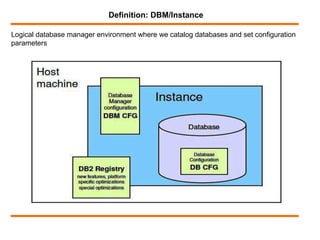
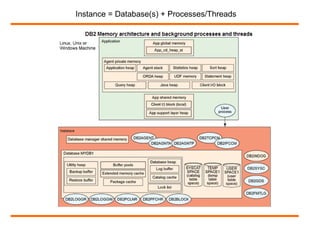
DB2 is a database manager that runs on Linux, Unix, and Windows operating systems. It allows users to catalog databases, start and stop instances, and configure parameters. Key commands for managing DB2 include db2icrt for creating instances, db2idrop for dropping instances, db2ilist for listing instances, and db2set for setting configuration parameters at the global, instance, and node level. The db2set command provides centralized control over environmental variables.








![$ db2 get instance
$ db2 ? get dbm cfg
GET DATABASE MANAGER CONFIGURATION [SHOW DETAIL]
$ db2 get dbm cfg
$ db2 get dbm cfg | grep NUMDB
$ db2 update dbm cfg using NUMDB 10
$ db2 attach to db2inst1
$ db2 get dbm cfg show detail
$ db2 reset dbm cfg
DBM CONFIGURATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2db2instancecreation-150707100835-lva1-app6892/85/2-db2-instance-creation-15-320.jpg)
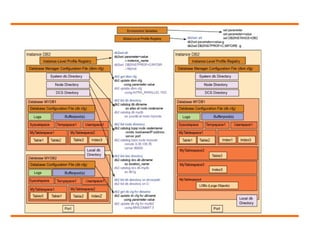
![IBM DB2 profile registry command
Allows for centralized control of environmental variables
4 Profile registries:
- Instance level profile registry [i] (~/sqllib/profile.env)
- Global level profile registry [g] (/var/db2/global.reg)
- Instance node level profile registry [n] (~/sqllib/nodes/node_number.env)
- Instance profile registry (/var/db2/global.reg)
db2set ?
db2set -lr
db2set
db2set registry_variable_name
db2set registry_variable_name=
db2set registry_variable_name=new_value
db2set registry_variable_name=new_value -i instance_name
db2set registry_variable_name=new_value -g
db2set registry_variable_name=new_value -i instance_name node_number
db2set -r registry_variable_name
db2set -r registry_variable_name node_number](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2db2instancecreation-150707100835-lva1-app6892/85/2-db2-instance-creation-17-320.jpg)


