This document discusses defining classes in C#, including defining simple classes, access modifiers, using classes and objects, and constructors.
It begins by explaining that classes model real-world objects and define attributes like properties and fields to represent state, as well as behaviors like methods to represent operations. It then discusses defining simple classes in C#, including class declarations, inherited classes or implemented interfaces, fields, constructors, properties, and methods.
The document also covers access modifiers like public, private, protected, and internal and how they restrict access to class members. It provides an example of defining a Dog class to demonstrate these concepts. Finally, it discusses using classes by creating instances, accessing properties and invoking methods, and defining






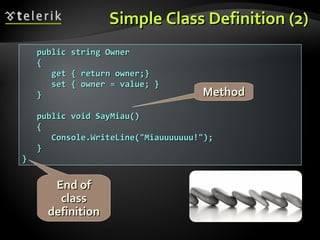





























![Static Members – ExampleStatic Members – Example
static class SqrtPrecalculatedstatic class SqrtPrecalculated
{{
public const int MAX_VALUE = 10000;public const int MAX_VALUE = 10000;
// Static field// Static field
private static int[] sqrtValues;private static int[] sqrtValues;
// Static constructor// Static constructor
static SqrtPrecalculated()static SqrtPrecalculated()
{{
sqrtValues = new int[MAX_VALUE + 1];sqrtValues = new int[MAX_VALUE + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < sqrtValues.Length; i++)for (int i = 0; i < sqrtValues.Length; i++)
{{
sqrtValues[i] = (int)Math.Sqrt(i);sqrtValues[i] = (int)Math.Sqrt(i);
}}
}}
(example continues)(example continues)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-defining-classes-110627100154-phpapp01-140828073446-phpapp01/85/14-Defining-classes-38-320.jpg)
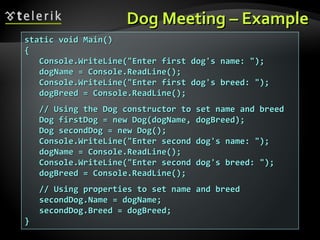
![Static Members – Example (2)Static Members – Example (2)
// Static method// Static method
public static int GetSqrt(int value)public static int GetSqrt(int value)
{{
return sqrtValues[value];return sqrtValues[value];
}}
}}
class SqrtTestclass SqrtTest
{{
static void Main()static void Main()
{{
Console.WriteLine(SqrtPrecalculated.GetSqrt(254));Console.WriteLine(SqrtPrecalculated.GetSqrt(254));
// Result: 15// Result: 15
}}
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-defining-classes-110627100154-phpapp01-140828073446-phpapp01/85/14-Defining-classes-39-320.jpg)