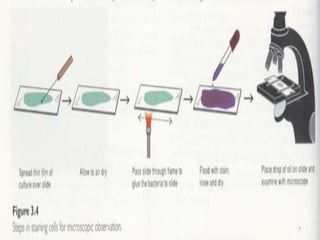
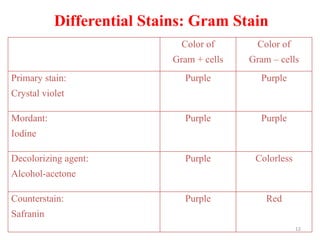
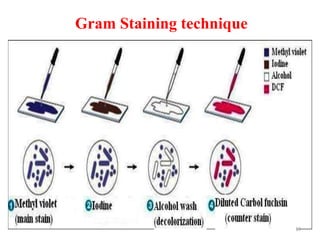
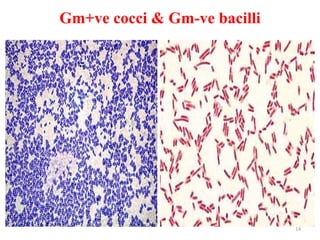
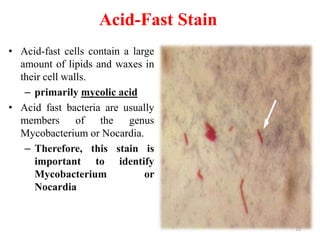
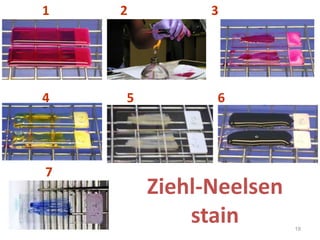
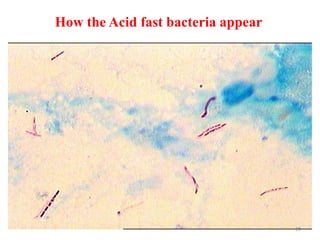
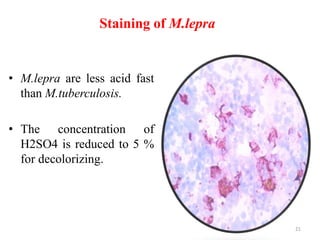
This document discusses different staining techniques used to visualize microbes under a microscope. Staining adds color to microbes, making them more visible. Simple stains use a single dye, while differential stains use multiple dyes to distinguish cell types. Gram staining differentiates bacteria based on cell wall composition, yielding purple Gram-positive and pink Gram-negative cells. Acid-fast staining targets mycobacteria, leaving them stained red after decolorization due to their waxy cell walls. Ziehl-Neelsen staining is commonly used to identify tuberculosis bacteria. Differential staining techniques provide structural and classification information not discernible from unstained microbes.