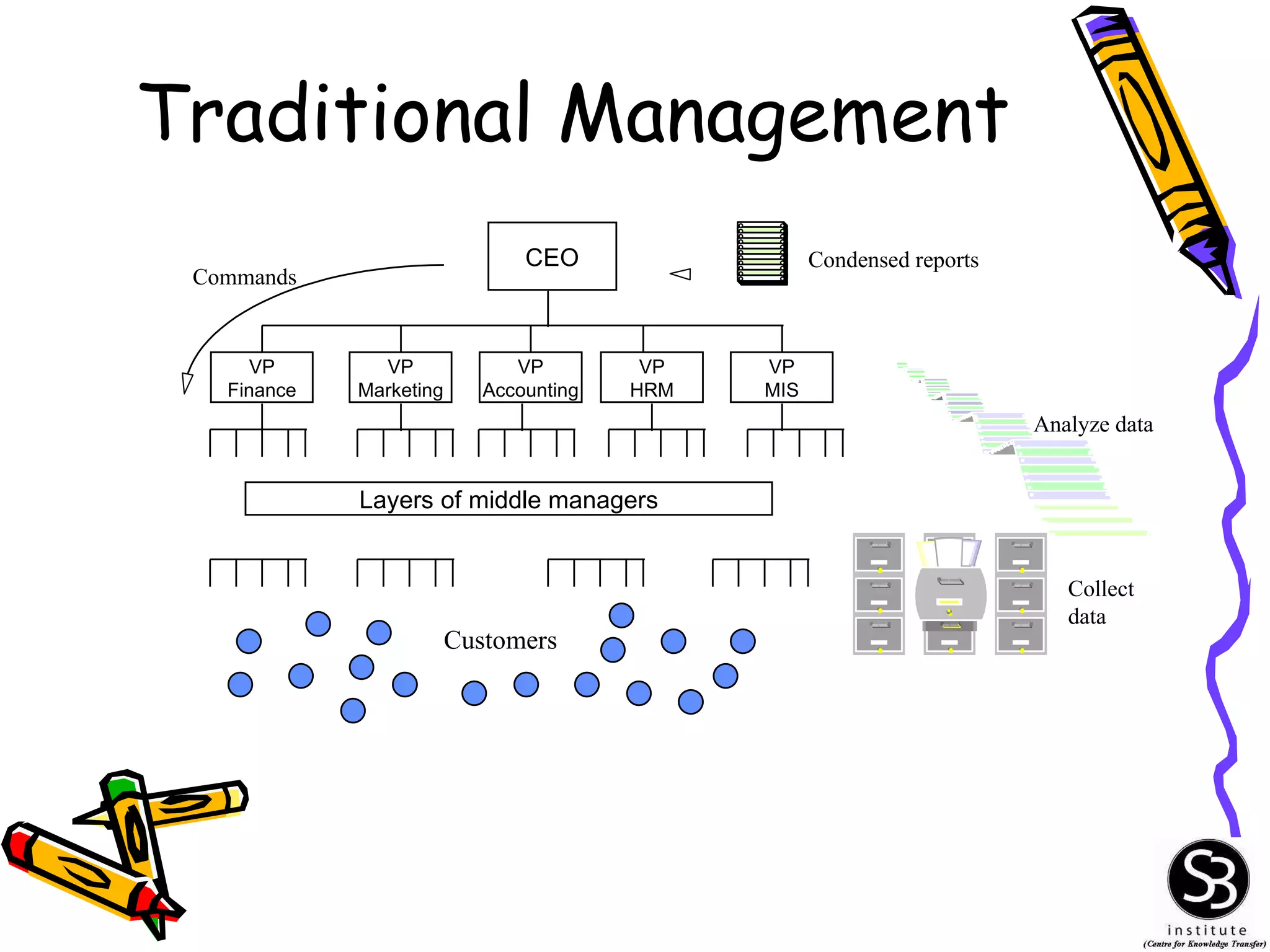
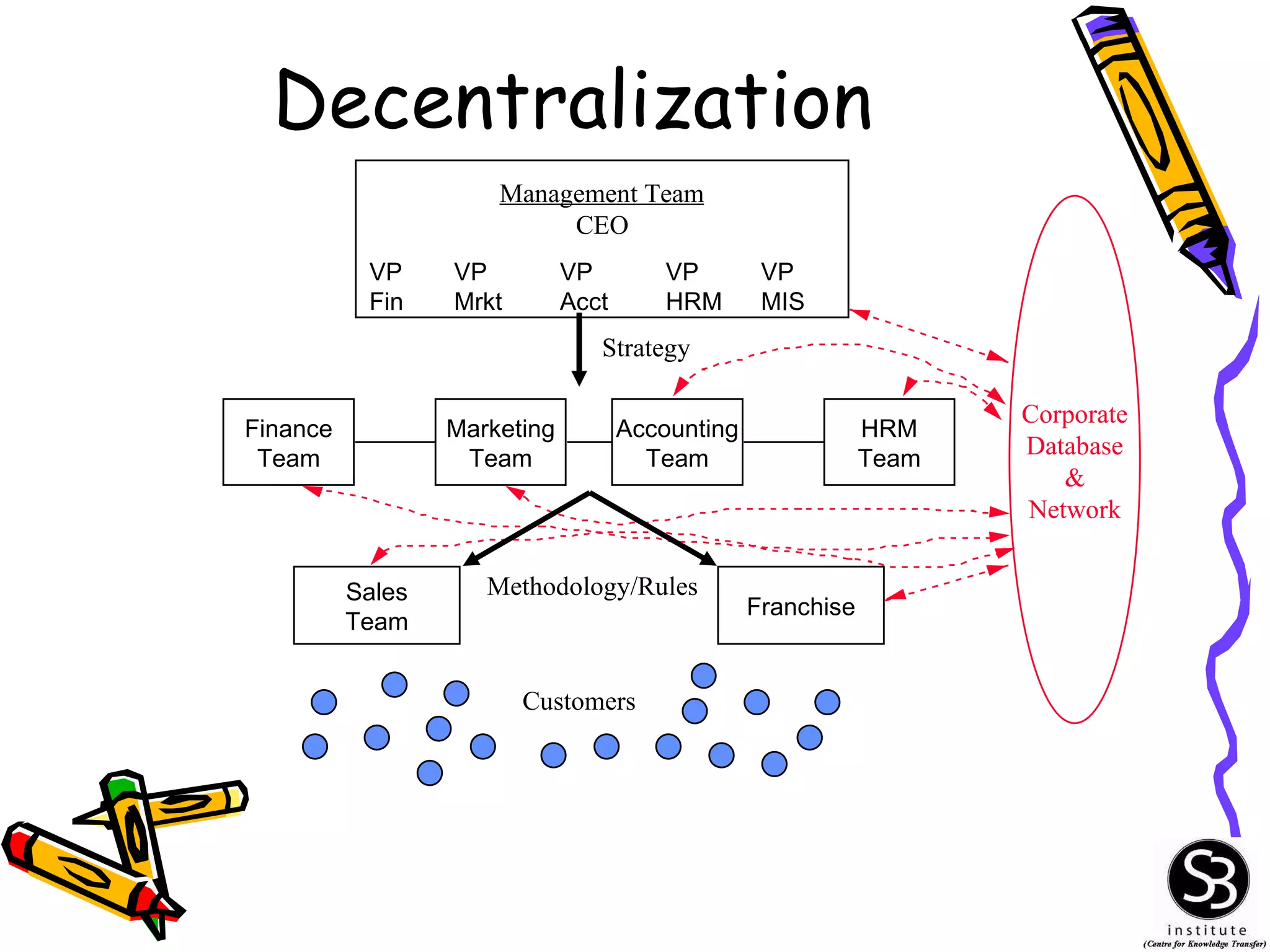
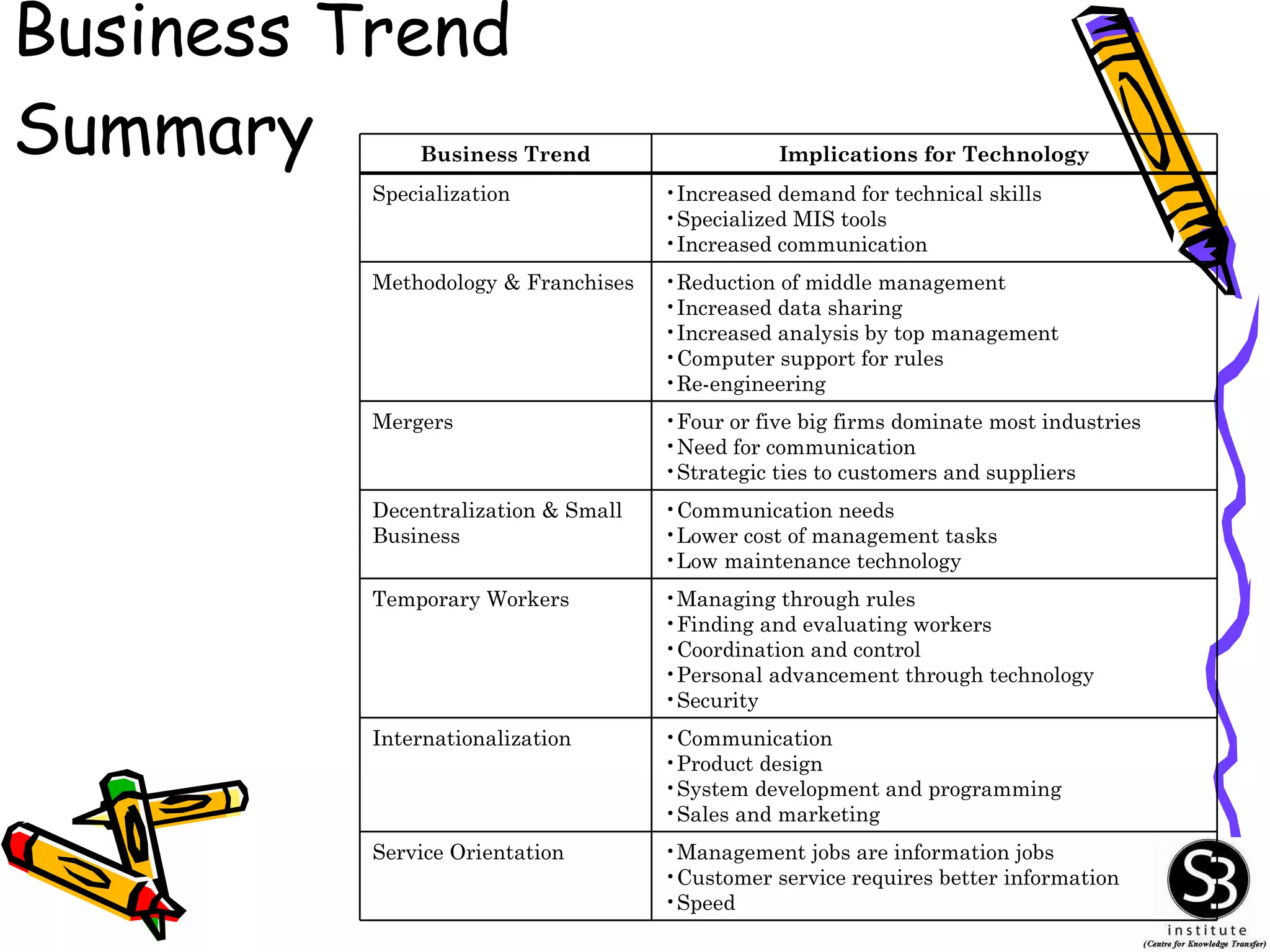
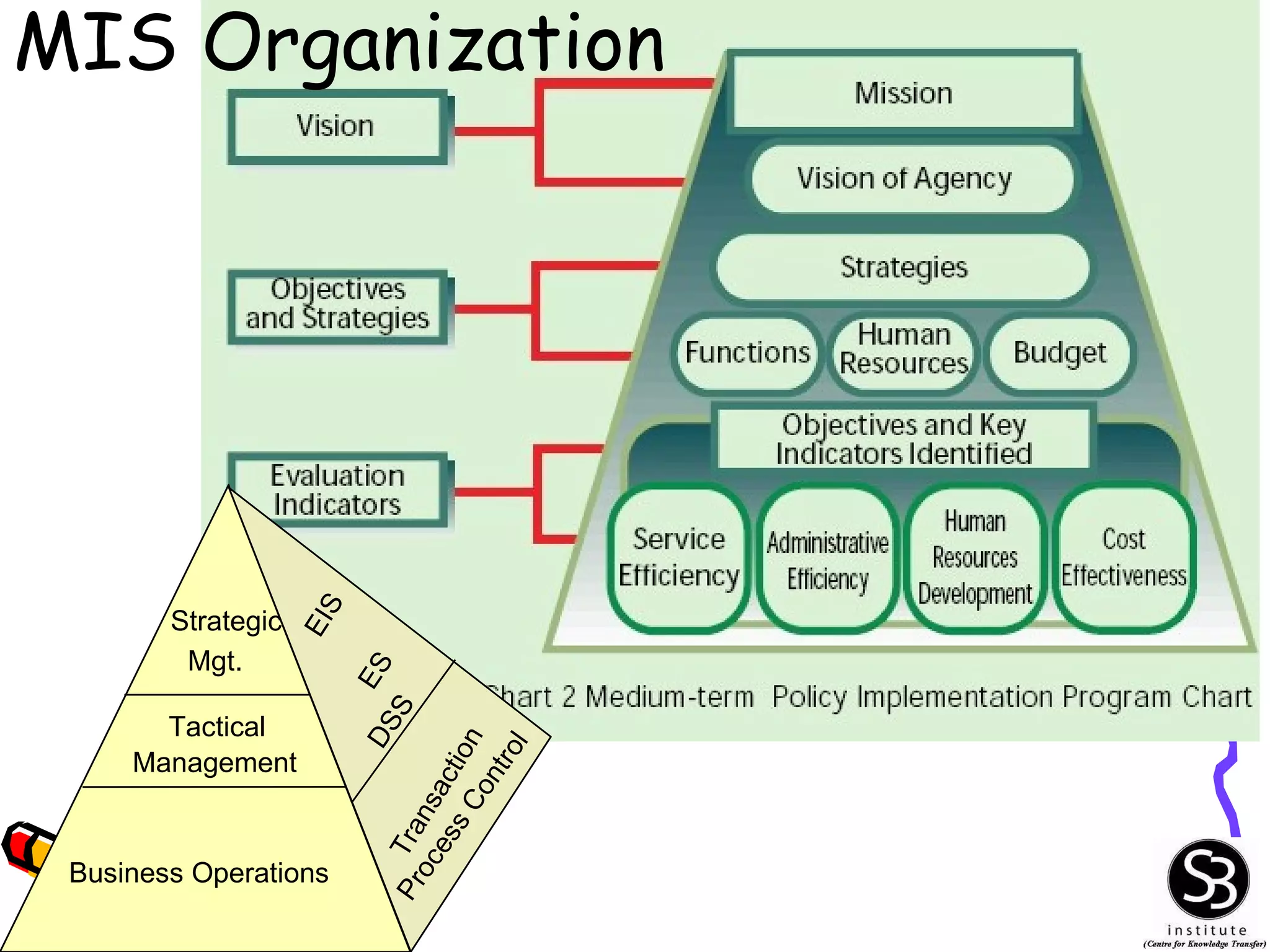
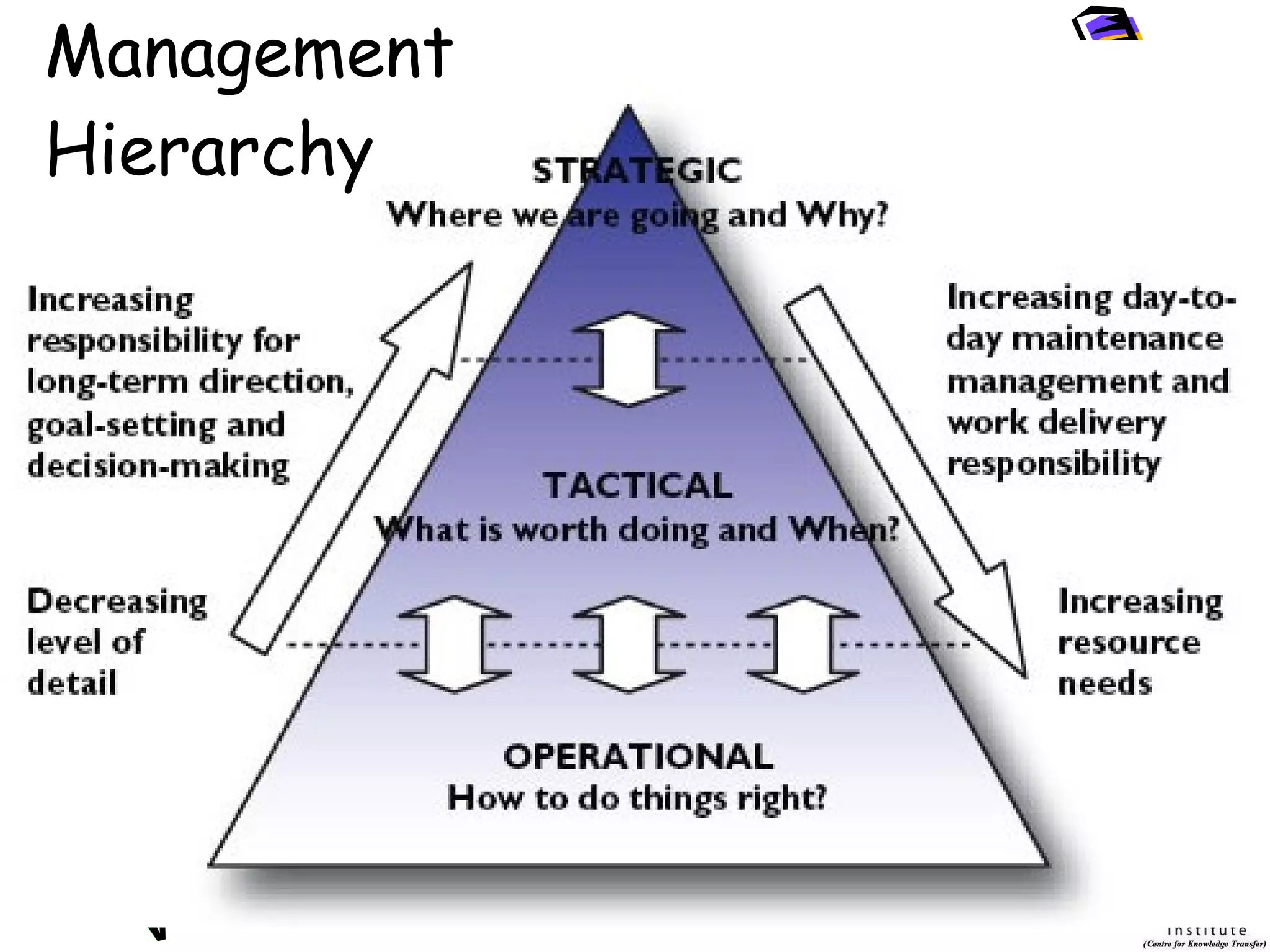
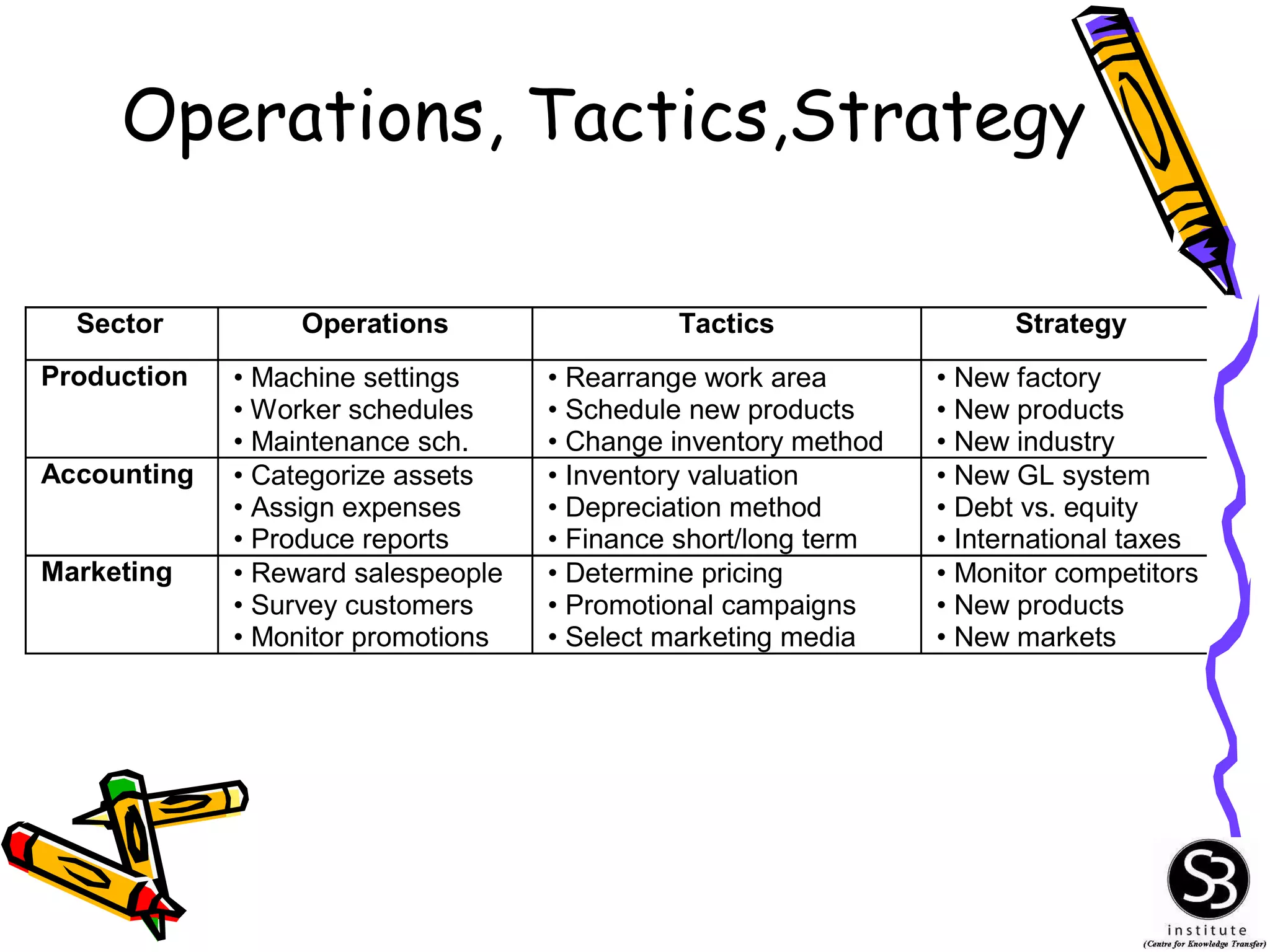
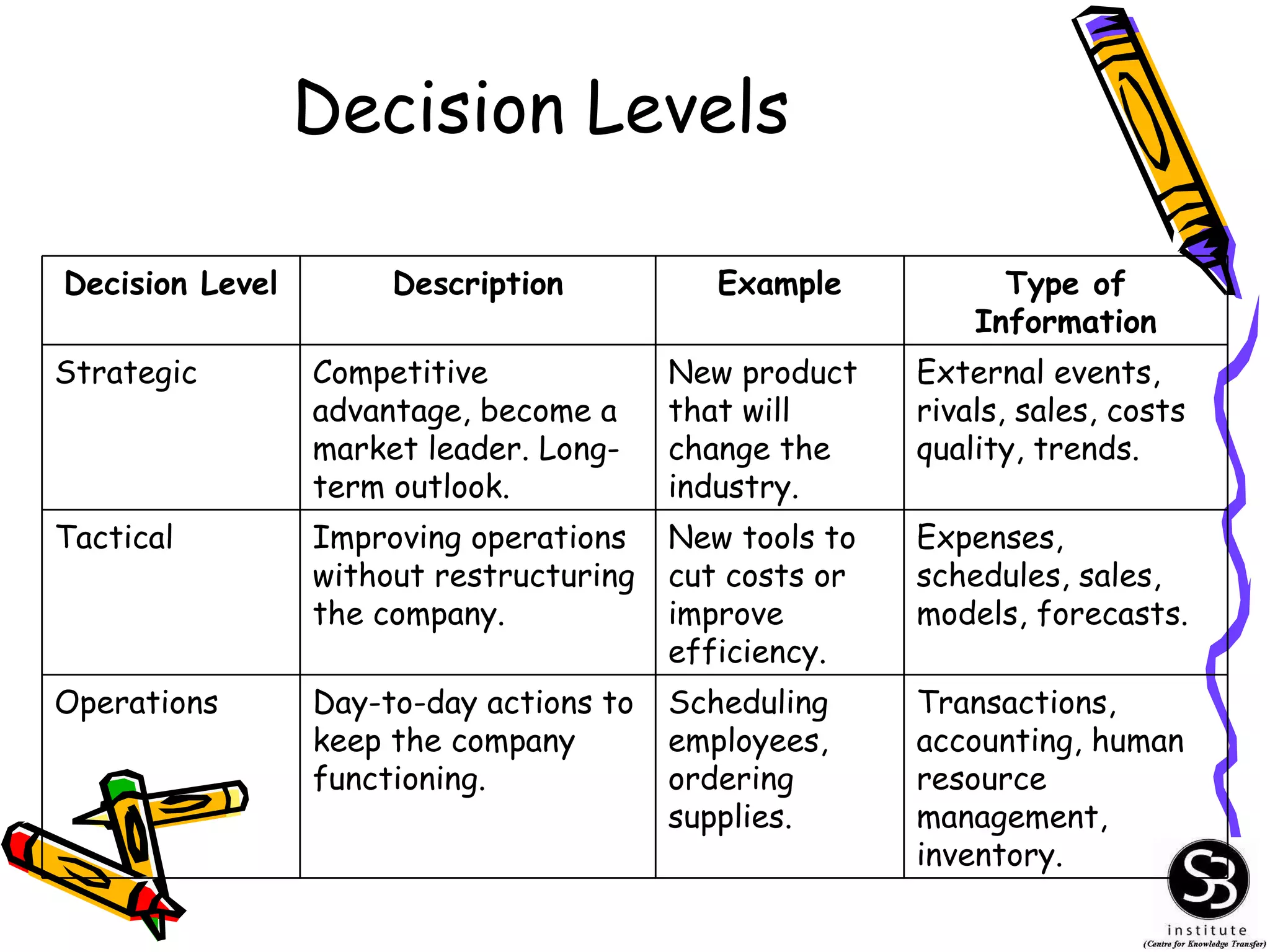
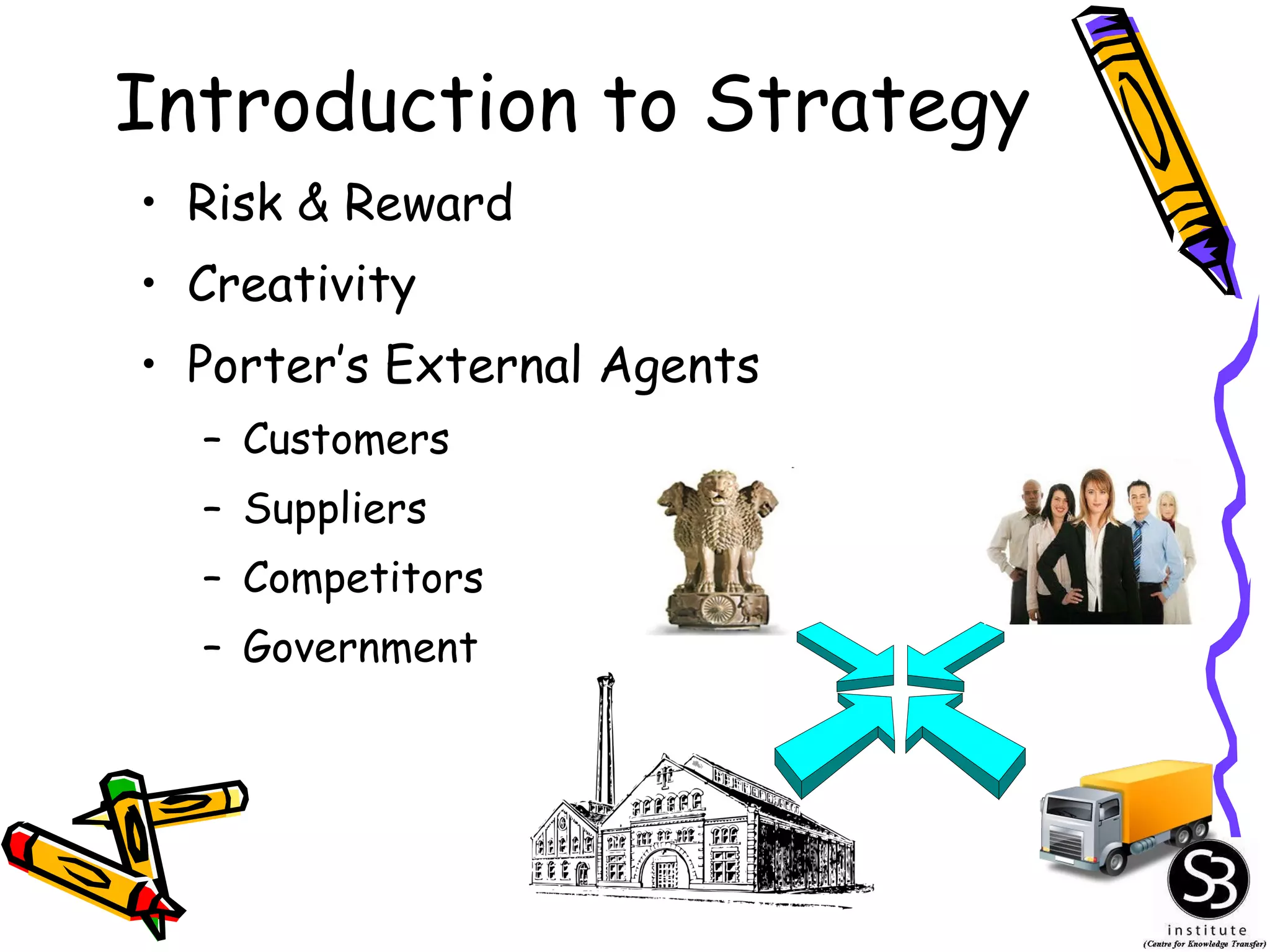
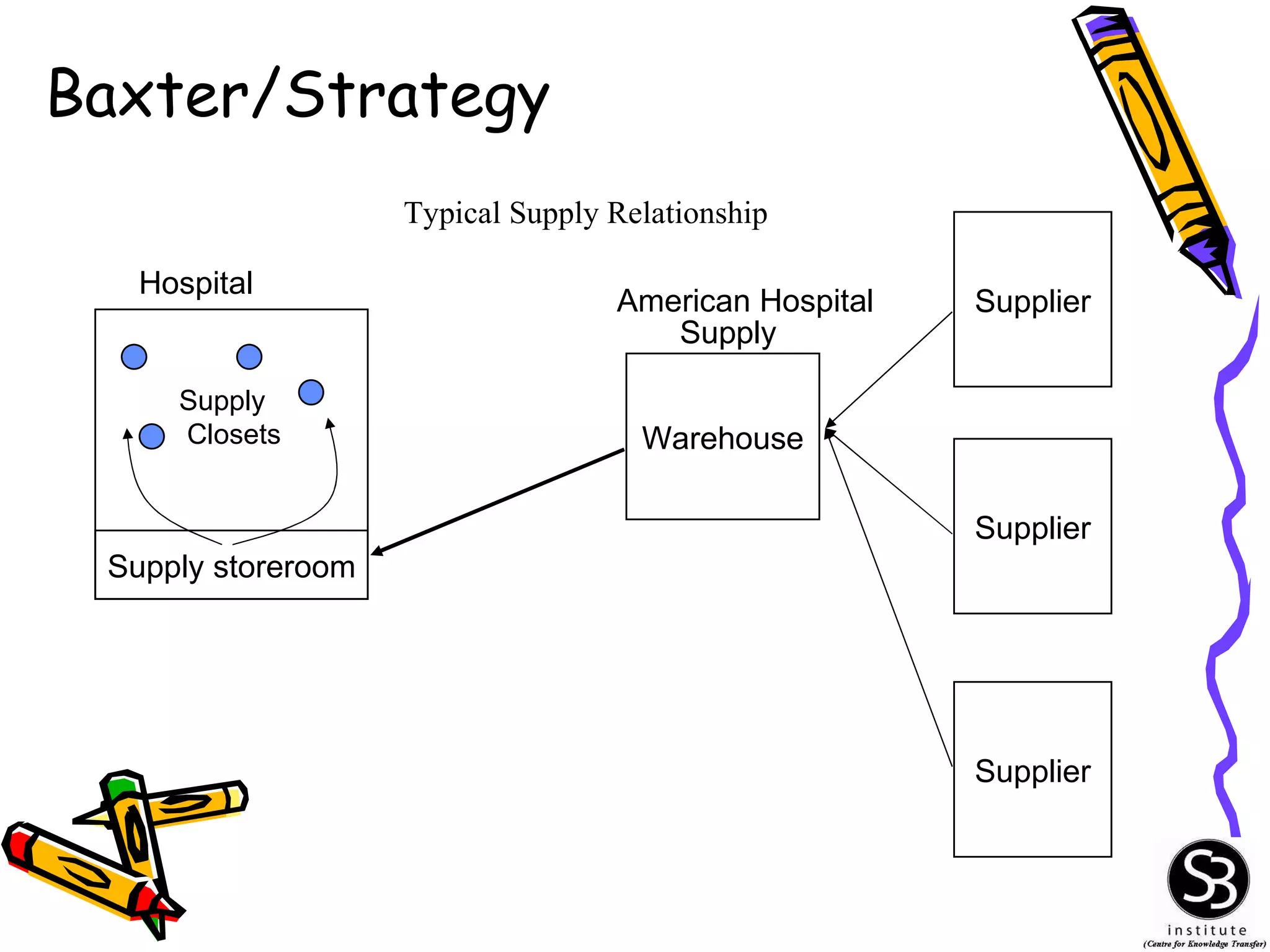
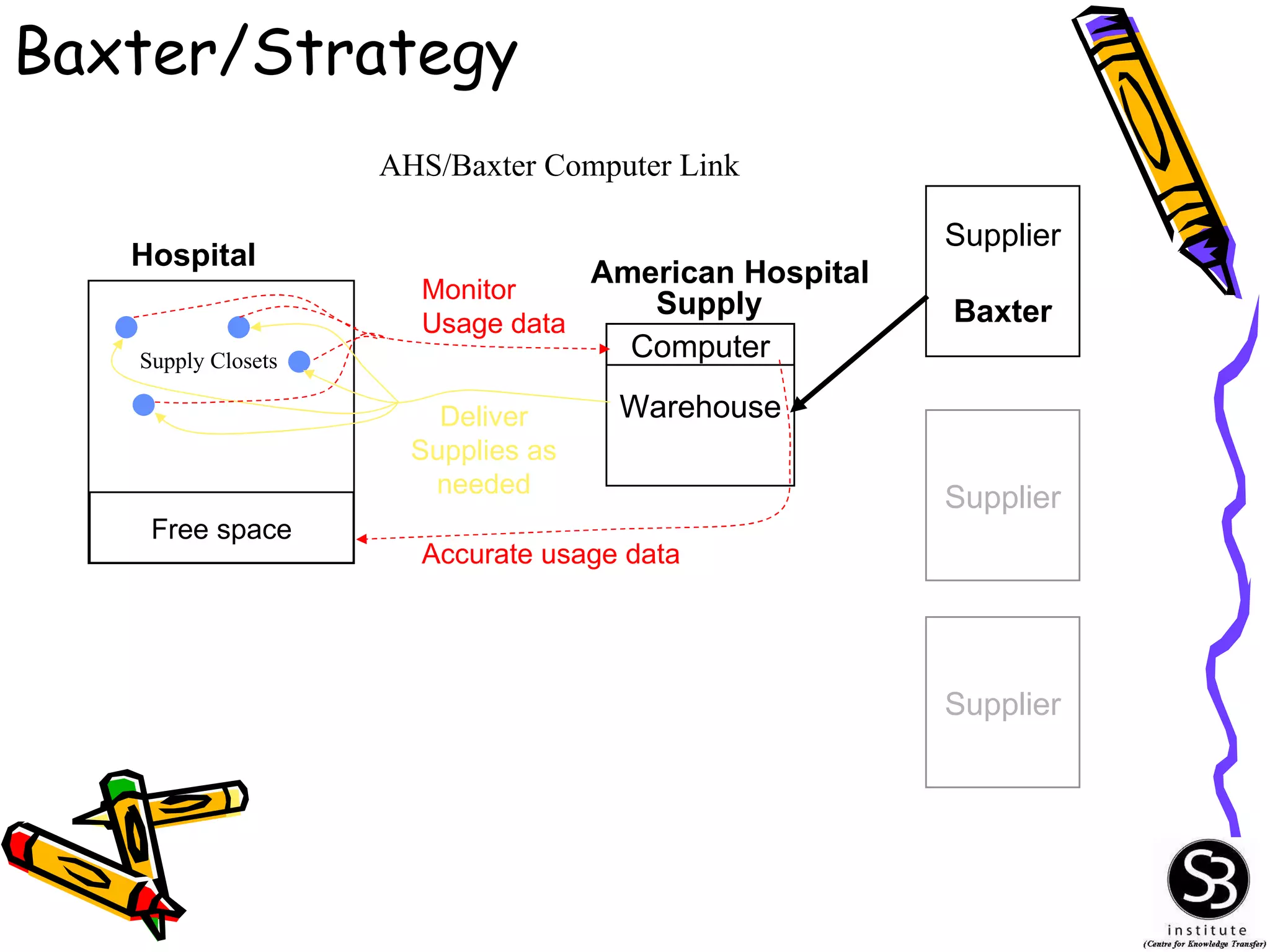
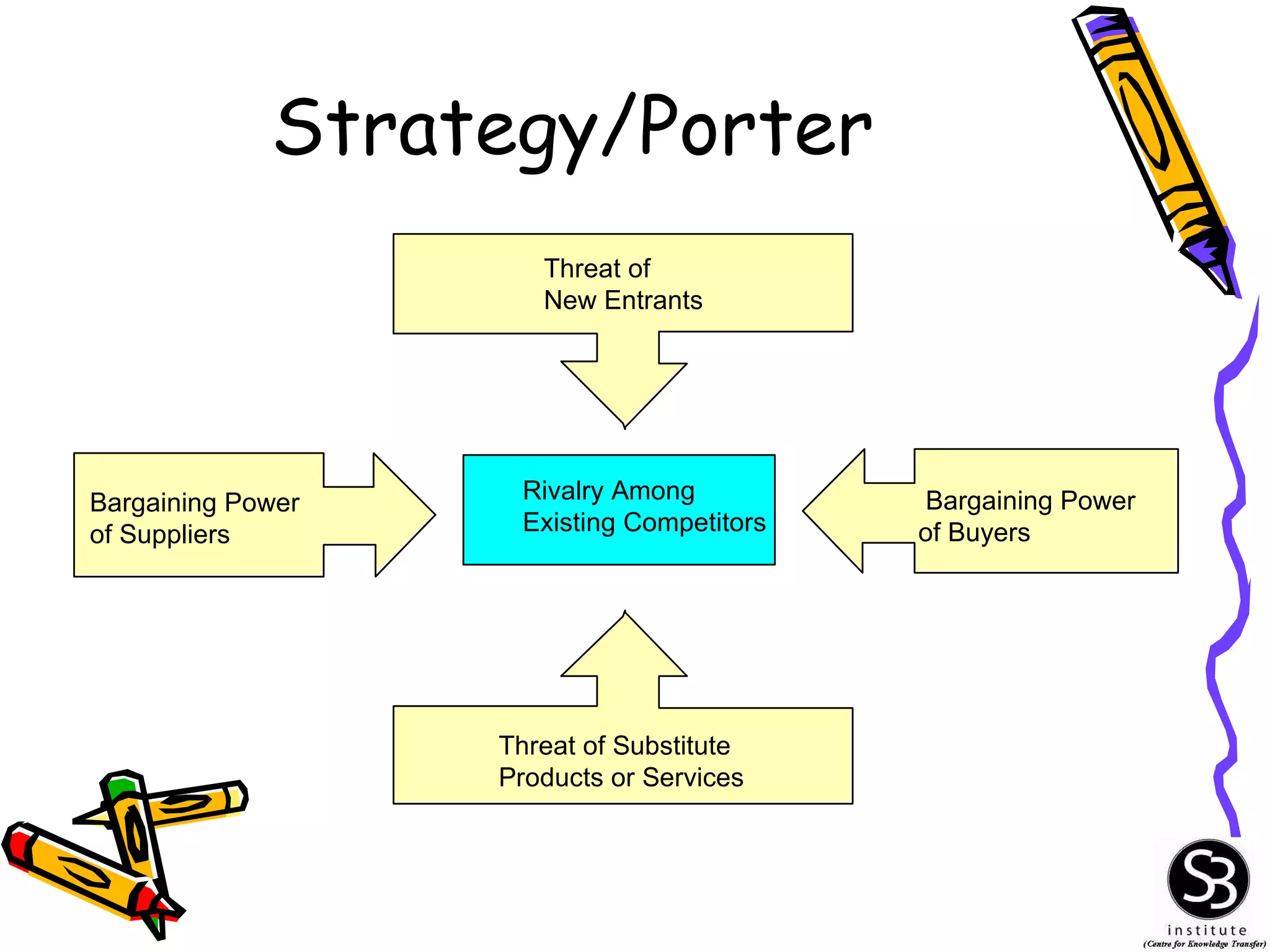
This document provides an introduction to management information systems (MIS). It discusses key topics such as what MIS is, why it is important, and how managers use information. It also covers business and technology trends that are shaping MIS, such as increased specialization, mergers, decentralization, and the need for improved communication and customer service. Managers are increasingly relying on information and technology to make strategic, tactical, and operational decisions to guide their organizations.