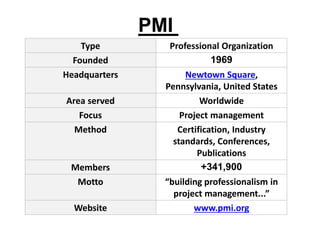
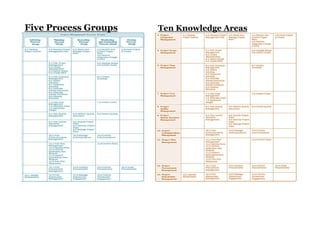
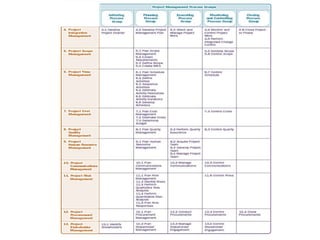
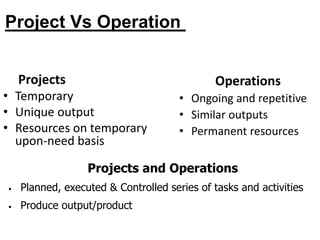
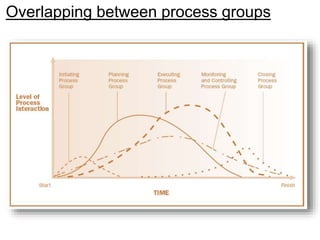
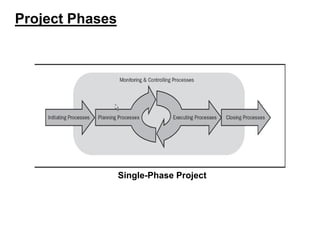
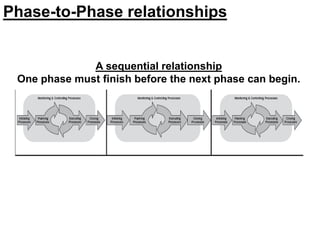
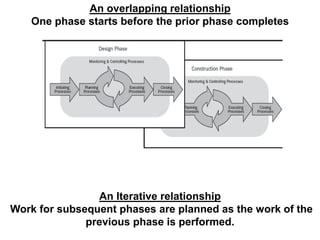
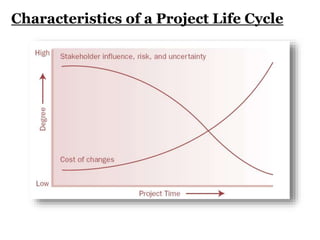
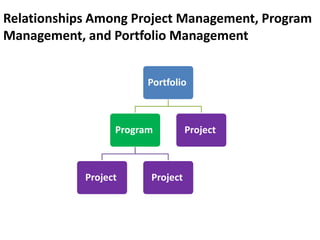
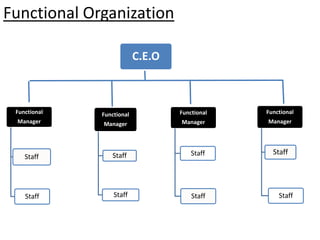
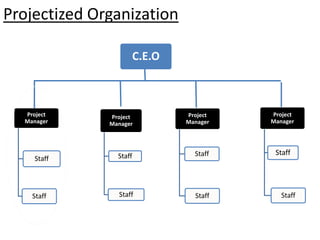
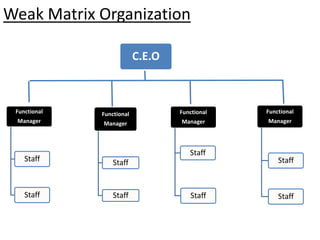
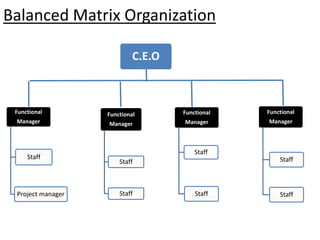
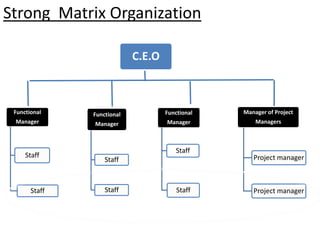
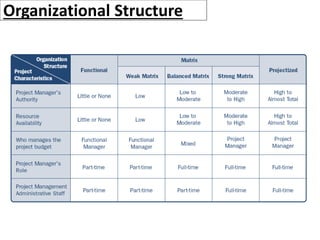
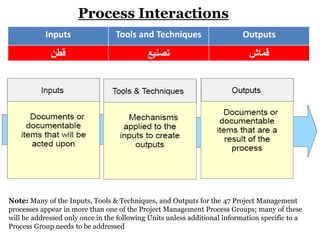
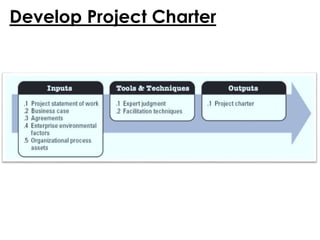
This document provides an overview of project management certification through the Project Management Institute (PMI). It discusses that PMI provides the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) as a global standard for managing projects. To become PMP certified, candidates must meet experience requirements, complete project management education hours, and pass the PMP exam. The exam tests knowledge across the 10 project management knowledge areas and 5 process groups outlined in PMBOK. Finally, the document summarizes key aspects of project vs operations management and organizational structures that support project management.