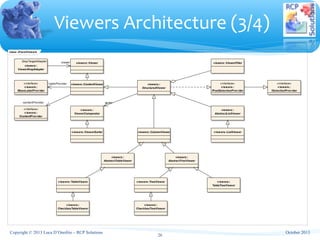
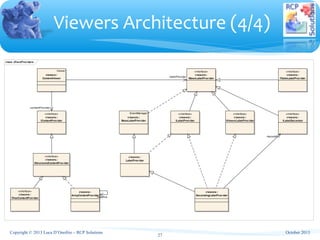
The document outlines a training course on Eclipse SWT (Standard Widget Toolkit) and JFace, focusing on Java-based user interface development. It covers essential topics including widget layouts, event handling, widget classes, and the model-view-controller architecture pattern, emphasizing the integration of complex object-oriented data into SWT. The material provides detailed descriptions of listener interfaces, widget hierarchy, and various components while also suggesting best practices for using SWT effectively.







![Main Methods
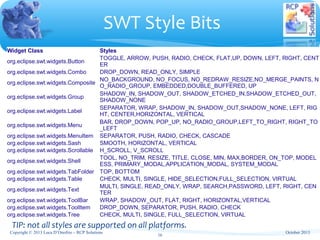
void addListener(int eventType, Listener listener)
Adds the listener to the collection of listeners who will be notified when an event of the given type occurs.
void dispose()
Disposes of the operating system resources associated with the receiver and all its descendants.
Object getData(String key)
Returns the application defined property of the receiver with the specified name, or null if it has not been set.
Display getDisplay()
Returns the Display that is associated with the receiver.
Listener[] getListeners(int eventType)
Returns an array of listeners who will be notified when an event of the given type occurs.
int getStyle()
Returns the receiver's style information.
boolean isDisposed()
Returns true if the widget has been disposed, and false otherwise.
boolean isListening(int eventType)
Returns true if there are any listeners for the specified event type associated with the receiver, and false otherwise.
void notifyListeners(int eventType, Event event)
Notifies all of the receiver's listeners for events of the given type that one such event has occurred by invoking their
handleEvent() method.
void removeListener(int eventType, Listener listener)
Removes the listener from the collection of listeners who will be notified when an event of the given type occurs.
protected
void
removeListener(int eventType, org.eclipse.swt.internal.SWTEventListener listener)
Removes the listener from the collection of listeners who will be notified when an event of the given type occurs.
void setData(Object data)
Sets the application defined widget data associated with the receiver to be the argument.
void setData(String key, Object value)
Sets the application defined property of the receiver with the specified name to the given value.
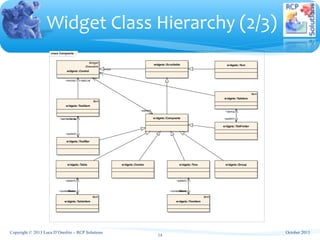
Widget Class Hierarchy (3/3)
15
October 2013Copyright © 2013 Luca D’Onofrio – RCP Solutions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-et-swtjface-131006094219-phpapp01/85/Eclipse-Training-SWT-JFace-15-320.jpg)