This document discusses timers, effects, and animations in JavaScript and jQuery. It covers the setTimeout(), setInterval(), and clearTimeout()/clearInterval() methods for running code based on time elements. It also covers various jQuery effects methods like show(), hide(), fadeIn(), fadeOut() etc. and how to chain and queue animations. It provides examples of using timers, effects, and custom animations using the animate() method.




![5
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var begin=setInterval('changeBanner()',2000);
var curBanner="cycle1";
});
function changeBanner()
{
if (curBanner == "cycle2")
{
document.images[0].src = "v500tec.gif";
curBanner = "cycle1";
}
else {
document.images[0].src = "showroom.gif";
curBanner = "cycle2";
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<p><img src="v500tec.gif" height="90px" width="700px"
alt="Banner images" /></p>
</body>
</html>
setInterval -continuous
CD
var variable = setInterval("code", millisecondsToRepeat);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14709302-220601081431-4d7d624b/85/14709302-ppt-5-320.jpg)


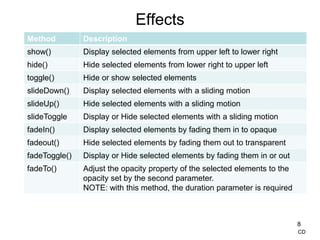
![Effects
• For all methods except fadeTo(), the primary parameter is the
duration parameter that determines how long the effect will take
– If duration is 5000, the element will be faded out over 5 seconds
– If duration is omitted, the effect occurs immediately – no animation
• Basic syntax for all methods except fadeTo() is:
– methodName([duration], [callback function])
• Basic syntax for fadeTo() is:
– methodName(duration, opacity [,callback function])
• Duration: can be ‘fast’, ‘slow’ or time in milliseconds
• Opacity: 0 through 1
• Callback function: called after the method finishes
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14709302-220601081431-4d7d624b/85/14709302-ppt-9-320.jpg)
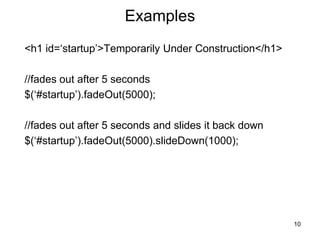



![SlideShow
$(document).ready(function() {
// create an array of the slide images
var imageCache = new Array();
imageCache[0] = 'images/casting1.jpg';
imageCache[1] = 'images/casting2.jpg';
imageCache[2] = 'images/catchrelease.jpg';
imageCache[3] = 'images/fish.jpg';
imageCache[4] = 'images/fish.jpg';
var imageTitle = new Array();
imageTitle[0]='Casting on the Upper Kings';
imageTitle[1]='Casting on the Lower Kings';
imageTitle[2]='Catch and Release on the Big Horn';
imageTitle[3]='Catching on the South Fork';
imageTitle[4]='The Lures for Catching';
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14709302-220601081431-4d7d624b/85/14709302-ppt-14-320.jpg)
![SlideShow
// start slide show
var imageCounter = 0;
var nextImage;
var timer = setInterval( function () {
$("#caption").fadeOut(1000);
$("#slide").fadeOut(1000,function() {
imageCounter = (imageCounter + 1) % imageCache.length;
nextImage = imageCache[imageCounter];
nextTitle = imageTitle[imageCounter];
$("#slide").attr("src", nextImage).fadeIn(1000);
$("#caption").text(nextTitle).fadeIn(1000);
}
);
},
3000);
})
15
CD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14709302-220601081431-4d7d624b/85/14709302-ppt-15-320.jpg)

![Custom effects - Animations
• The animate() function lets you animate any CSS
property that accepts numeric values
– Requires a very good understanding of CSS 3
• Basic syntax:
animate({properties}[,duration][,callback function]);
Properties map: CSS that goes inside the curly braces
consists of name:value pairs (its CSS)
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14709302-220601081431-4d7d624b/85/14709302-ppt-17-320.jpg)







![Stopping Animations
• Stops animation or effect before it finishes
– Useful for slideshows, advertisements
• Syntax:
$(selector).stop([clearQueue][,jumpToEnd]);
– clearQueue indicates whether also the animation queue should
be cleared or not
• default is false, only the active animation will be stopped
• any queued animations will still be performed
– jumpToEnd indicates whether or not to complete the current
animation immediately
• default is false
27
CD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14709302-220601081431-4d7d624b/85/14709302-ppt-27-320.jpg)


![Easing
• Syntax for all effects except fadeTo()
– methodName([duration][,easing][,callback])
• Syntax for fadeTo()
– methodName(duration,opacity,[,easing][,callback])
• Syntax for basic animate
– animate({properties}[,duration][,easing][,callback])
30
CD
https://matthewlein.com/experiments/easing.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14709302-220601081431-4d7d624b/85/14709302-ppt-30-320.jpg)