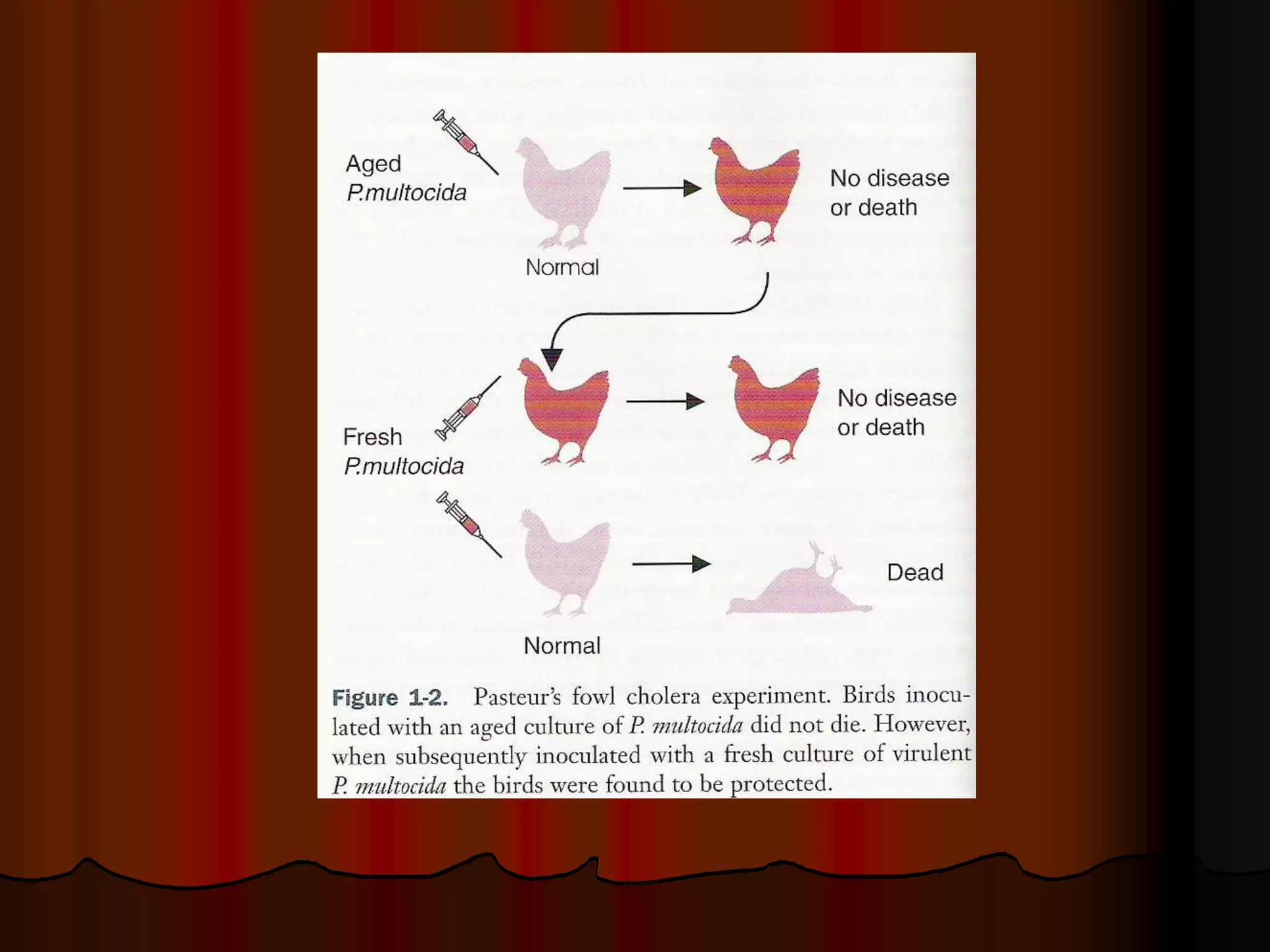
This document provides an overview of the PATH 201 General Pathology course. It includes the course contents which cover topics like cell injury, growth disturbances, inflammation, and neoplasia. Recommended textbooks are listed. The document also defines pathology as the study of derangements in living organisms in response to injuries. It briefly outlines some career paths in veterinary pathology and discusses the history of pathology from ancient concepts to modern developments in anatomy, microscopy, germ theory, and molecular biology.