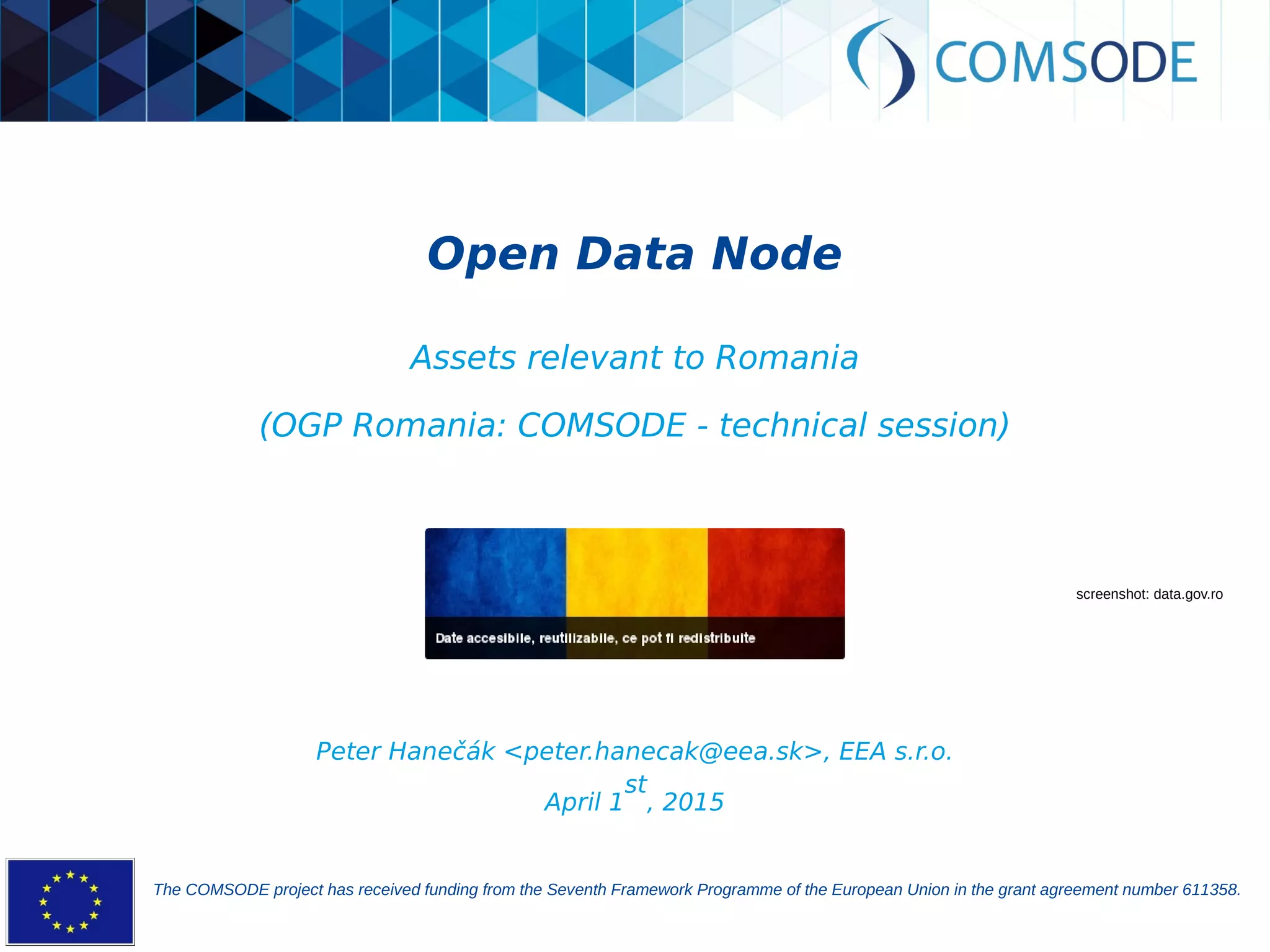
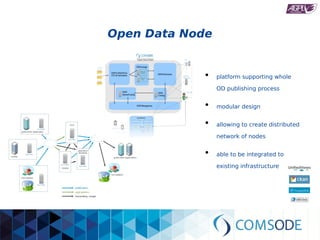
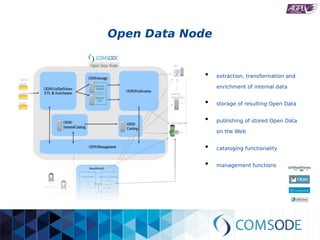
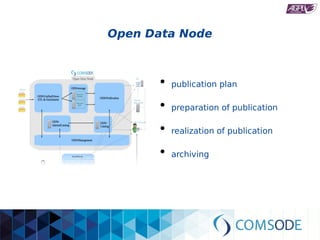
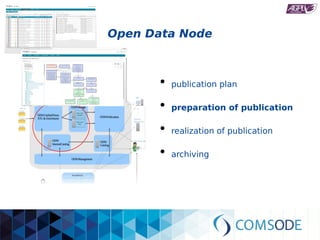
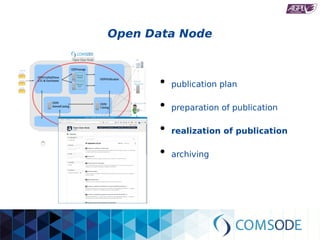
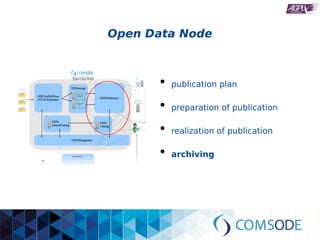
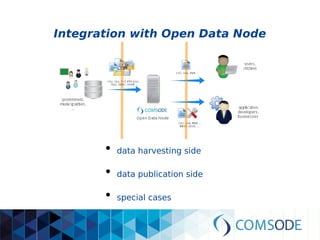
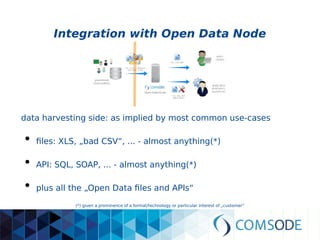
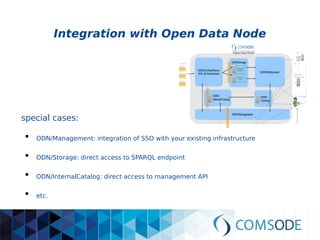
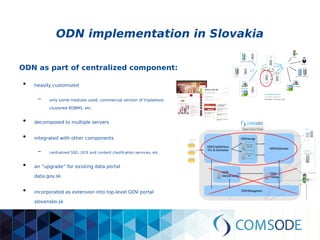
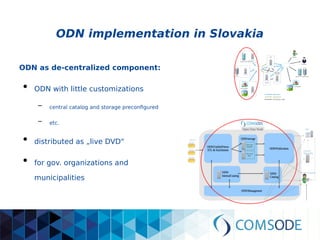
The comsode project, funded by the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme, aims to develop the Open Data Node (ODN) platform that facilitates the publication of open data through a modular and integrated system. The project offers a methodology for organizations with limited experience in open data, providing guidance and tools for data publication and management. Future sustainability relies on strong community support and the success of commercial partners utilizing the ODN.