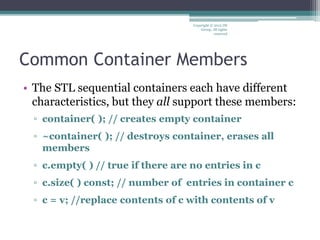
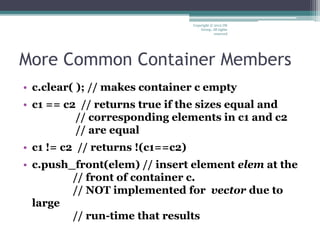
The document discusses the Standard Template Library (STL) in C++. It describes how STL uses containers to hold objects, algorithms to act on those objects, and iterators to access objects in containers. It provides examples of common STL containers like vectors, queues, stacks, and lists. It also summarizes common functions supported by STL containers, such as inserting and erasing elements, checking sizes, comparing containers, and more. Finally, it introduces the concept of generic algorithms in STL that can work on different container types using iterators.