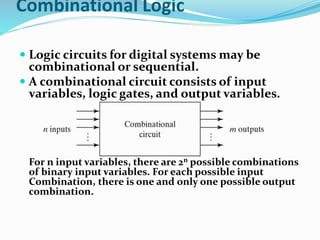
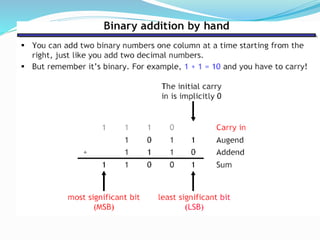
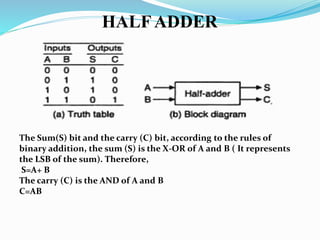
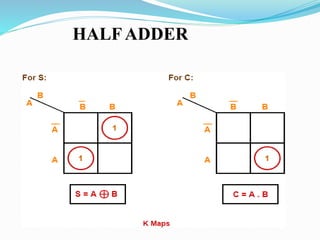
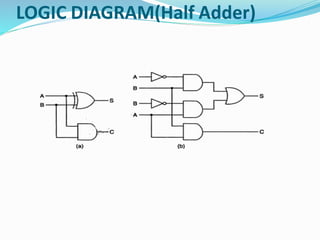
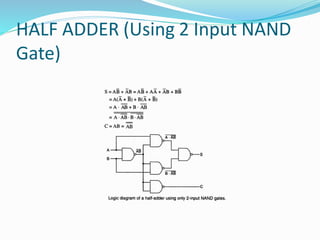
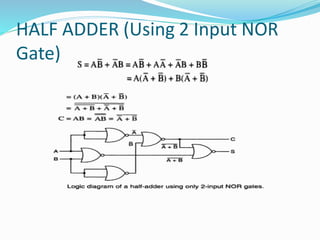
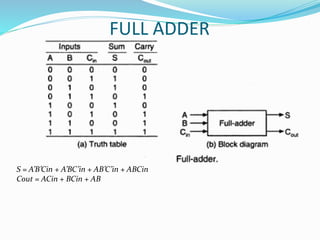
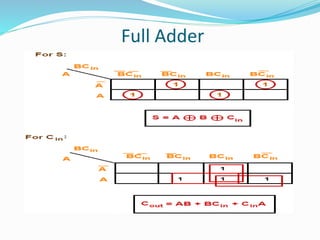
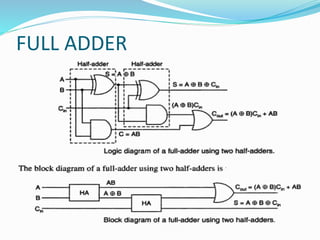
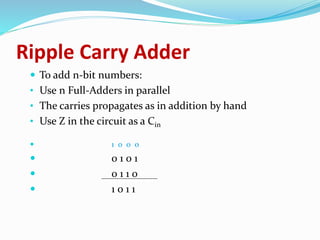
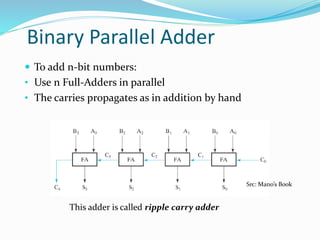
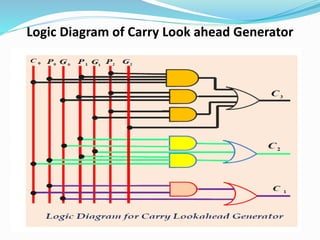
The document discusses combinational logic circuits and different types of adders. It begins by defining combinational circuits and describing their characteristics. It then explains half adders and full adders. A half adder can add two bits but cannot account for carry bits from previous additions. A full adder can add two bits and an additional carry bit. The document discusses implementing full adders using logic gates. It also describes how multiple full adders can be used in parallel in a ripple carry adder or carry lookahead adder to add multiple bit numbers.