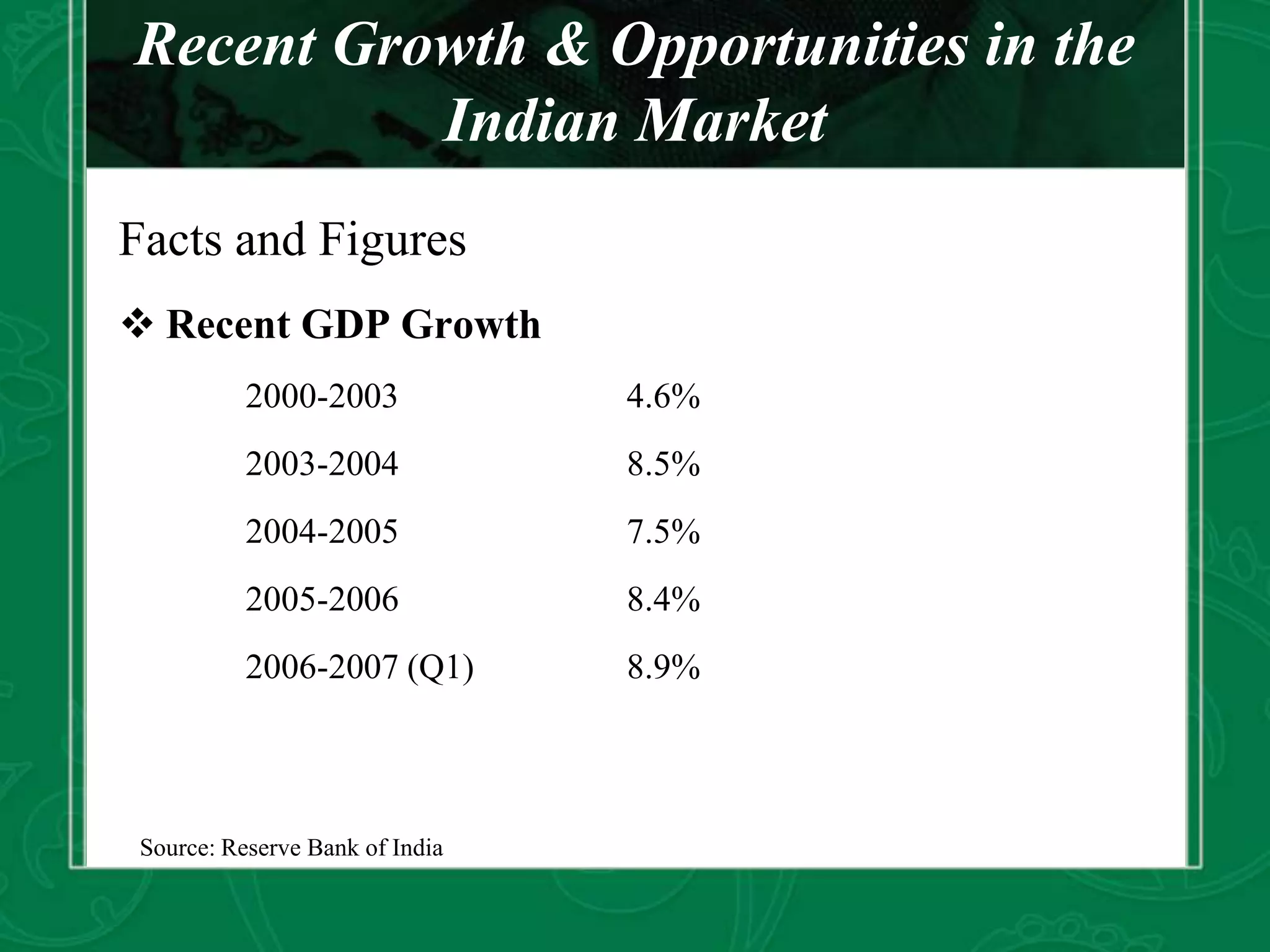
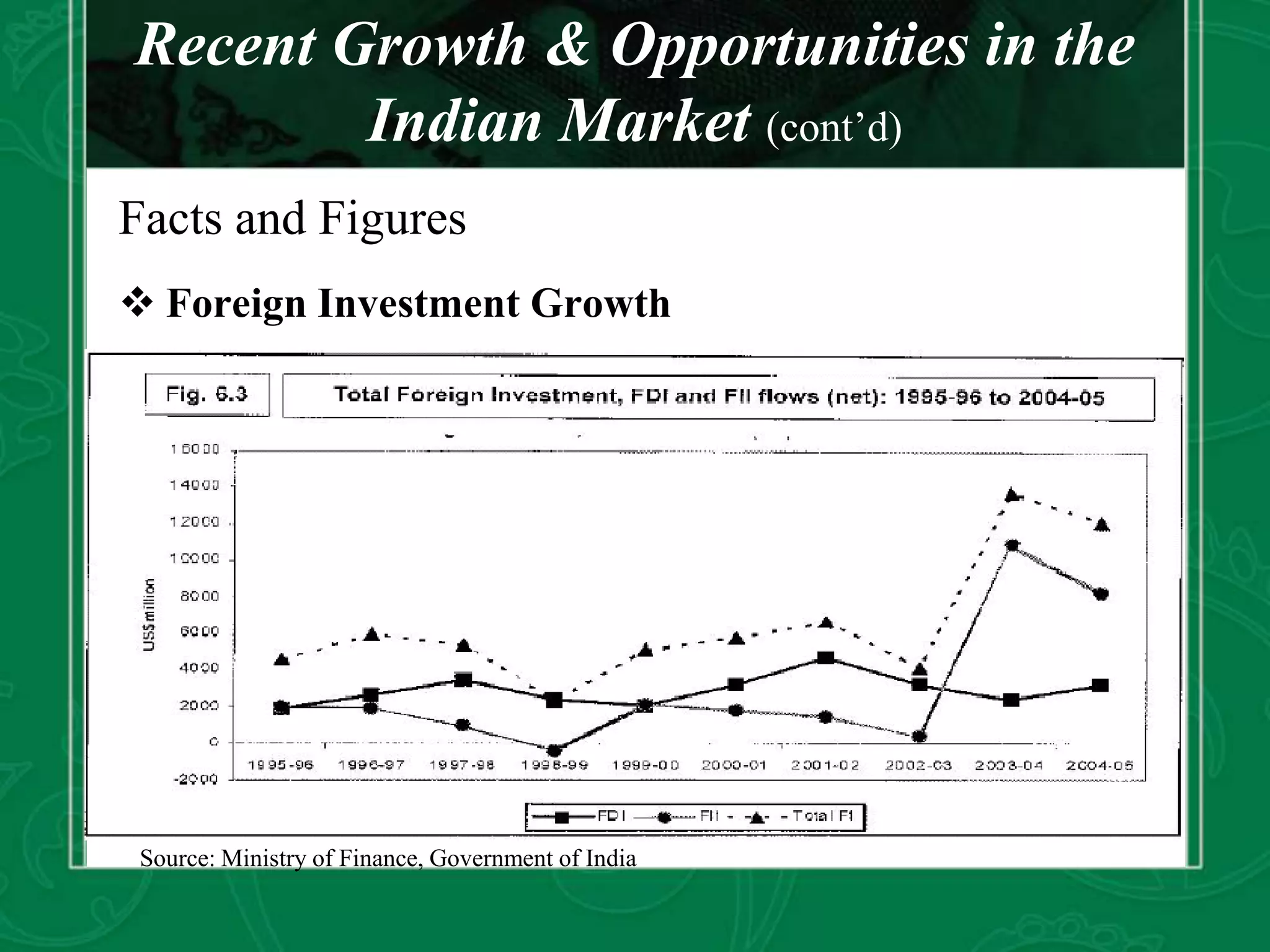
This document summarizes foreign investment opportunities and regulations in India. It outlines three main routes for foreign investment: foreign direct investment (FDI), investment as a foreign institutional investor (FII), and as a foreign venture capital investor (FVCI). FDI can be through the automatic route for smaller investments or the approval route for larger investments. FIIs and FVCs must register and meet qualifications. Infrastructure development, especially power and transportation, is emphasized as a focus area given India's projected growth and need for investment. Overall foreign investment in India is growing significantly across many sectors.