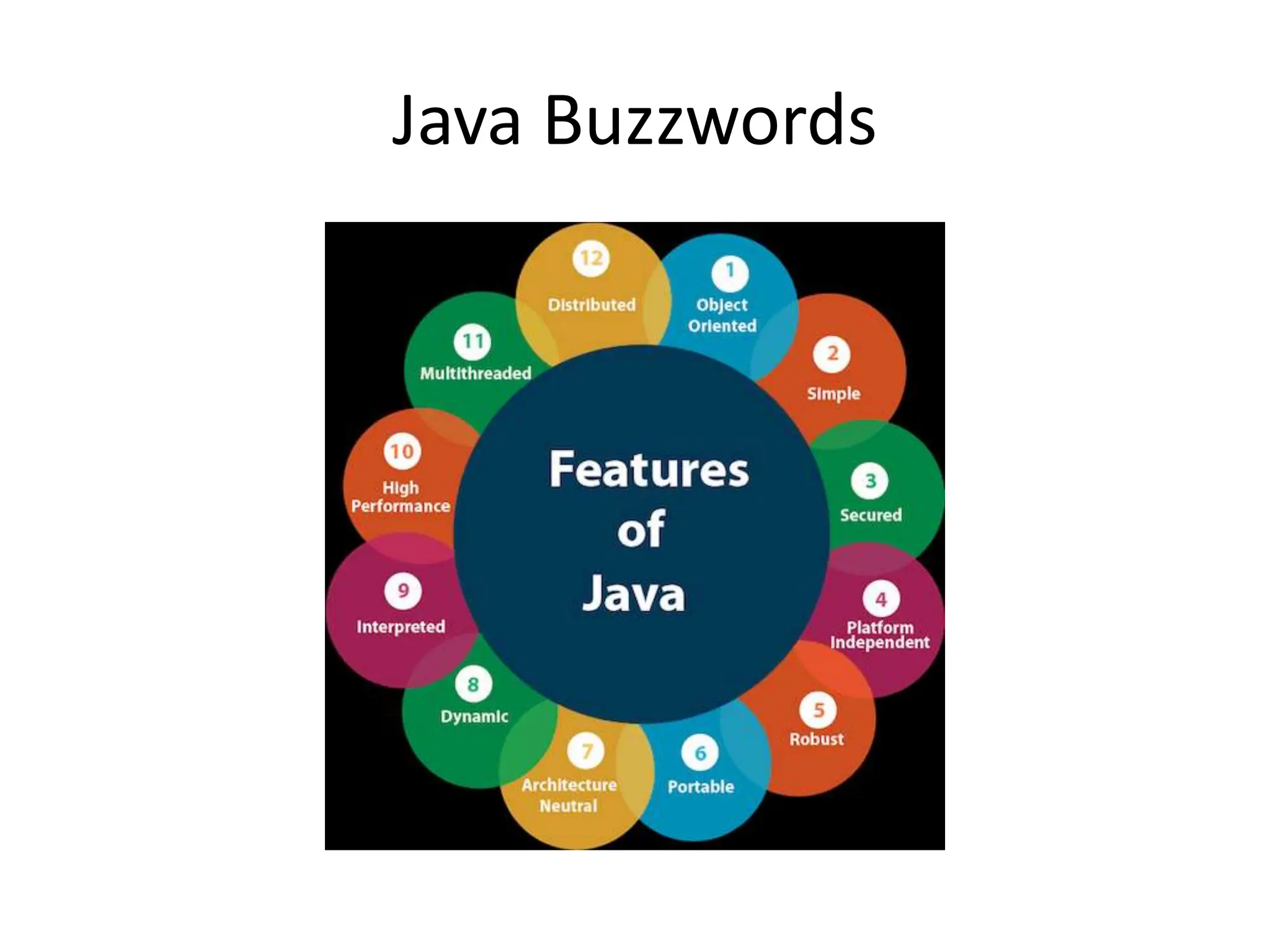
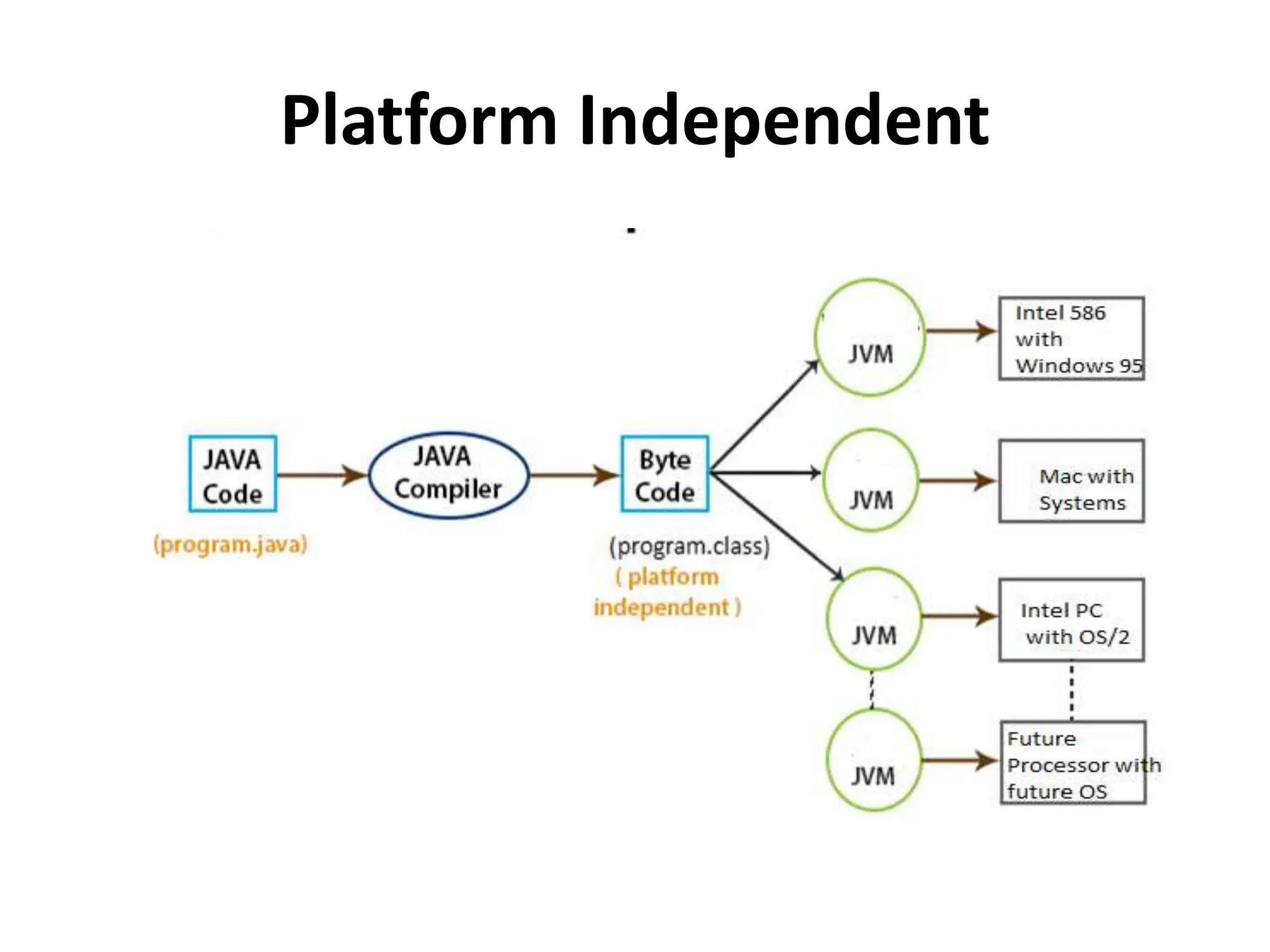
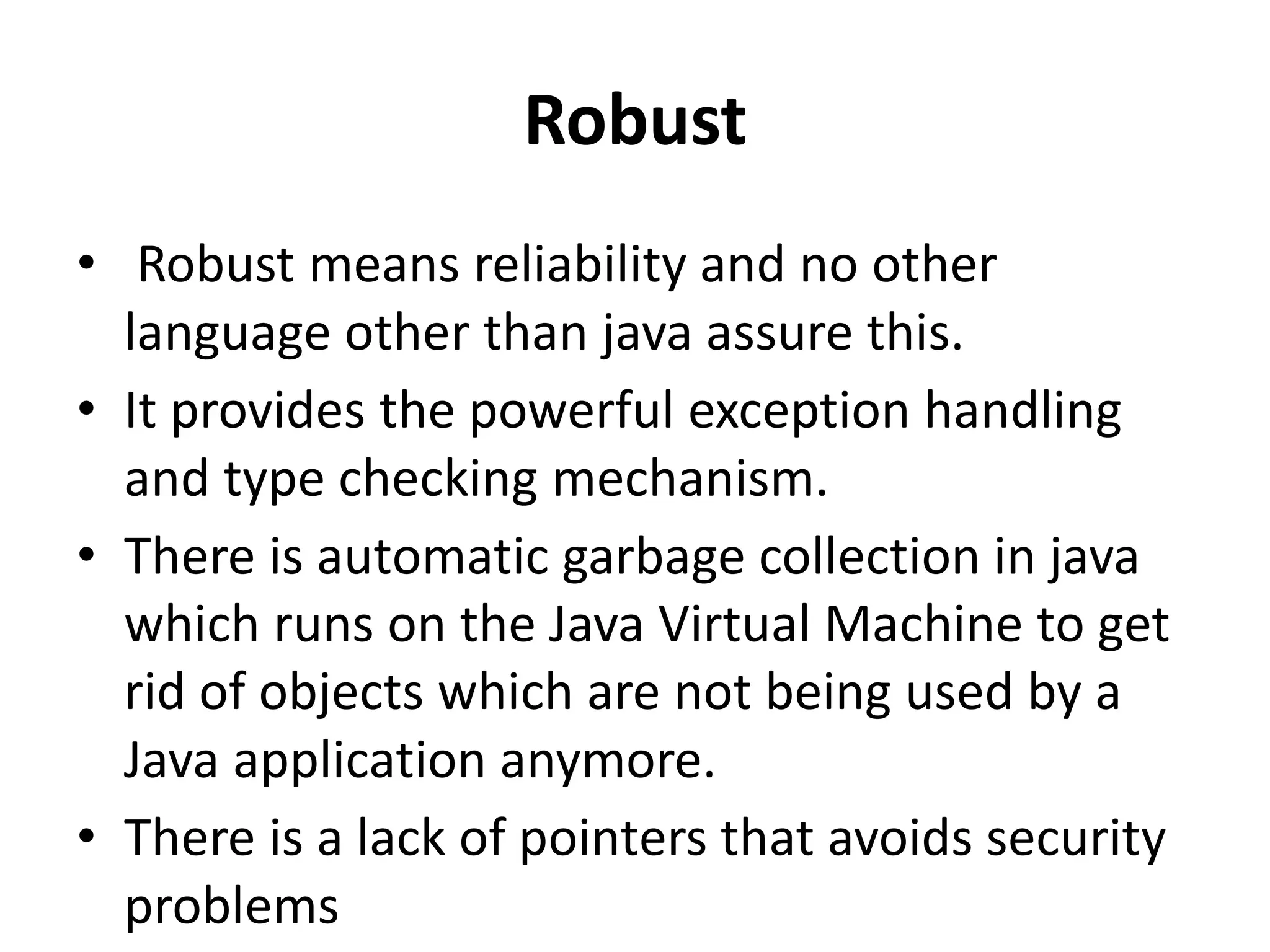
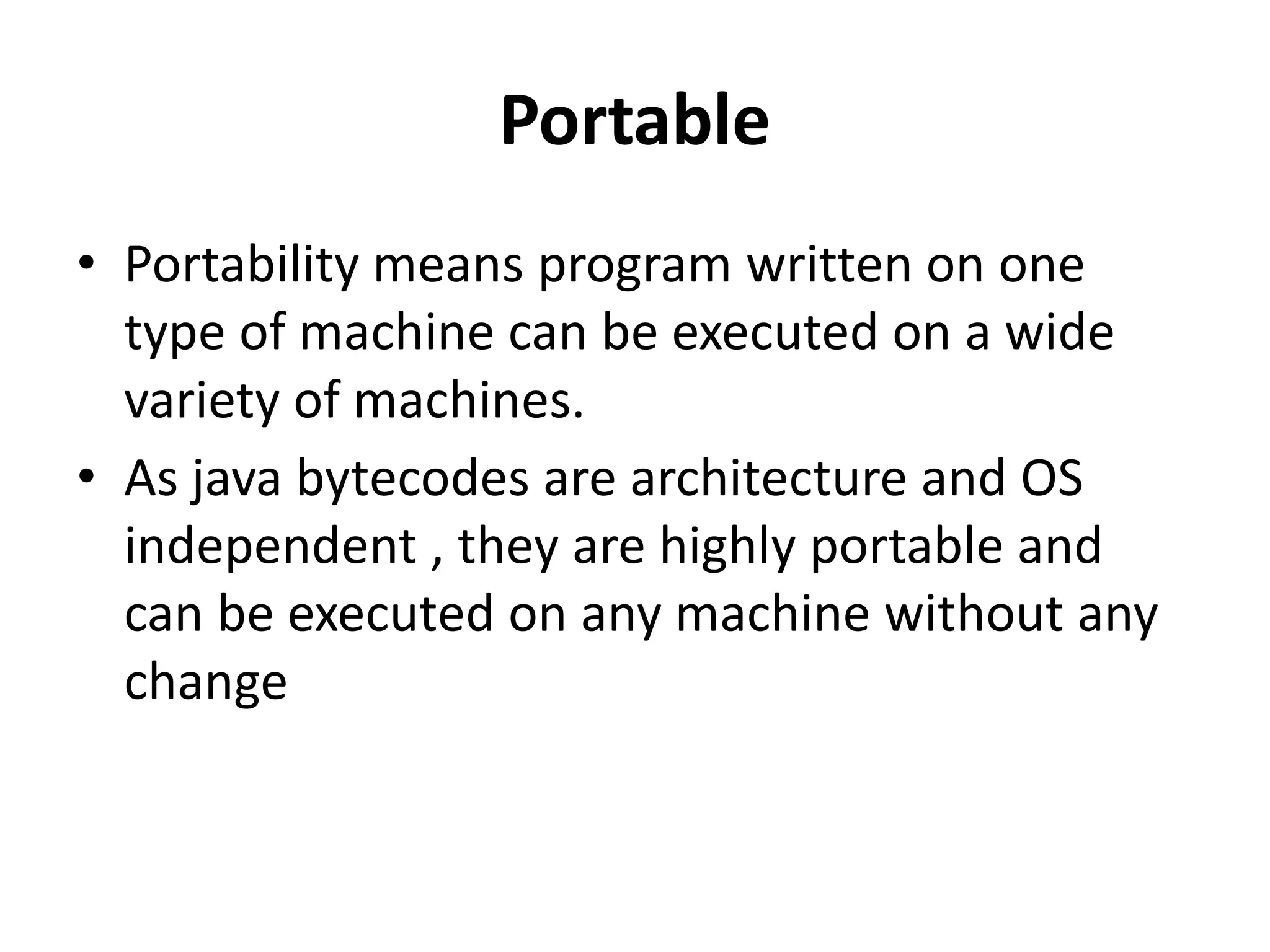
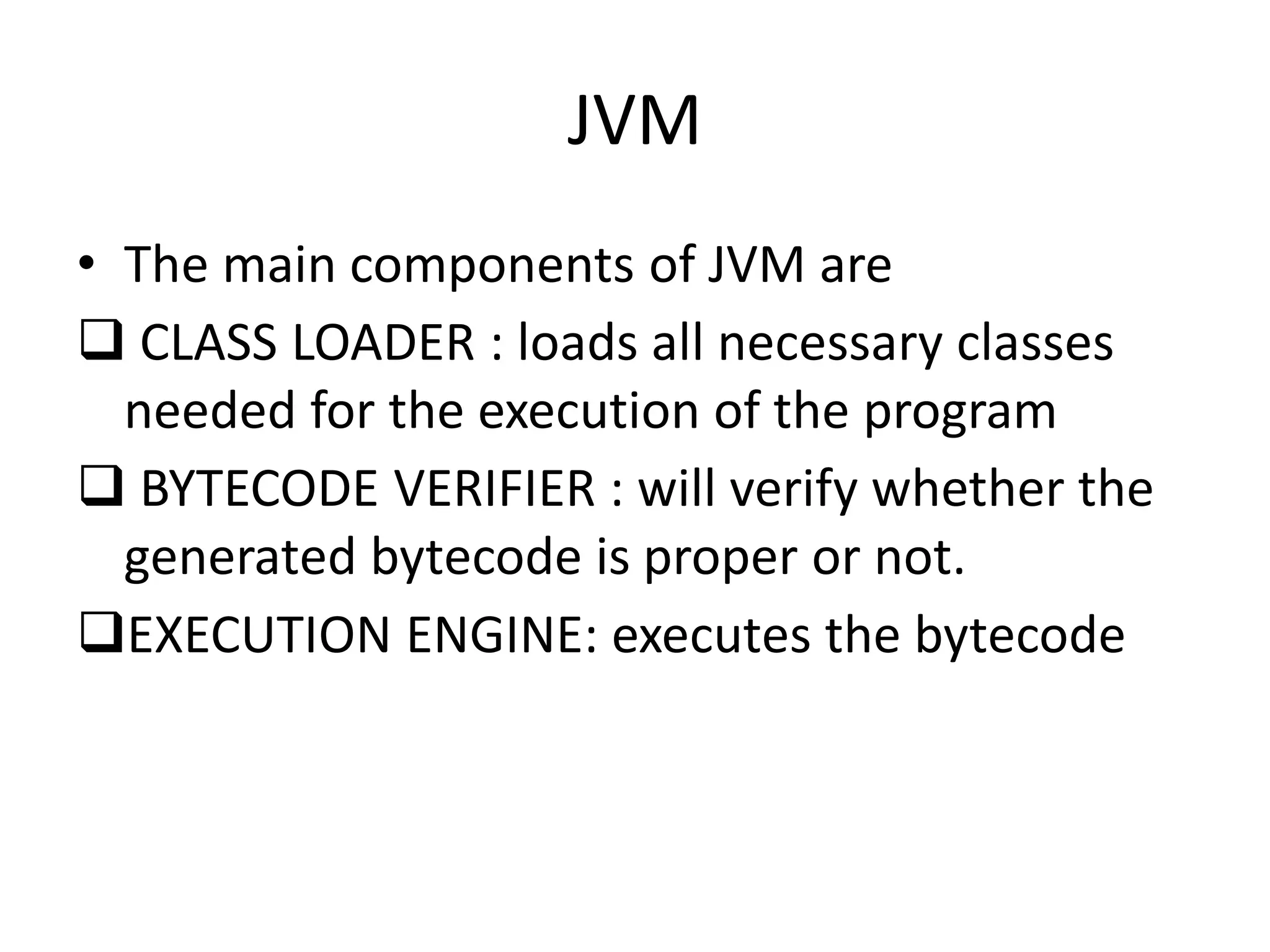
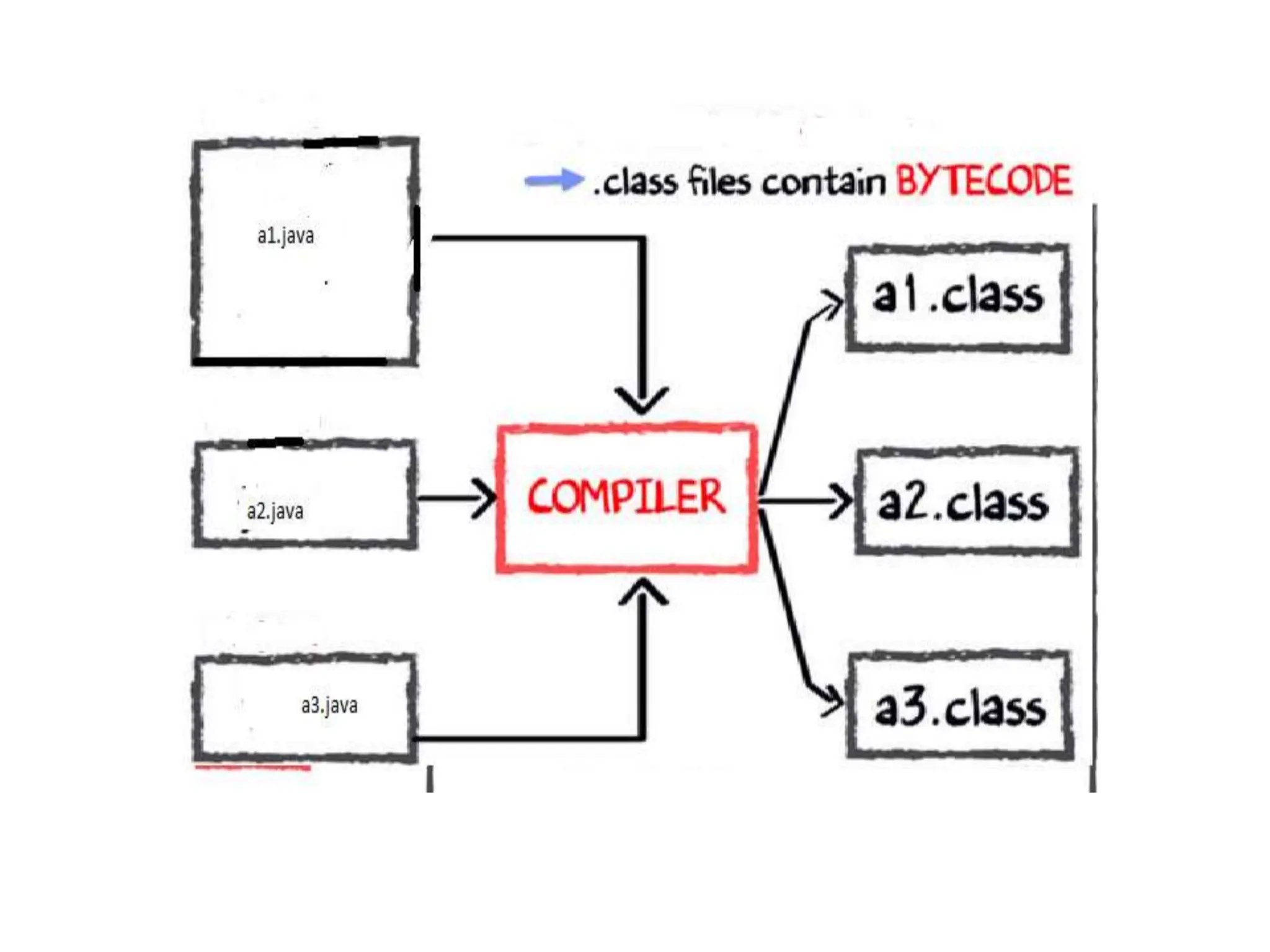
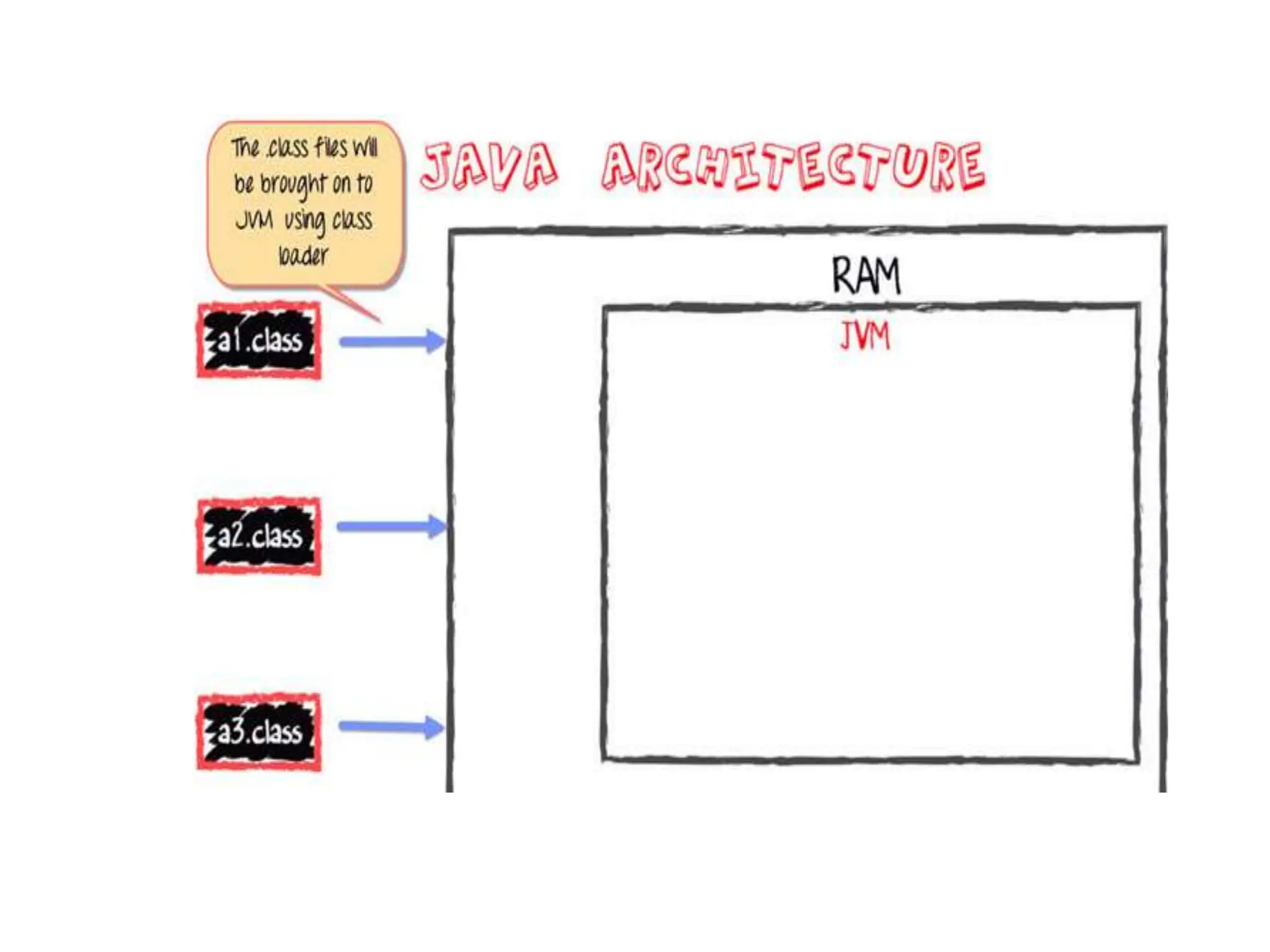
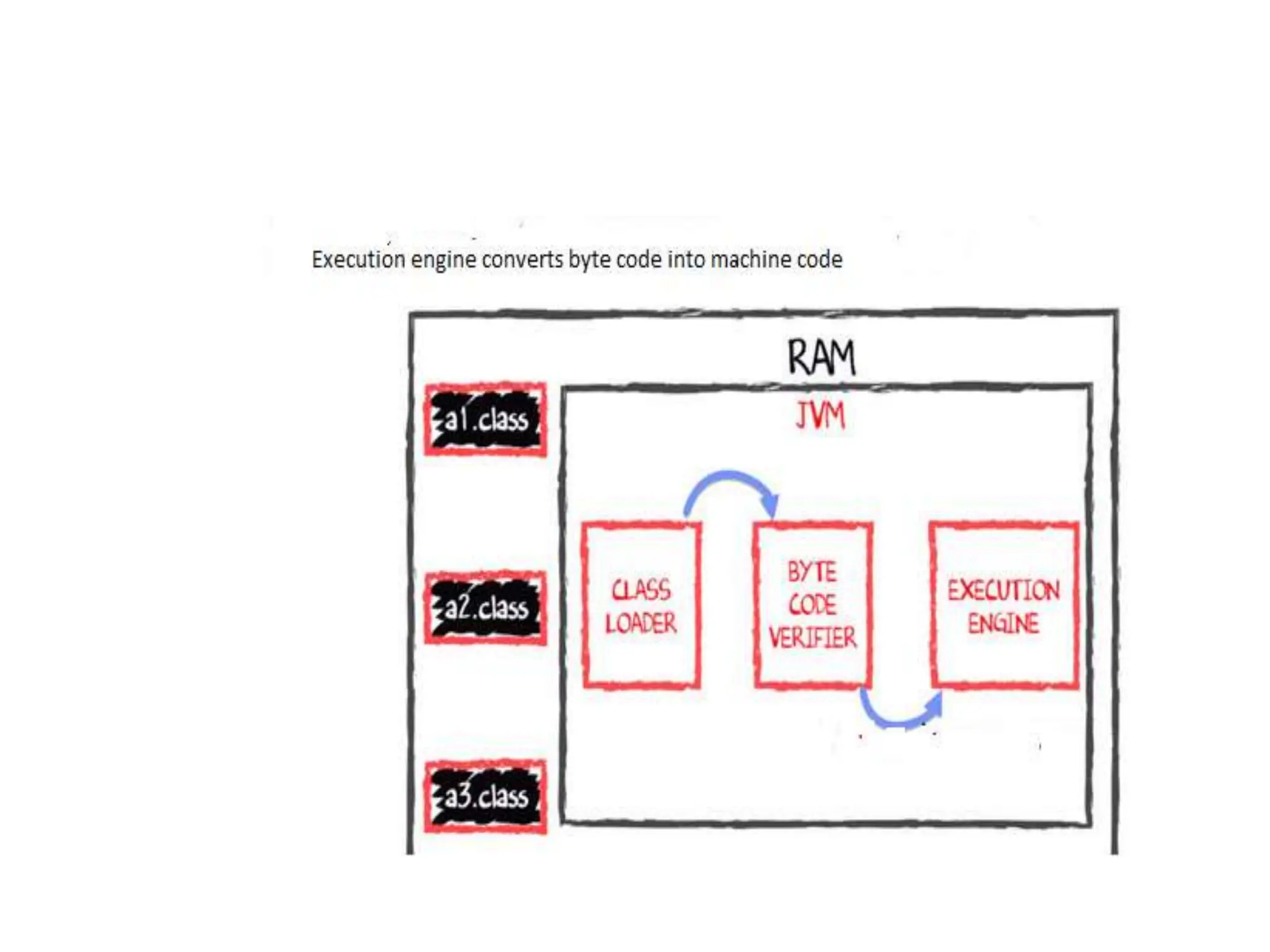
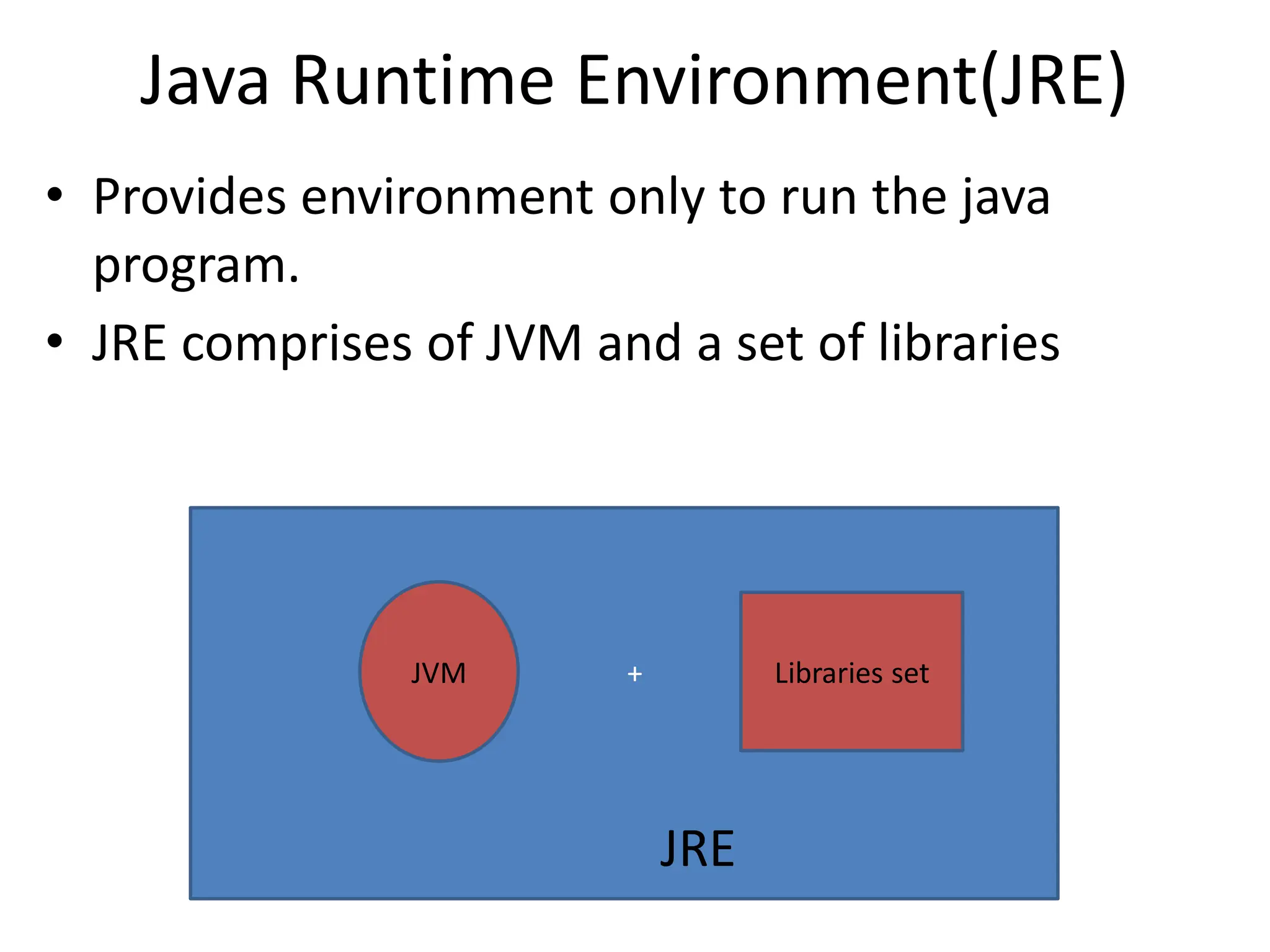
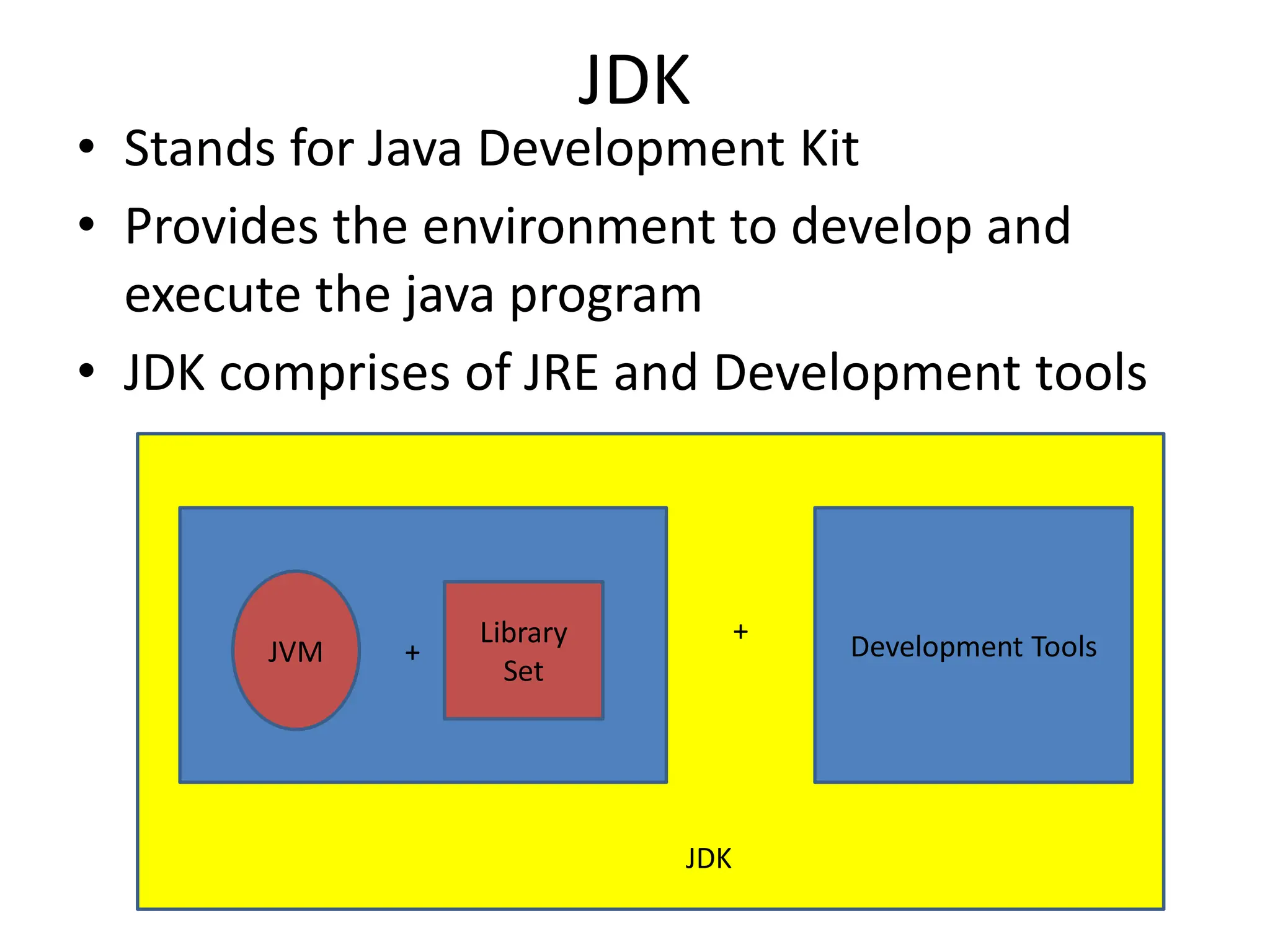
The document provides an overview of the Java programming language. It discusses that Java was created by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems in 1995 and the latest version is Java SE 14. It then describes several key concepts and features of Java including: it being object-oriented, simple, secure, platform independent, robust, portable, dynamic, architecture neutral, high performance, multithreaded, and distributed. It also discusses the Java Virtual Machine, Java Runtime Environment, Java Development Kit, and main Java platforms.