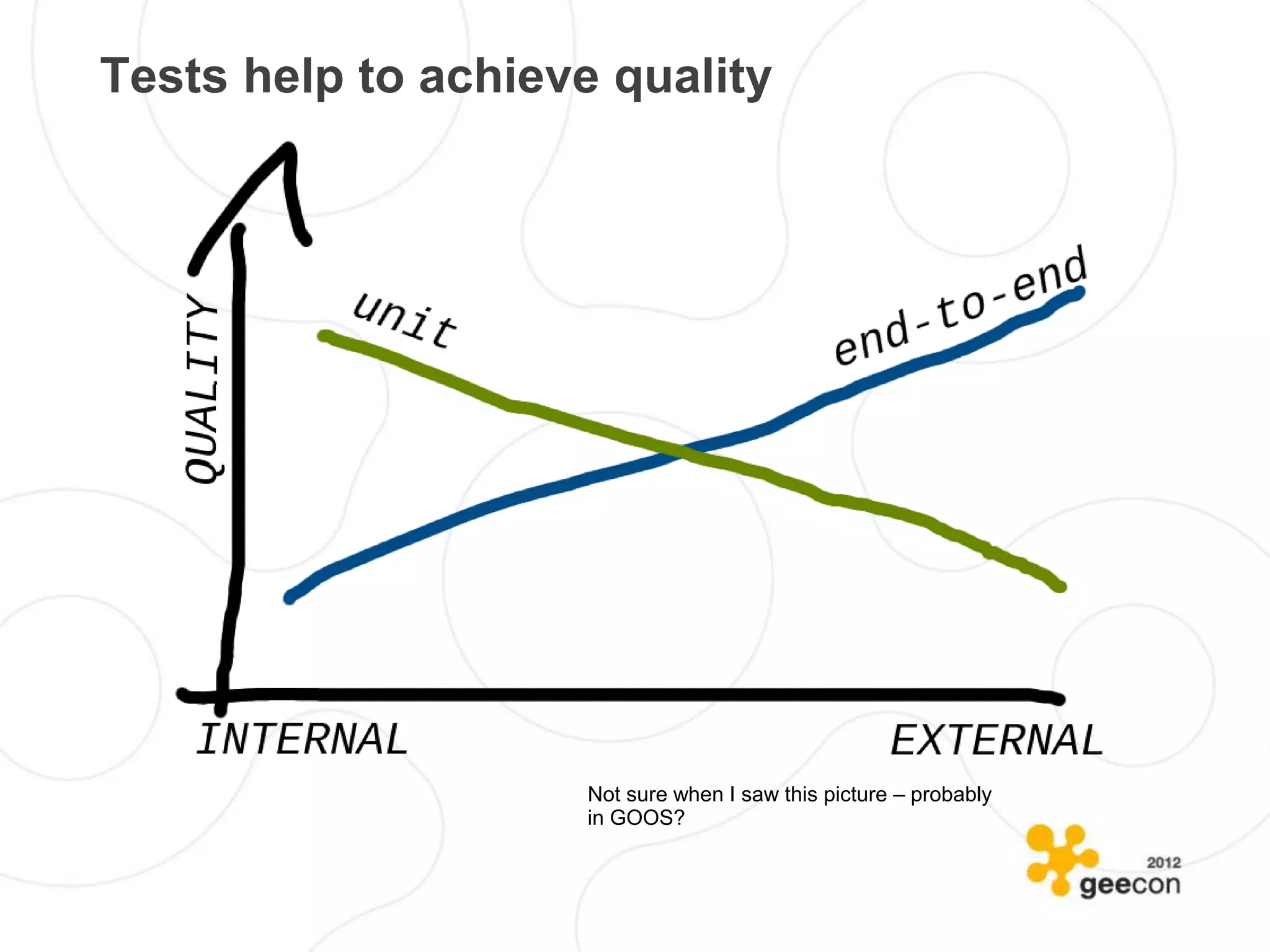
The document discusses the challenges and nuances of writing effective unit tests, highlighting historical context and automation aspects. It reviews both bad and good testing practices, emphasizing the importance of clear outcomes and the significance of mastering testing tools. The document ultimately stresses that tests should enhance quality and mitigate potential issues in software development.










![Tests are boring – let us autogenerate them!
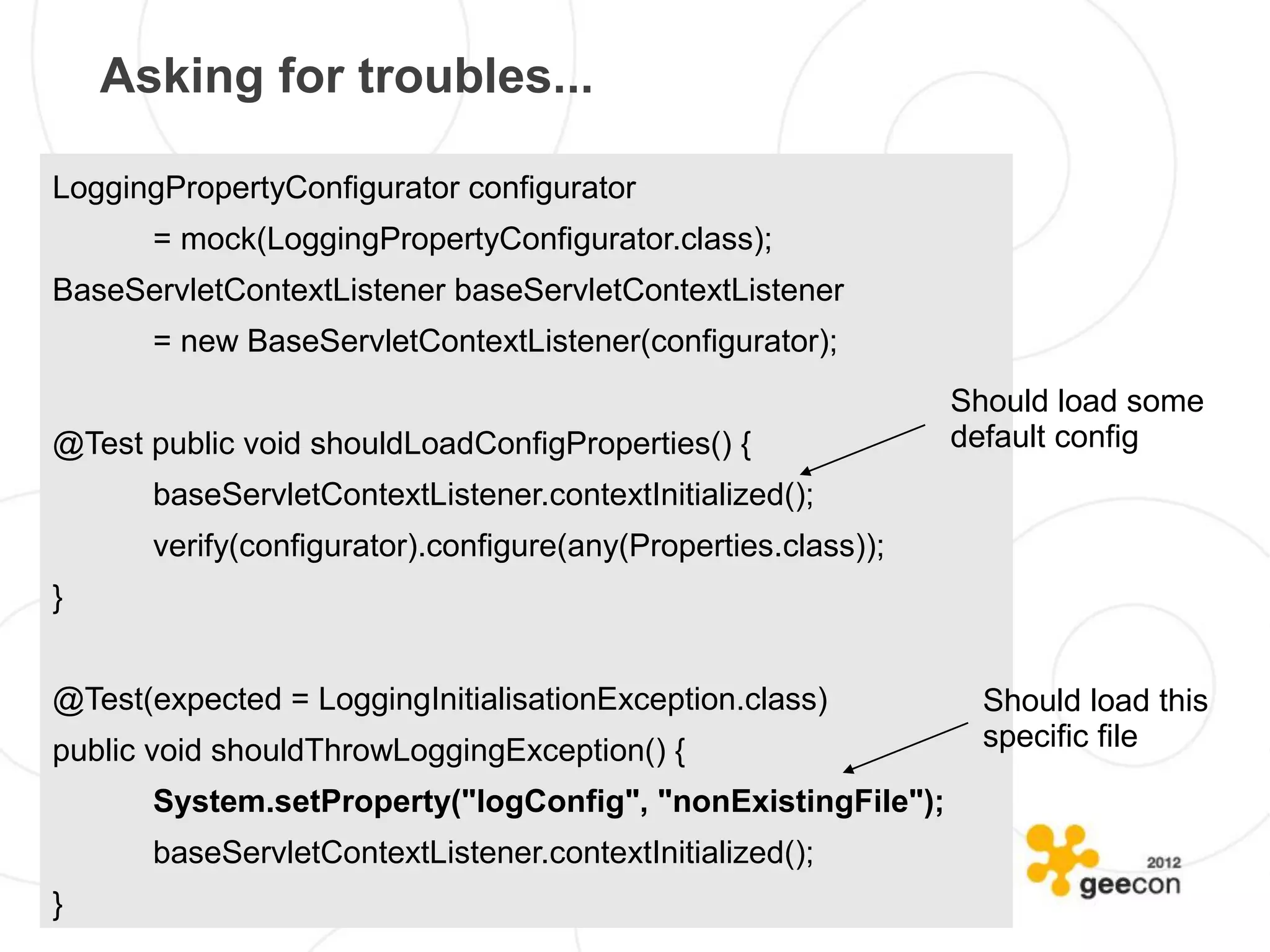
/** protected void tearDown() throws Exception {
* Generated by JUnitDoclet, a tool provided by // JUnitDoclet begin method testcase.tearDown
* ObjectFab GmbH under LGPL. adapter = null;
* Please see www.junitdoclet.org, www.gnu.org super.tearDown();
* and www.objectfab.de for informations about // JUnitDoclet end method testcase.tearDown
* the tool, the licence and the authors.
*/ public void testMain() throws Exception {
public class AdapterTest // JUnitDoclet begin method testMain
// JUnitDoclet begin extends_implements Adapter.main(new String [] {"ADAPTER"});
extends TestCase // JUnitDoclet end method testMain
// JUnitDoclet end extends_implements }
{
// JUnitDoclet begin class
Adapter adapter = null; /**
// JUnitDoclet end class * JUnitDoclet moves marker to this method, if there is not match
* for them in the regenerated code and if the marker is not empty.
public AdapterTest(String name) { * This way, no test gets lost when regenerating after renaming.
// JUnitDoclet begin method AdapterTest * Method testVault is supposed to be empty.
super(name); */
// JUnitDoclet end method AdapterTest public void testVault() throws Exception {
} // JUnitDoclet begin method testcase.testVault
// JUnitDoclet end method testcase.testVault
public Adapter createInstance() throws Exception { }
// JUnitDoclet begin method testcase.createInstance
return new Adapter(); public static void main(String[] args) {
// JUnitDoclet end method testcase.createInstance // JUnitDoclet begin method testcase.main
} junit.textui.TestRunner.run(AdapterTest.class);
// JUnitDoclet end method testcase.main
protected void setUp() throws Exception { }
// JUnitDoclet begin method testcase.setUp }
super.setUp();
adapter = createInstance();
// JUnitDoclet end method testcase.setUp
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-11-2048.jpg)
![Tests are boring – let us autogenerate them!
public void testSetGetTimestamp() throws Exception {
// JUnitDoclet begin method setTimestamp getTimestamp
java.util.Calendar[] tests = {new GregorianCalendar(), null};
for (int i = 0; i < tests.length; i++) {
adapter.setTimestamp(tests[i]);
assertEquals(tests[i], adapter.getTimestamp());
}
// JUnitDoclet end method setTimestamp getTimestamp
}
public void testSetGetParam() throws Exception {
// JUnitDoclet begin method setParam getParam
String[] tests = {"a", "aaa", "---", "23121313", "", null};
for (int i = 0; i < tests.length; i++) {
adapter.setParam(tests[i]);
assertEquals(tests[i], adapter.getParam());
}
// JUnitDoclet end method setParam getParam
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-12-2048.jpg)

















![Testing two things at once
@DataProvider
public Object[][] data() {
return new Object[][] { {"48", true}, {"+48", true},
{"++48", true}, {"+48503", true}, {"+4", false},
{"++4", false}, {"", false},
{null, false}, {" ", false}, };
}
@Test(dataProvider = "data")
public void testQueryVerification(String query, boolean expected) {
assertEquals(expected, FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(query));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-34-2048.jpg)
![Testing two things at once
@DataProvider
public Object[][] data() {
return new Object[][] { {"48", true}, {"+48", true}, Data
{"++48", true}, {"+48503", true}, {"+4", false},
{"++4", false}, {"", false},
{null, false}, {" ", false}, };
}
@Test(dataProvider = "data") Algorithm / Logic
public void testQueryVerification(String query, boolean expected) {
assertEquals(expected, FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(query));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-35-2048.jpg)
![Testing two things at once
@DataProvider
public Object[][] data() {
return new Object[][] { {"48", true}, {"+48", true},
{"++48", true}, {"+48503", true}, {"+4", false},
{"++4", false}, {"", false},
{null, false}, {" ", false}, };
}
@Test(dataProvider = "data")
public void testQueryVerification(String query, boolean expected) {
assertEquals(expected, FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(query));
}
testQueryVerification1() {
assertEquals(true, FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(„48”));
}
testQueryVerification2() {
assertEquals(true, FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(„+48”));
}
testQueryVerification3() {
assertEquals(true, FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(„++48”));
}
testQueryVerification4() {
assertEquals(true, FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(„+48503”));
}
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-36-2048.jpg)
![Testing two things at once
@DataProvider
public Object[][] data() {
return new Object[][] { {"48", true}, {"+48", true},
{"++48", true}, {"+48503", true}, {"+4", false},
{"++4", false}, {"", false},
{null, false}, {" ", false}, };
}
@Test(dataProvider = "data")
public void testQueryVerification(String query, boolean expected) {
assertEquals(expected, FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(query));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-37-2048.jpg)
![Concentrate on one feature
@DataProvider
public Object[][] validQueries() {
return new Object[][] { {"48"}, {"48123"},
{"+48"}, {"++48"}, {"+48503"}};
}
@Test(dataProvider = "validQueries")
public void shouldRecognizeValidQueries(
String validQuery) {
assertTrue(FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(validQuery));
}
@DataProvider
public Object[][] invalidQueries() {
return new Object[][] {
{"+4"}, {"++4"},
{""}, {null}, {" "} };
}
@Test(dataProvider = "invalidQueries")
public void shouldRejectInvalidQueries(
String invalidQuery) {
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidQuery(invalidQuery));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-38-2048.jpg)






![Who the heck is “user_2” ?
@DataProvider
public static Object[][] usersPermissions() {
return new Object[][]{
{"user_1", Permission.READ},
{"user_1", Permission.WRITE},
{"user_1", Permission.REMOVE},
{"user_2", Permission.WRITE},
{"user_2", Permission.READ},
{"user_3", Permission.READ}
};
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-45-2048.jpg)
![Ah, logged user can read and write...
@DataProvider
public static Object[][] usersPermissions() {
return new Object[][]{
{ADMIN, Permission.READ},
{ADMIN, Permission.WRITE},
{ADMIN, Permission.REMOVE},
{LOGGED, Permission.WRITE},
{LOGGED, Permission.READ},
{GUEST, Permission.READ}
};
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-46-2048.jpg)




![What is really important?
@DataProvider
public Object[][] snapshotArtifacts() {
return new Object[][]{
{"a", "b", "2.2-SNAPSHOT", Artifact.JAR },
{"c", "d", "2.2.4.6-SNAPSHOT", Artifact.JAR},
{"e", "f", "2-SNAPSHOT", Artifact.JAR}
};
}
@Test(dataProvider = "snapshotArtifacts")
public void shouldRecognizeSnapshots(
String groupId, String artifactId,
String version, Type type) {
Artifact artifact
= new Artifact(groupId, artifactId, version, type);
assertThat(artifact.isSnapshot()).isTrue();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-51-2048.jpg)
![Only version matters
@DataProvider
public Object[][] snapshotVersions() {
return new Object[][]{
{"2.2-SNAPSHOT"},
{"2.2.4.6-SNAPSHOT"},
{"2-SNAPSHOT"}
};
}
@Test(dataProvider = "snapshotVersions")
public void shouldRecognizeSnapshots(String version) {
Artifact artifact
= new Artifact(VALID_GROUP, VALID_ARTIFACT_ID,
version, VALID_TYPE);
assertThat(artifact.isSnapshot()).isTrue();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-52-2048.jpg)










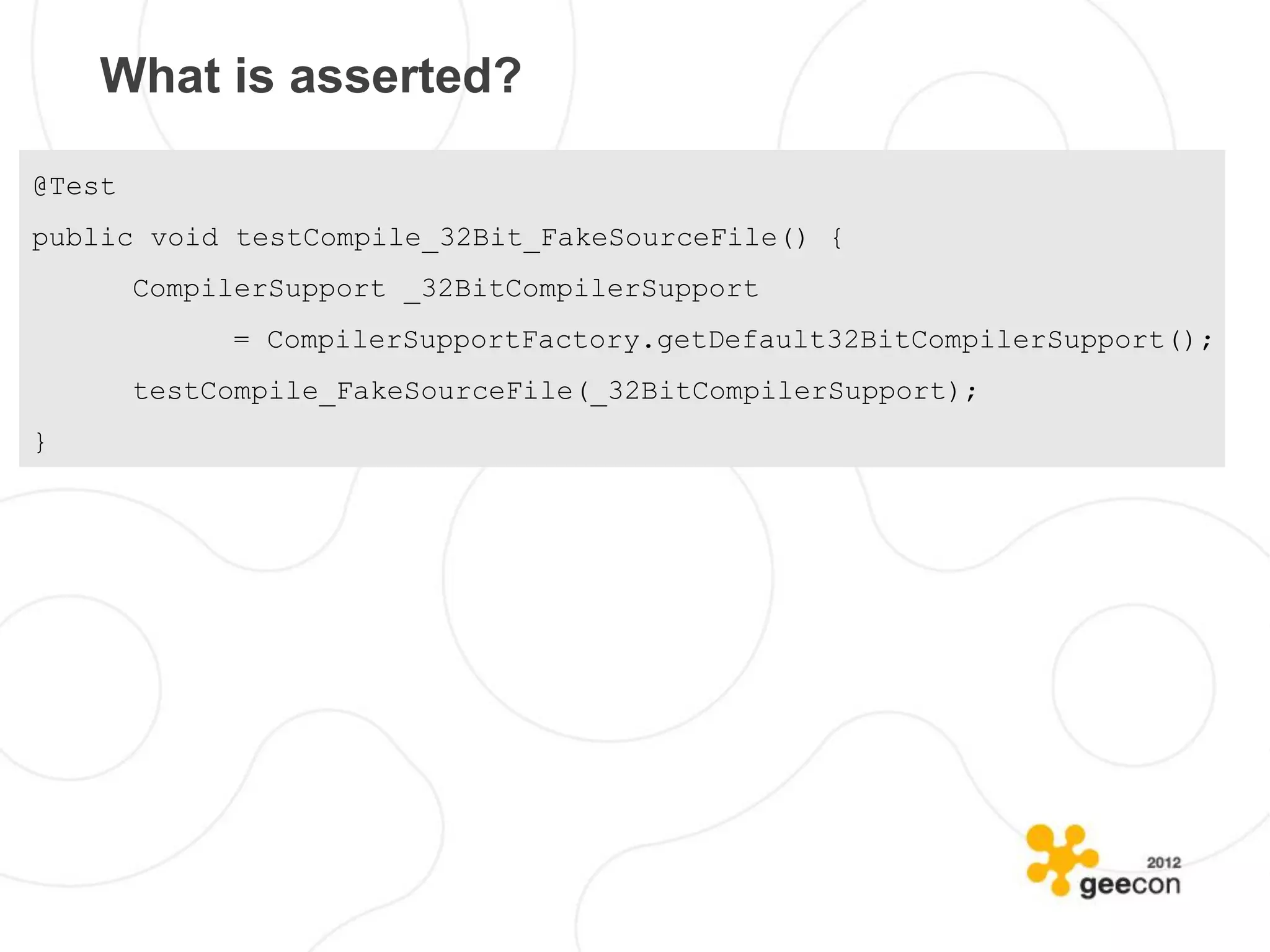
![What is asserted?
@Test
public void testCompile_32Bit_FakeSourceFile() {
CompilerSupport _32BitCompilerSupport
= CompilerSupportFactory.getDefault32BitCompilerSupport();
testCompile_FakeSourceFile(_32BitCompilerSupport);
}
private void testCompile_FakeSourceFile(
CompilerSupport compilerSupport) {
compiledFiles
= compilerSupport.compile(new File[] { new File("fake") });
assertThat(compiledFiles, is(emptyArray()));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-66-2048.jpg)












![Doing it wrong
public void myTest() {
SomeObject obj = new SomeObject(
a, b, c, productCode());
// testing of obj here
}
private String productCode(){
String[] codes = {"Code A", "Code B",
"Code C", "Code D"};
int index = rand.nextInt(codes.length);
return codes[index];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-80-2048.jpg)





![Always TDD?
For six or eight hours spread over the next few weeks I
struggled to get the first test written and running. Writing
tests for Eclipse plug-ins is not trivial, so it’s not
surprising I had some trouble. [...] In six or eight hours
of solid programming time, I can still make significant
progress. If I’d just written some stuff and verified it by
hand, I would probably have the final answer to whether
my idea is actually worth money by now. Instead, all I
have is a complicated test that doesn’t work, a pile
of frustration, eight fewer hours in my life, and the
motivation to write another essay.
Ken Beck, Just Ship, Baby](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012geeconkaczanowskibadtestsgoodtests-120520141949-phpapp02/75/GeeCON-2012-Bad-Tests-Good-Tests-86-2048.jpg)