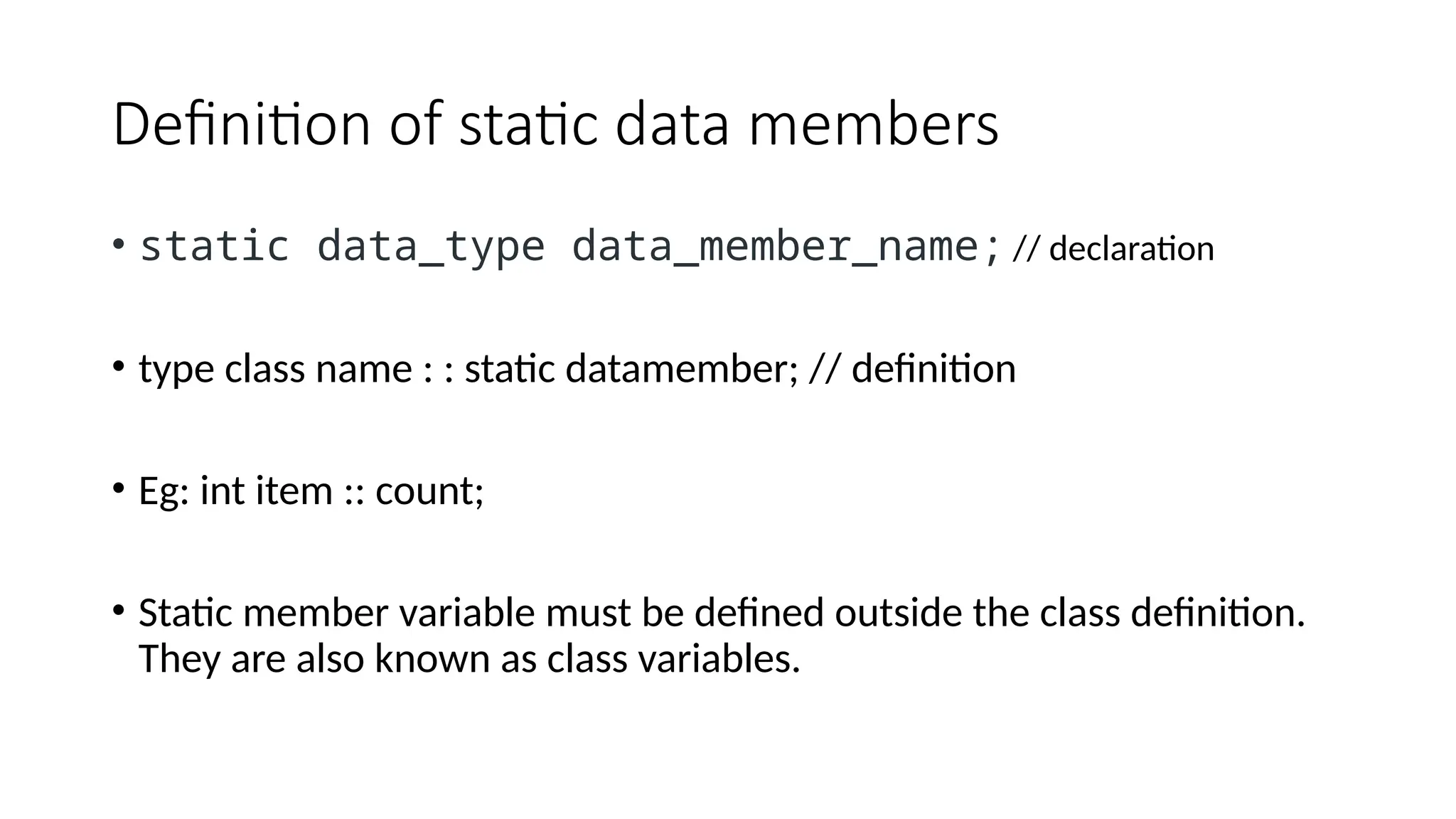
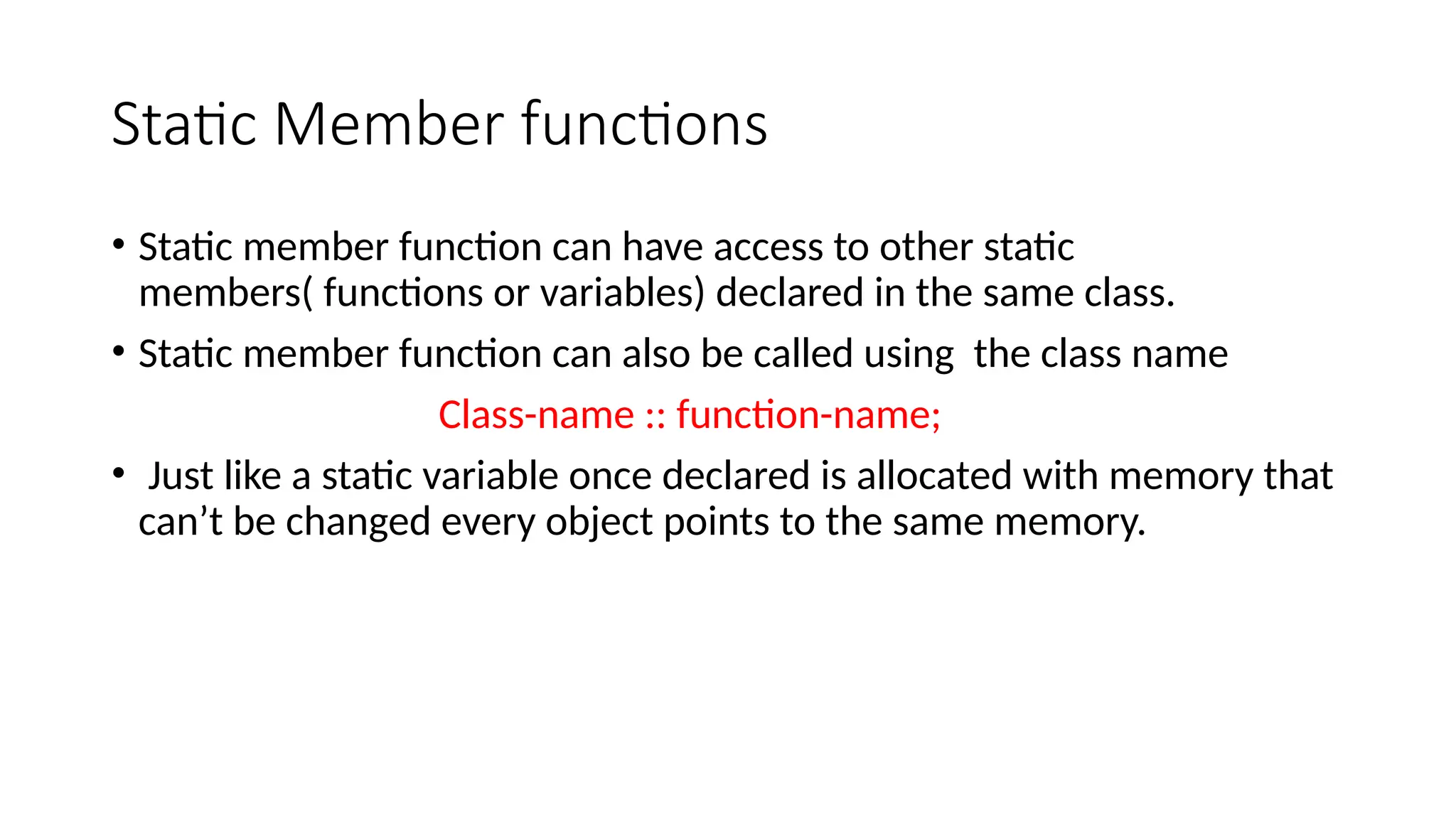
Static data members in C++ are shared across all objects of a class, initialized to zero upon class instantiation, and maintain values common to the class. They must be declared within the class and defined outside of it, functioning as class variables. Static member functions can access static members and are invoked using the class name.