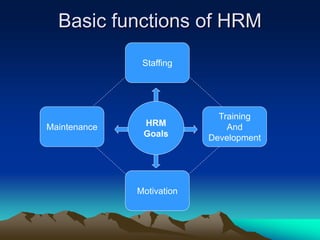
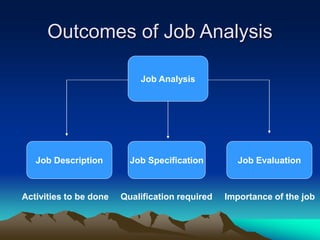
The document discusses the staffing function of human resource management. It describes strategic HR planning which involves forecasting workforce needs, job analysis to understand job requirements, and developing job descriptions and specifications. It also discusses recruiting through internal and external sources, and selection which involves screening applications, testing candidates, interviews, background checks, and making job offers. The goal is to attract and hire qualified people to fill organizational roles.











![2. Recruiting (2)
Where to look for potential job candidates?
– From inside the organization :
• The development function enables an organization to have
the right number of people when they are needed
• Job positions are advertised through inter office memos,
internal communication and on the company notice board
• Some organizations maintain a Human Resource
Information System [HRIS]
– From outside the organization:
• Attracting potential job candidates through job
advertisement in the newspaper, company website and on
the internet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/06-theorganizingfunction-staffing-230420091802-836dbcb3/85/06-The-Organizing-function-Staffing-ppt-14-320.jpg)

