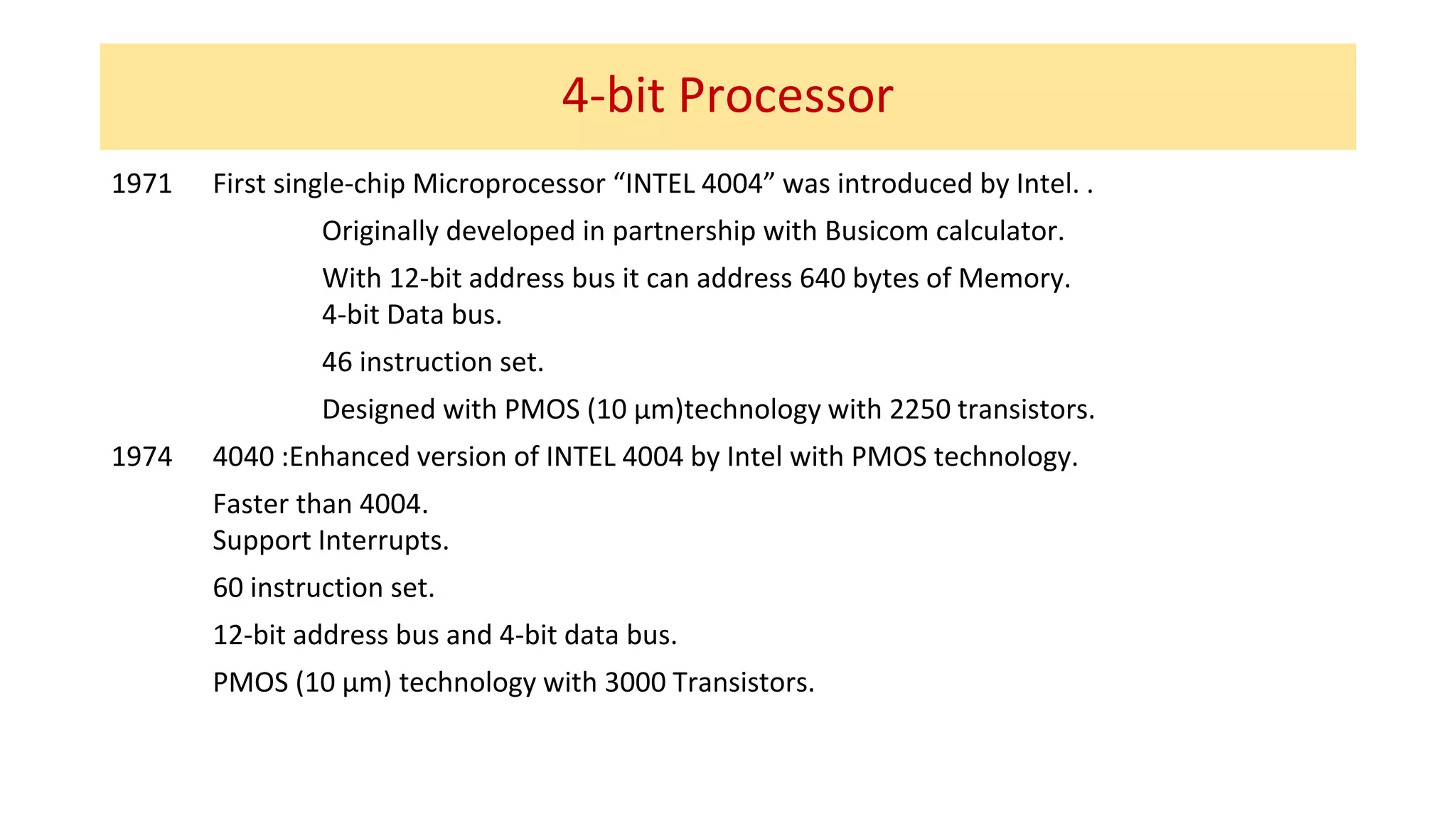
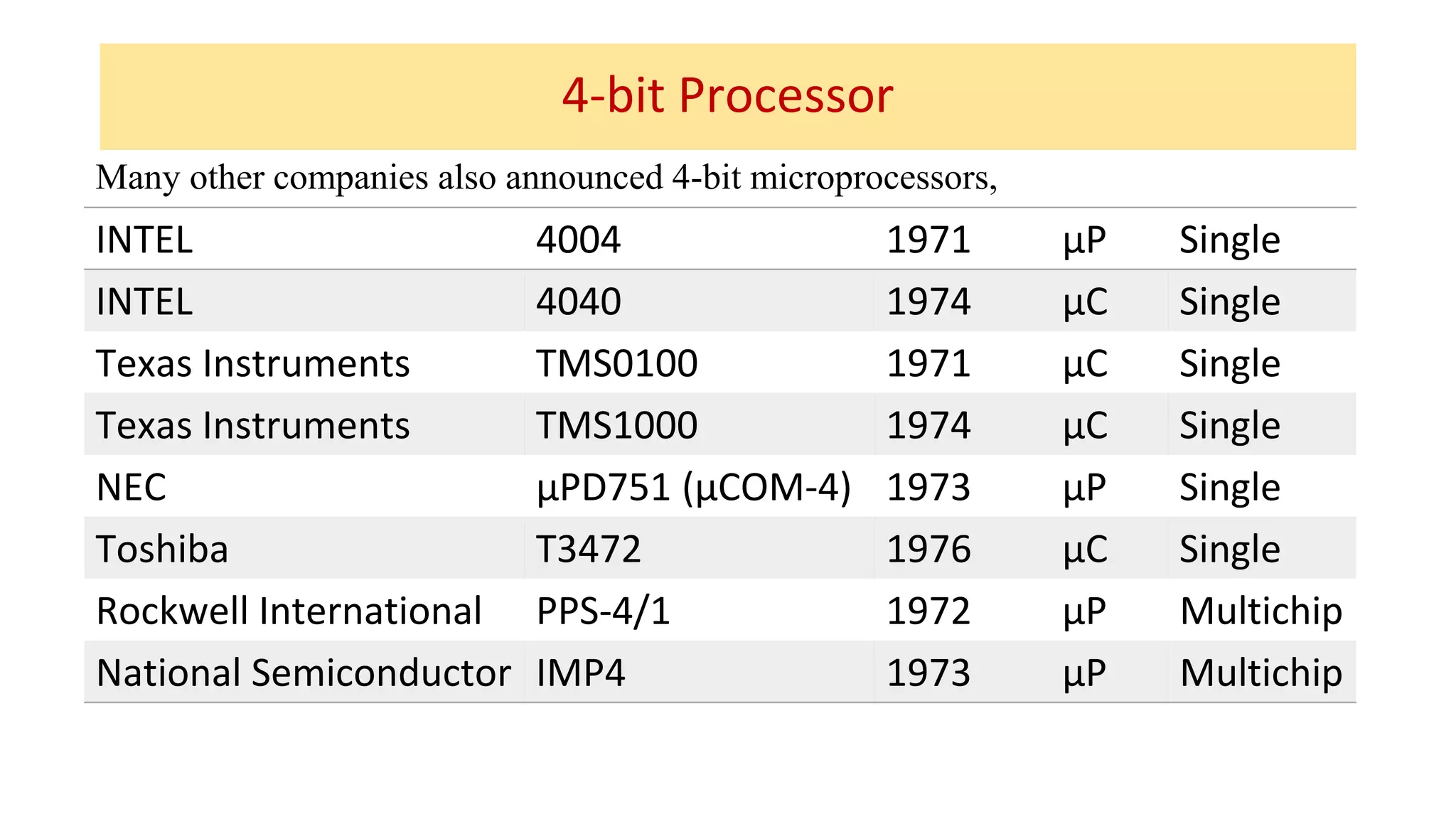
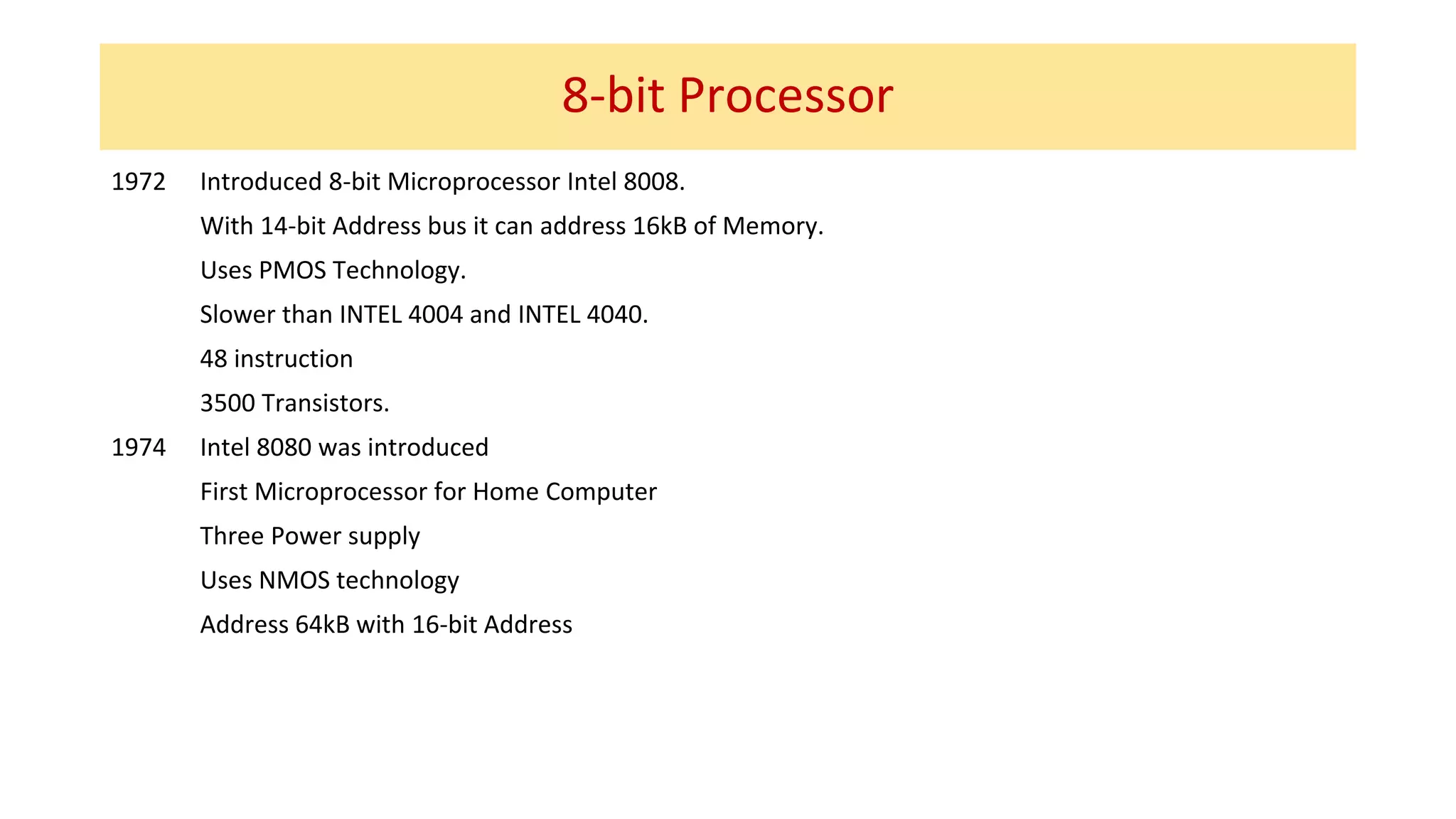
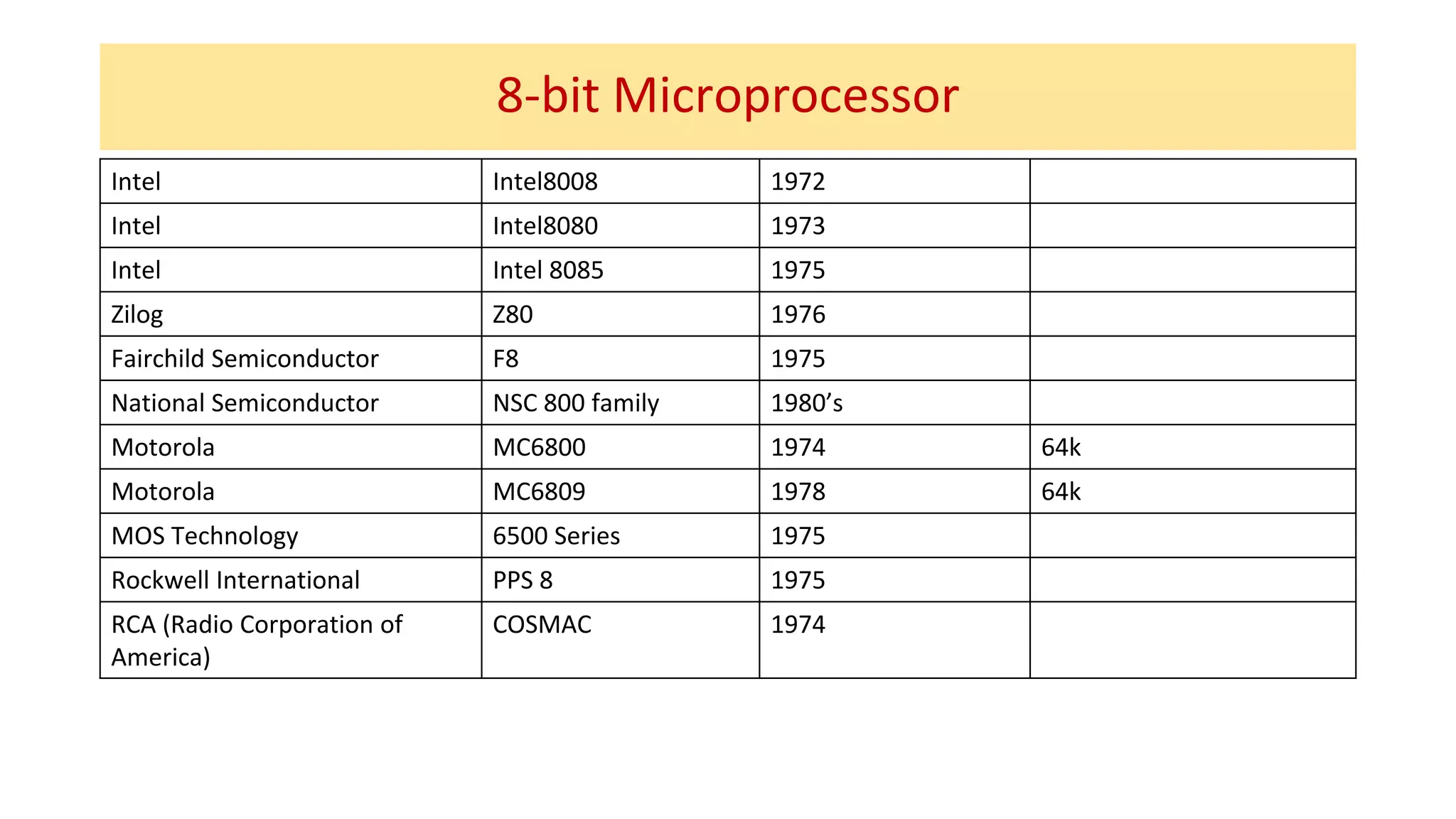
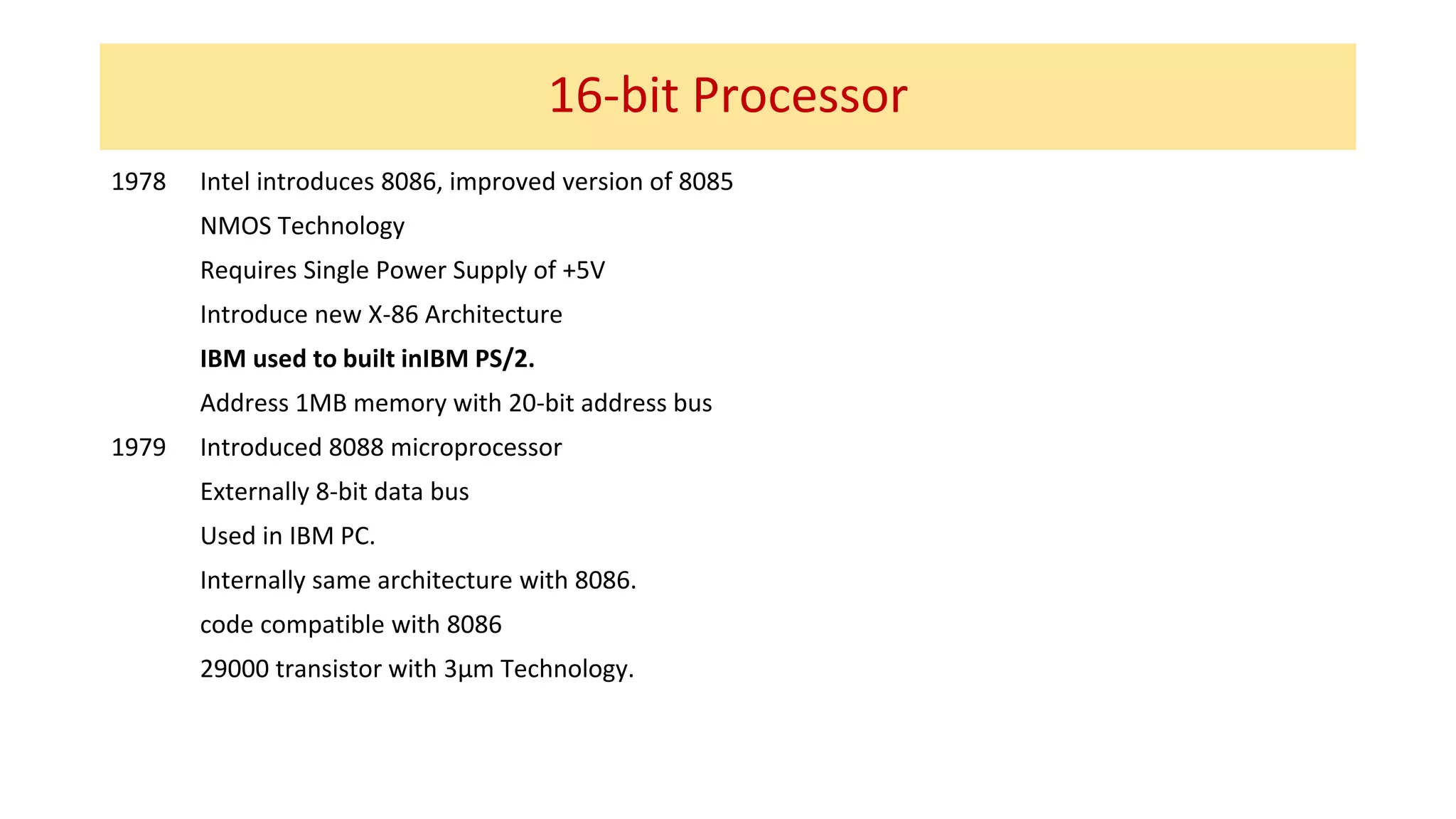
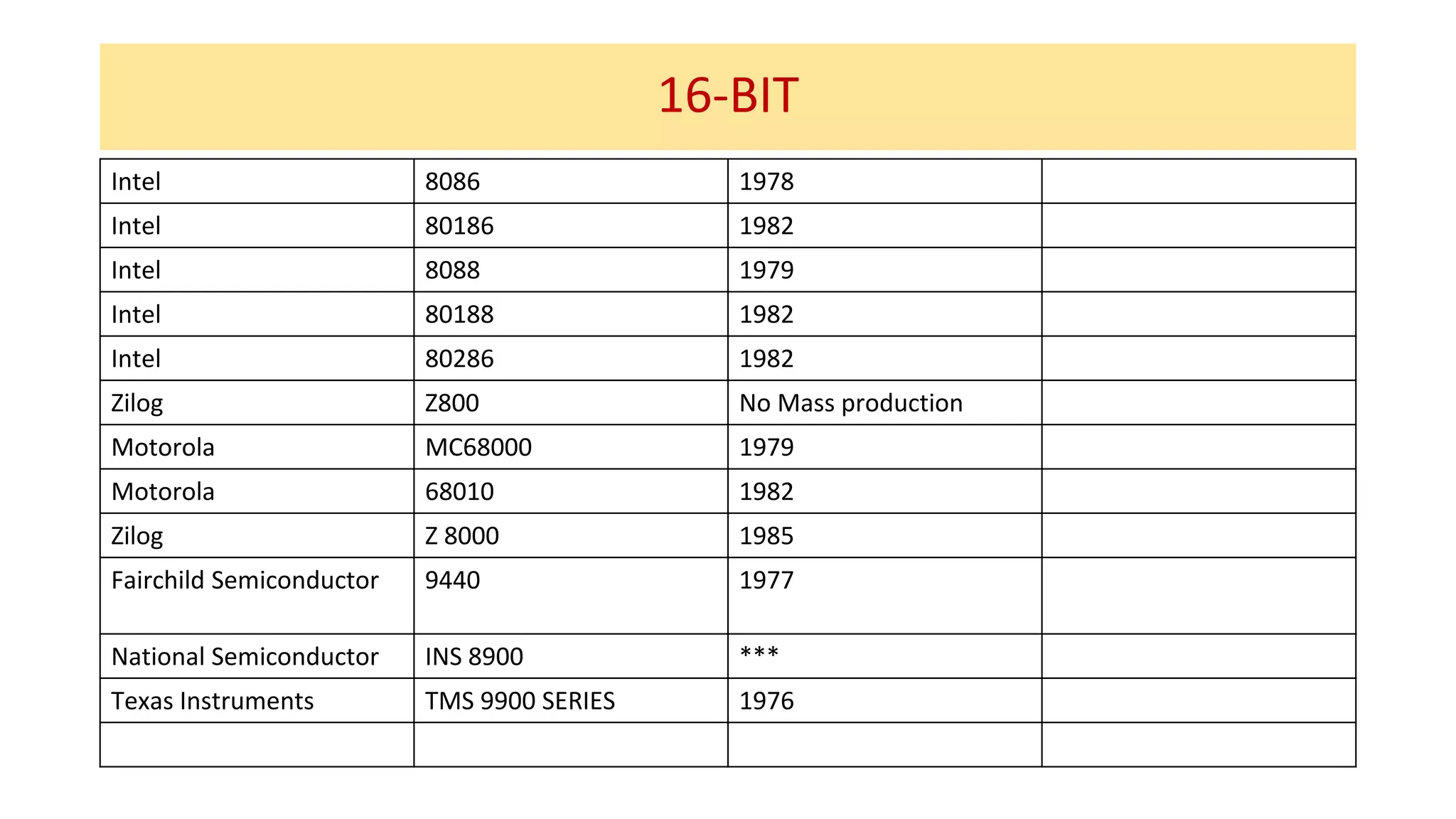
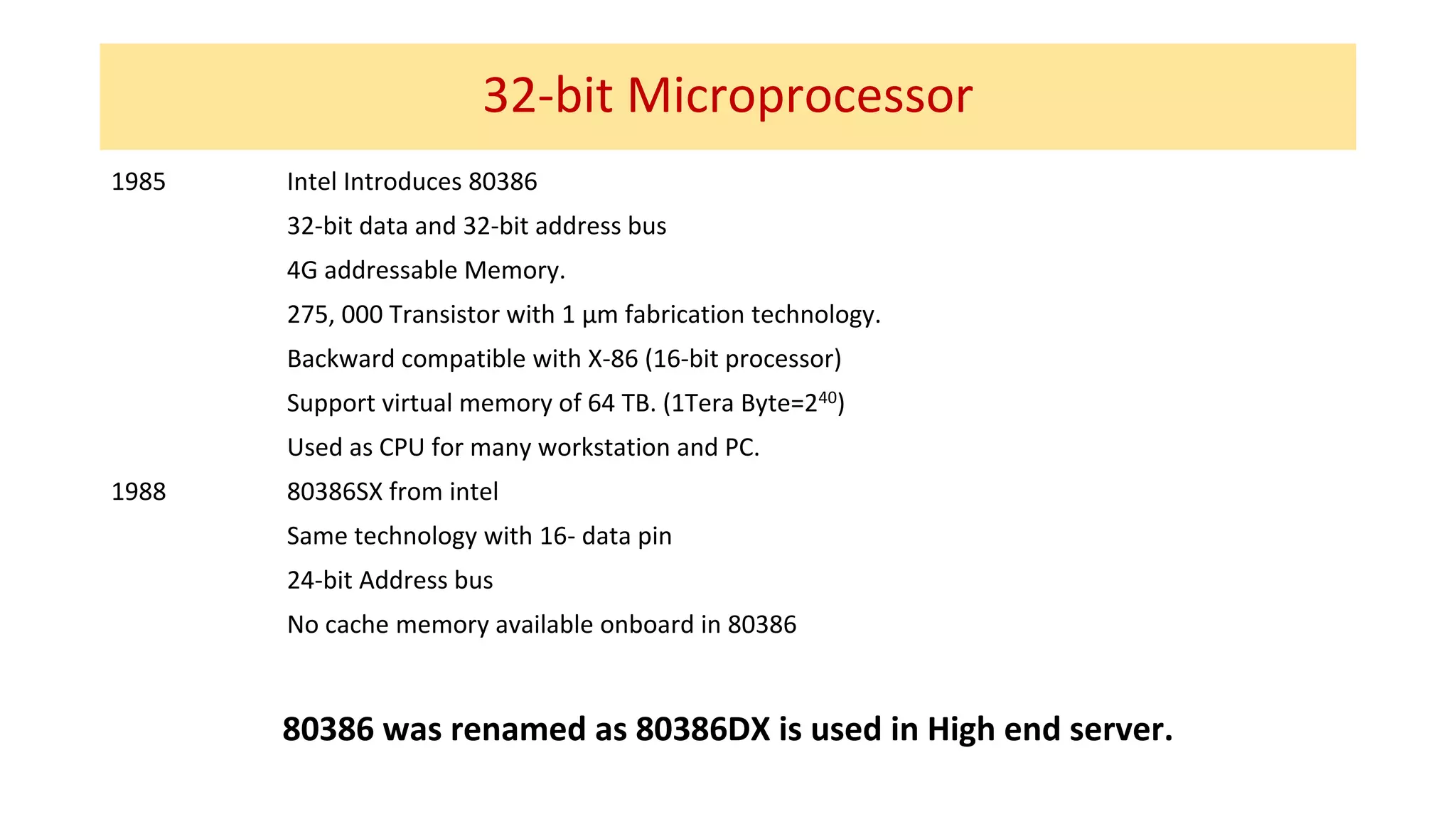
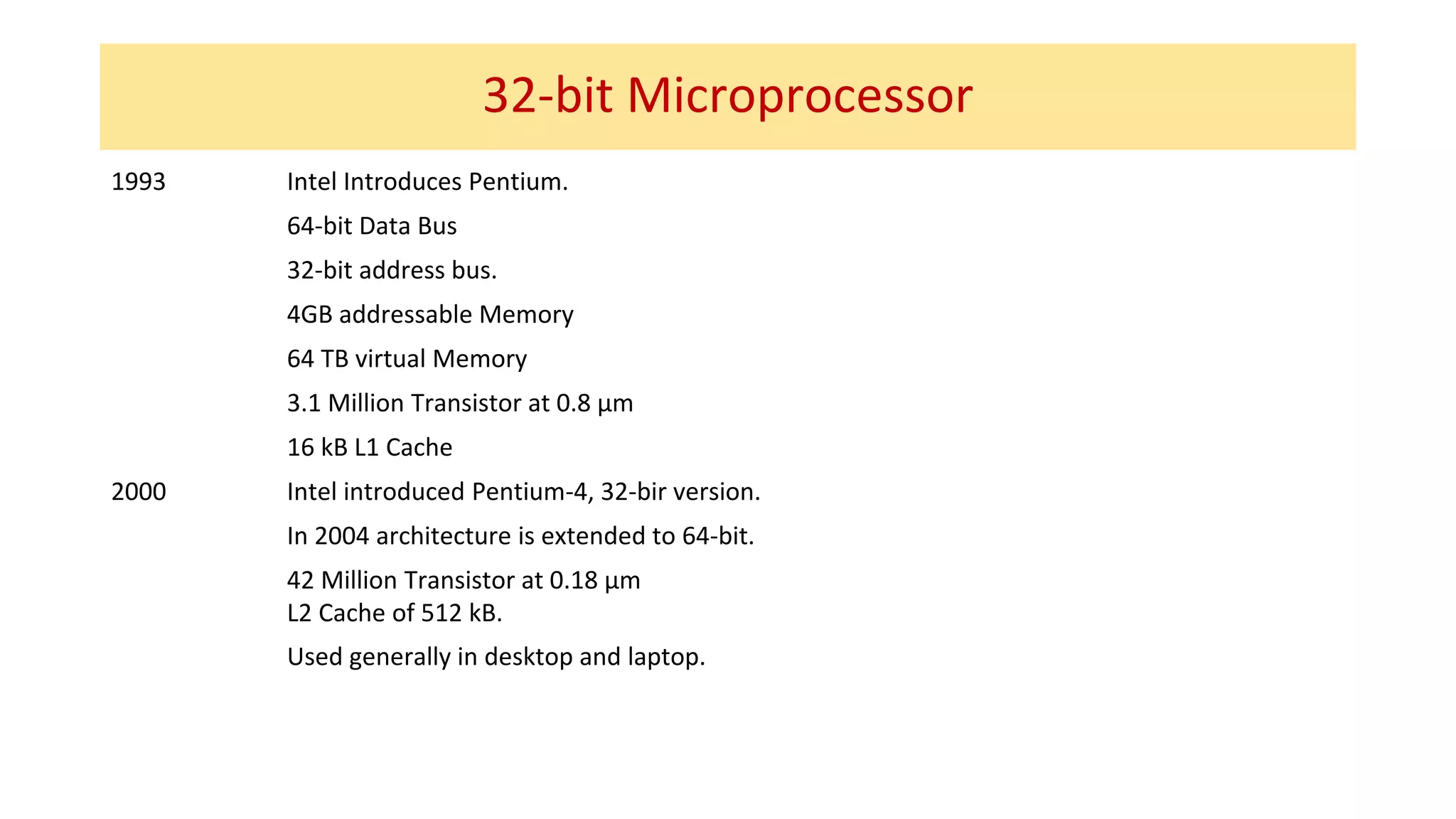
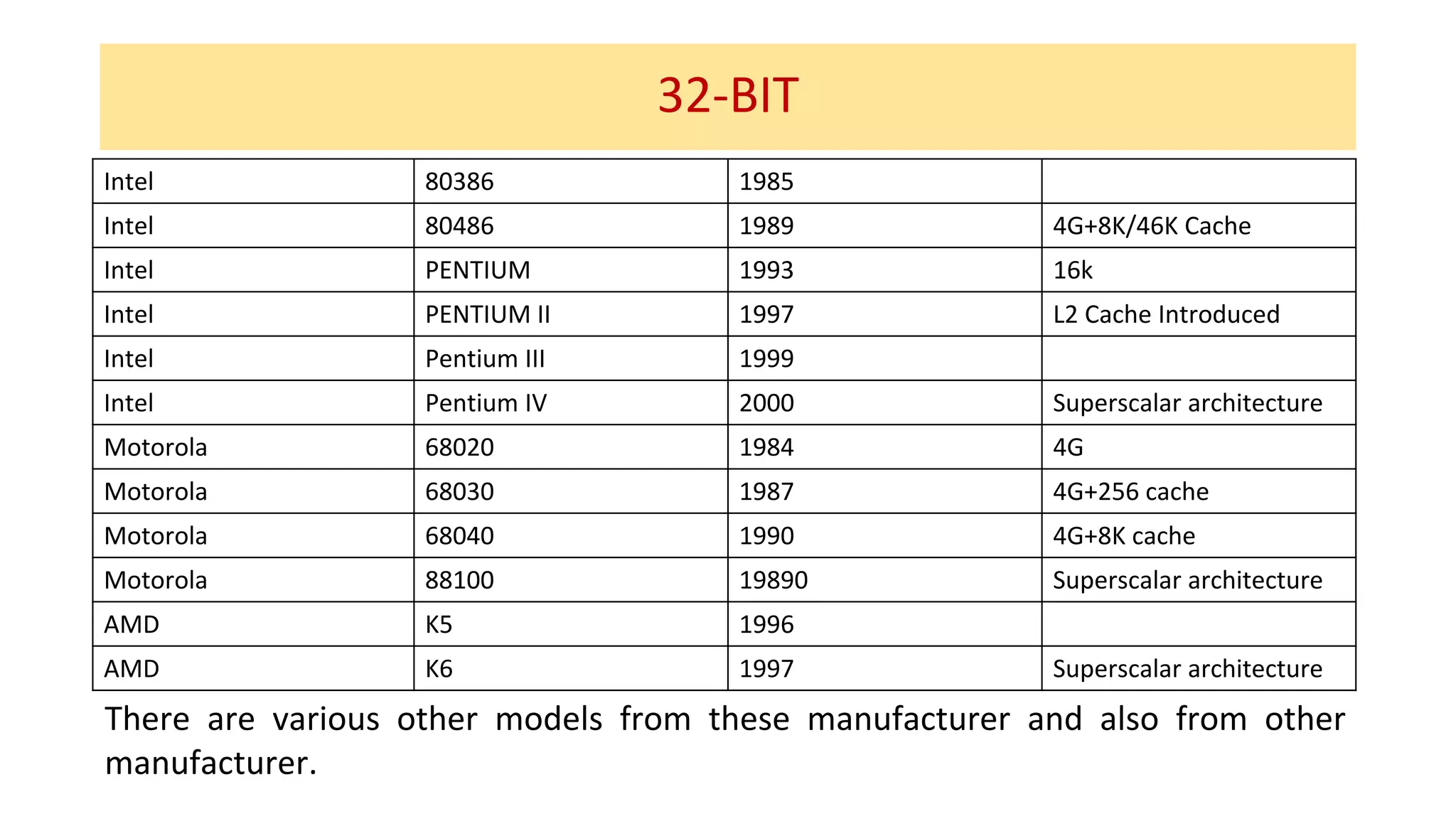
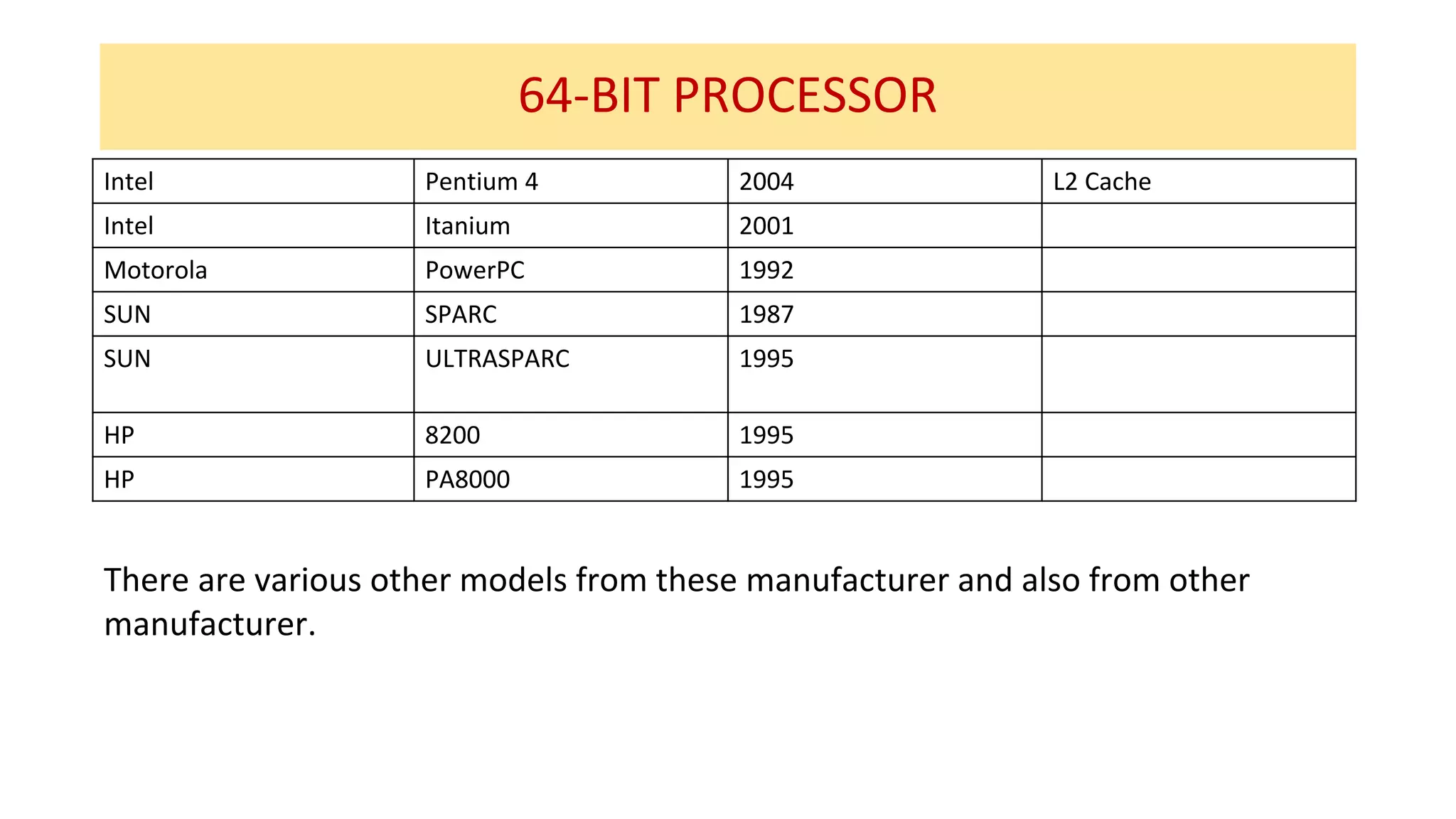
The microprocessor has evolved significantly since the Intel 4004 was introduced in 1971. Early microprocessors had 4-bit architectures with limited memory addressing. Throughout the 1970s, 8-bit microprocessors became prominent with expanded addressing. In the 1980s, 16-bit and 32-bit processors allowed for greater memory and improved performance. Modern multicore 64-bit processors can have dozens of cores and address petabytes of memory.