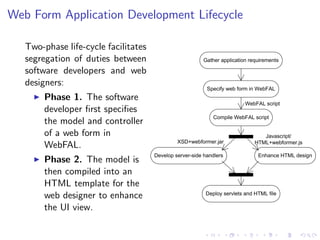
Webformer is a rapid application development toolkit designed to simplify the creation of AJAX web forms using an XML-based scripting language called Web Form Application Language (WebFAL). The toolkit provides a two-phase development lifecycle, separating duties between developers and designers, and generates JavaScript/HTML code along with handling MVC interactions. Future enhancements include options for selecting HTML controls for data fields and improved inter-field data validation.



![Sample Web Form Application
1. The user enters his username.
The entered username is
validated on-the-fly against
the server database.
2. The user enters the album
name while the server
suggests the possible names
that match what the user
types.
3. The user can upload multiple photos. He can click on the
[Add Photo] or the [Delete Photo] link to add or delete a
upload entry.
4. In each upload entry, the user specifies the photo file name,
whether he wants to share the photo, and the number of
prints of the photo he wants to order.
5. The user clicks on the Submit button to send the form data
to the server.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/069slides-130405033021-phpapp02/85/Webformer-a-Rapid-Application-Development-Toolkit-for-Writing-Ajax-Web-Form-Application-5-320.jpg)








![Sample Generated Code Fragments
<html>
<head>
<title>PhotoUpload</title>
<script language="JavaScript" src="webformer.js"></script>
...
<input type="Album" id="Album_1.1" onkeyup="selfld(this) "/>
...
<input type="text" id="Photo.Prints_1.1" onblur="valfld(this)"/>
...
<a href="javascript:addgrp(Photo)" id="Photo">[Add Photo]</a>
...
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/069slides-130405033021-phpapp02/85/Webformer-a-Rapid-Application-Development-Toolkit-for-Writing-Ajax-Web-Form-Application-14-320.jpg)
