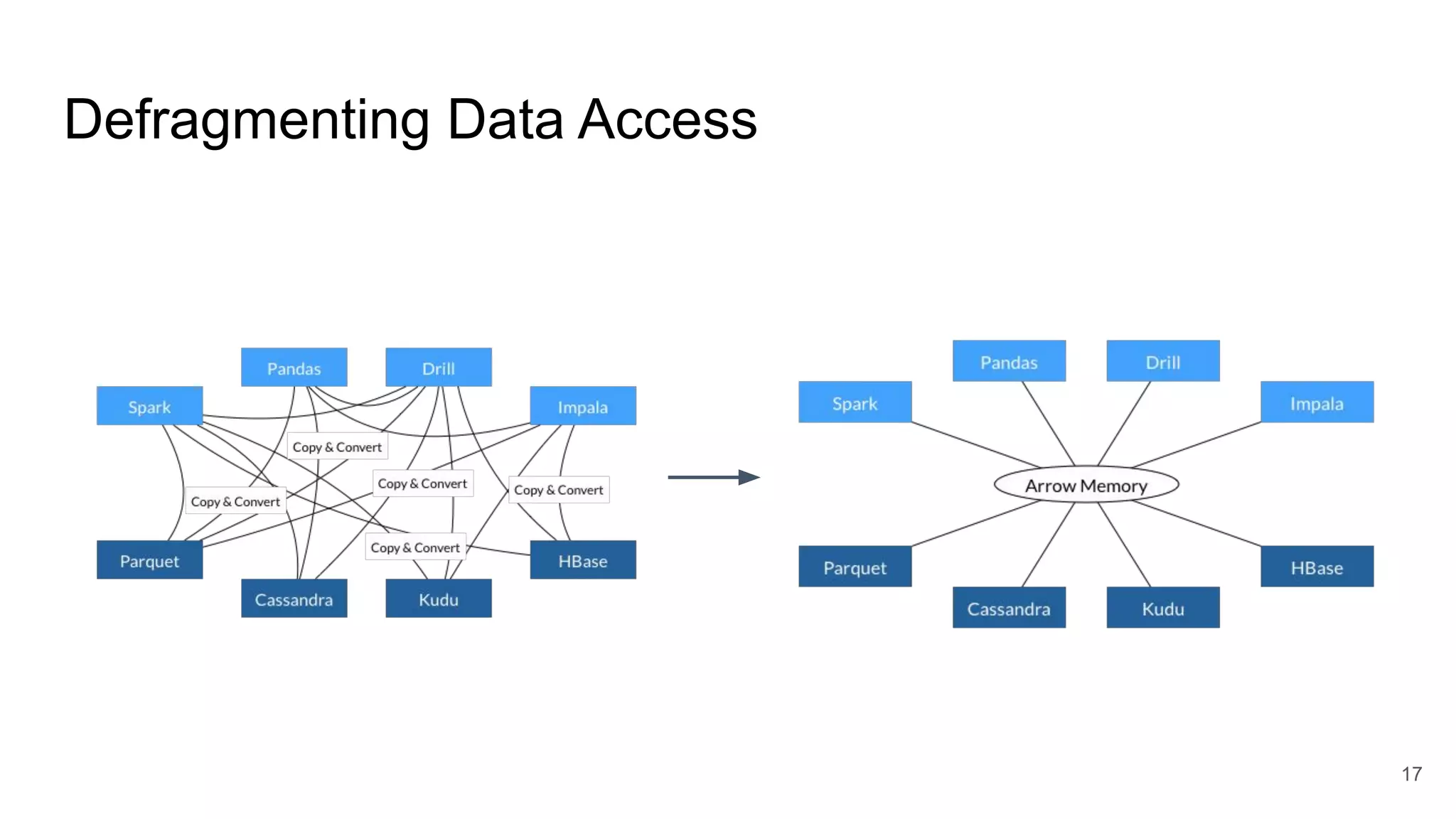
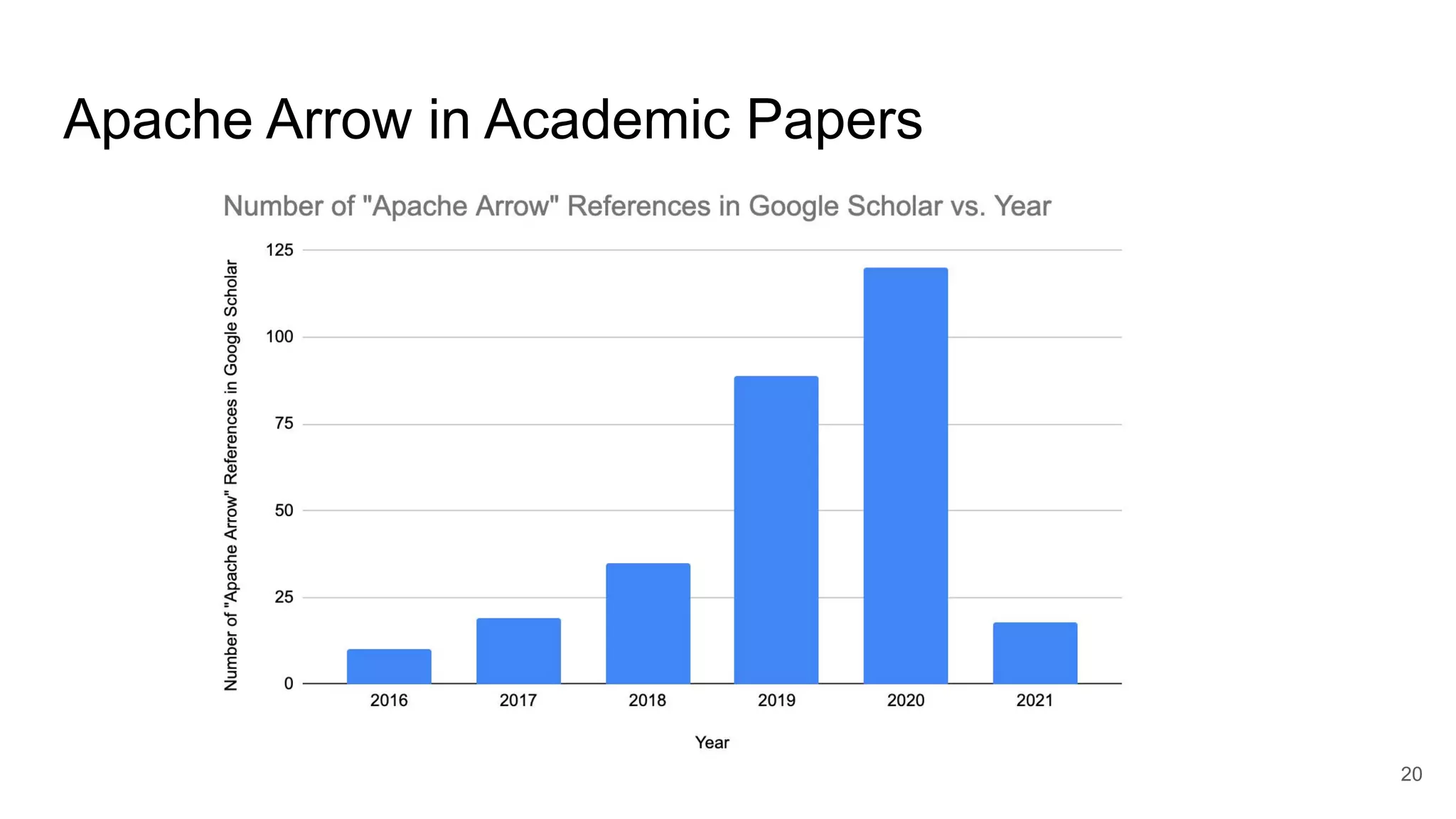
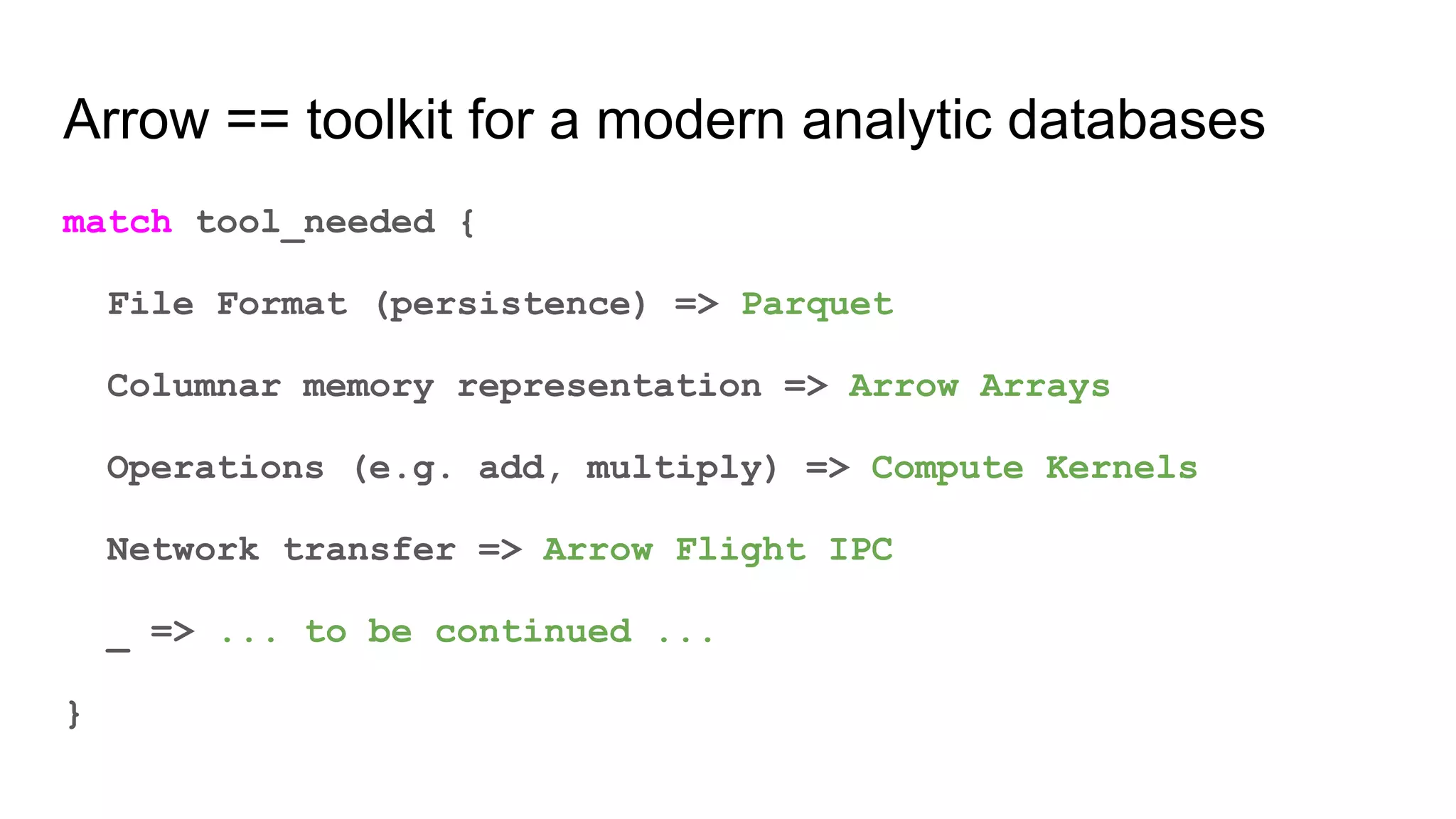
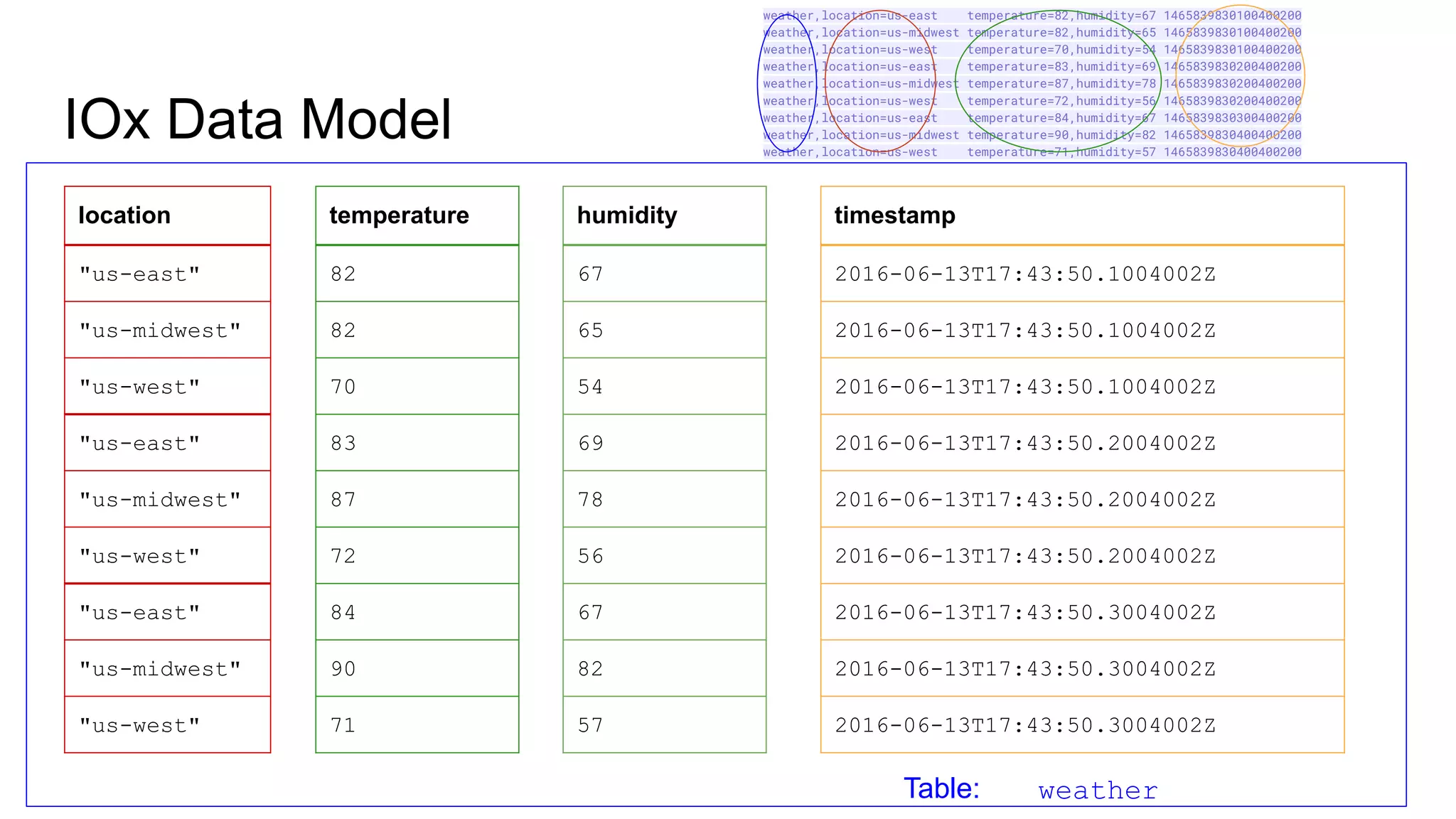
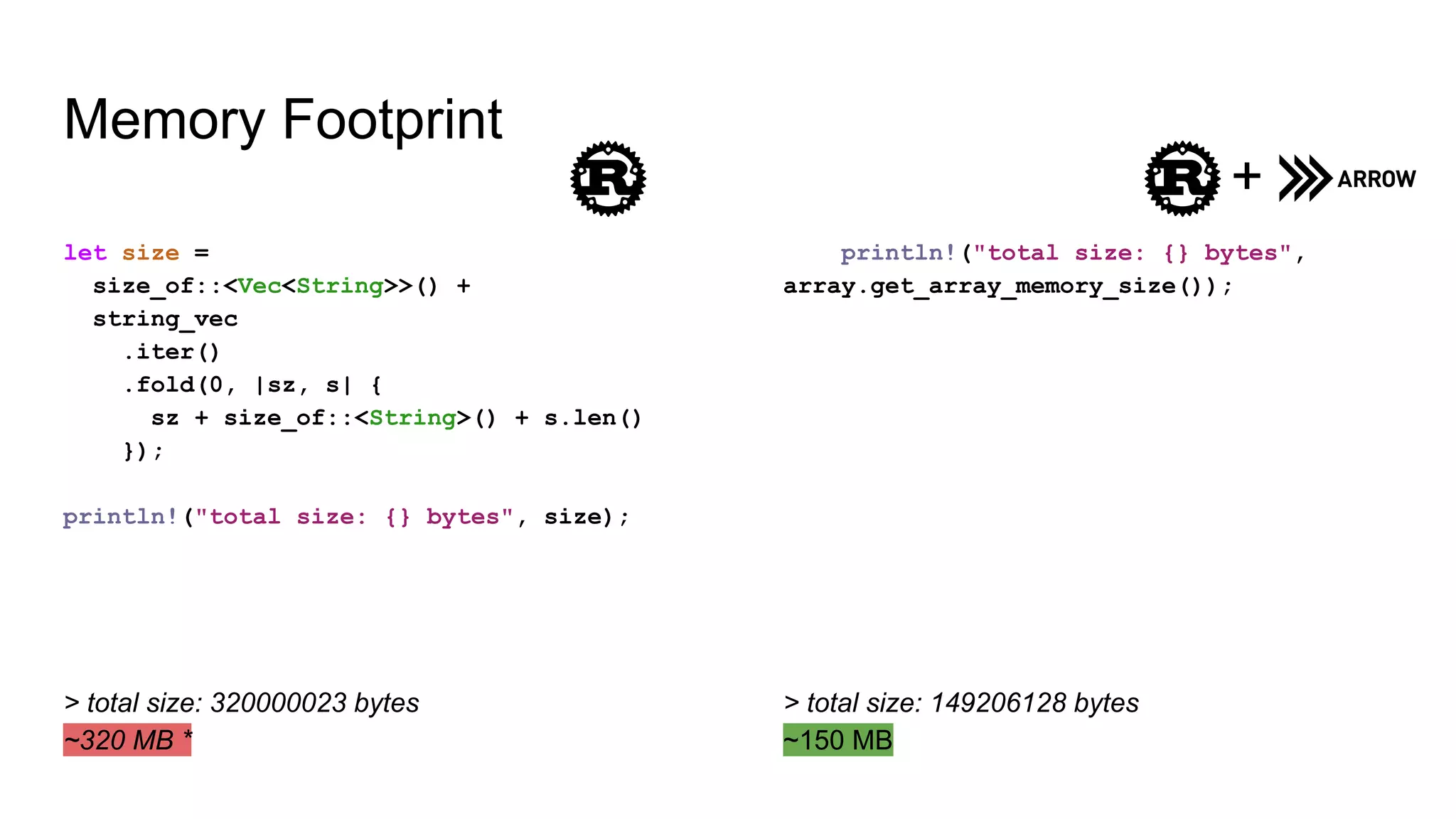
The document outlines a guest lecture by Andrew Lamb on Apache Arrow and its relevance to modern database systems, specifically for time series databases. It discusses the evolution of database architectures, the specialization of database types, and introduces InfluxDB's iox, which leverages the Arrow ecosystem for enhanced performance and flexibility. The content also covers various features and implementation considerations for developing new database systems using modern techniques and technologies.



















![Materialize rows for future processing
let not_west: Vec<String> = not_west_bitset
.iter()
.enumerate()
.filter_map(|(i, &v)| {
if v {
Some(string_vec[i].clone())
} else {
None
}
})
.collect();
let not_west = filter(
&array,
¬_west_bitset
).unwrap();
> Made array of 6666667 Strings not in west
~450 ms
> Made array of 6666667 Strings not in west
~50 ms
+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2021-04-20apachearrowanditsimpactonthedatabaseindustry-210421132222/75/2021-04-20-apache-arrow-and-its-impact-on-the-database-industry-pptx-32-2048.jpg)
![More efficient encoding (dictionary)
let vb = StringBuilder::new();
let kb = Int8Builder::new();
let mut builder =
StringDictionaryBuilder::new(vb,kb);
(0..NUM_TAGS)
.enumerate()
.for_each(|(i, _)| {
let location = match i % 3 {
0 => "us-east",
1 => "us-midwest",
2 => "us-west",
};
builder.append(location).unwrap();
});
let array = builder.finish();
> total size: 10000688 bytes
10MB
250 ms
+
dictionary
"us-east"
"us-midwest"
"us-west"
Location
0
1
2
0
1
2
0
1
2
[0]
[1]
[2]
[u8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2021-04-20apachearrowanditsimpactonthedatabaseindustry-210421132222/75/2021-04-20-apache-arrow-and-its-impact-on-the-database-industry-pptx-33-2048.jpg)
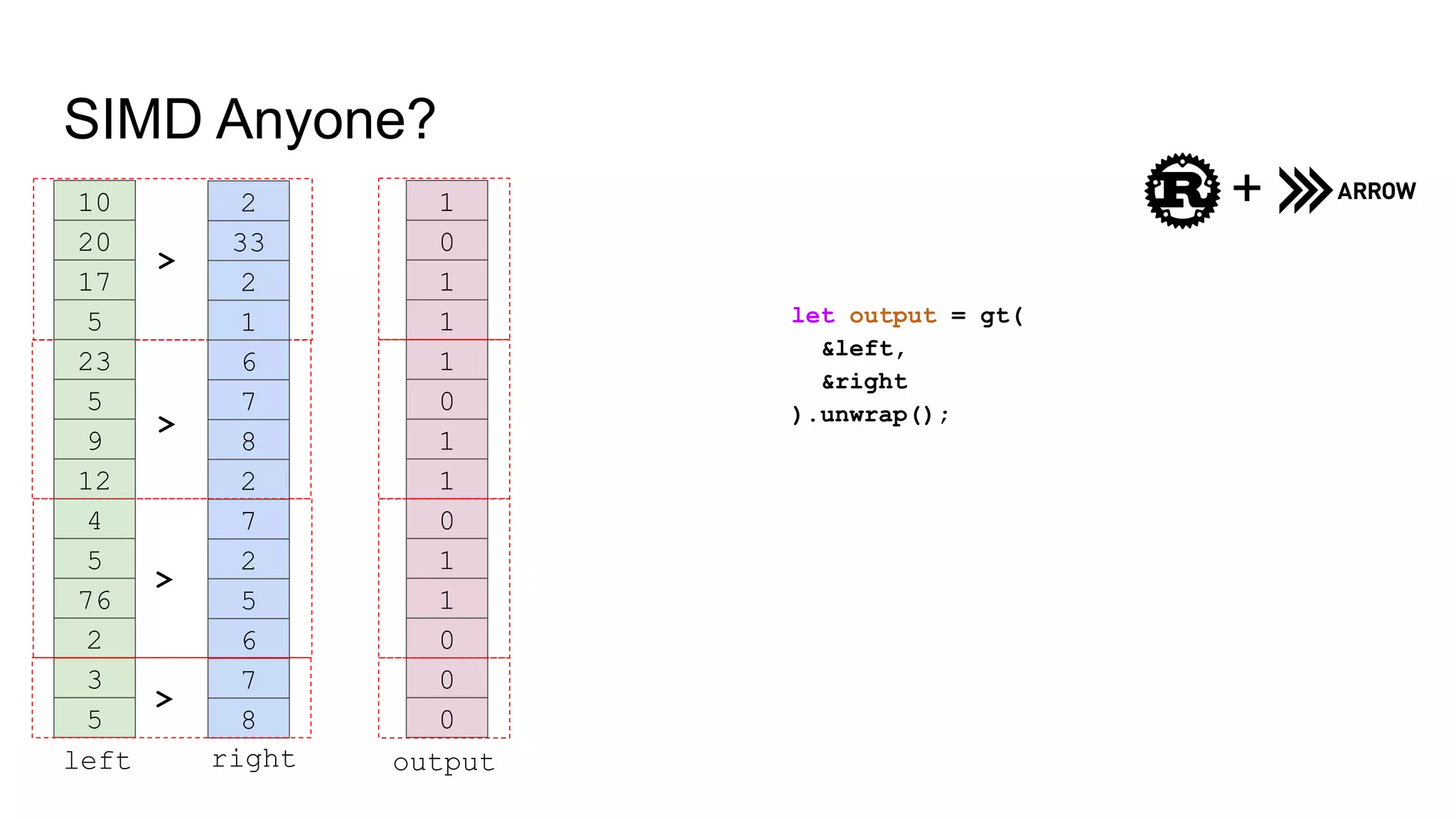
![SIMD Implementation
#[cfg(all(any(target_arch = "x86", target_arch = "x86_64"),
feature = "simd"))]
fn simd_compare_op<T, F>(left: &PrimitiveArray<T>,
right: &PrimitiveArray<T>, op: F) -> Result<BooleanArray>
where
T: ArrowNumericType,
F: Fn(T::Simd, T::Simd) -> T::SimdMask,
{
// use / error checking elided
let null_bit_buffer = combine_option_bitmap(
left.data_ref(), right.data_ref(), len
)?;
let lanes = T::lanes();
let mut result = MutableBuffer::new(
left.len() * mem::size_of::<bool>()
);
let rem = len % lanes;
for i in (0..len - rem).step_by(lanes) {
let simd_left = T::load(left.value_slice(i, lanes));
let simd_right = T::load(right.value_slice(i, lanes));
let simd_result = op(simd_left, simd_right);
T::bitmask(&simd_result, |b| {
result.write(b).unwrap();
});
}
Source: arrow/src/compute/kernels/comparison.rs
if rem > 0 {
let simd_left = T::load(left.value_slice(len - rem, lanes));
let simd_right = T::load(right.value_slice(len - rem,
lanes));
let simd_result = op(simd_left, simd_right);
let rem_buffer_size = (rem as f32 / 8f32).ceil() as usize;
T::bitmask(&simd_result, |b| {
result.write(&b[0..rem_buffer_size]).unwrap();
});
}
let data = ArrayData::new(
DataType::Boolean,
left.len(),
None,
null_bit_buffer,
0,
vec![result.freeze()],
vec![],
);
Ok(PrimitiveArray::<BooleanType>::from(Arc::new(data)))
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2021-04-20apachearrowanditsimpactonthedatabaseindustry-210421132222/75/2021-04-20-apache-arrow-and-its-impact-on-the-database-industry-pptx-35-2048.jpg)